|
78th (Highlanders) Regiment Of Foot
The 78th (Highlanders) Regiment of Foot was a Scottish regiment, Highland Infantry Regiment of the Line, raised in 1793. Under the Childers Reforms it amalgamated with 72nd Regiment, Duke of Albany's Own Highlanders to form the Seaforth Highlanders in 1881. History Early history The regiment was raised by Francis Mackenzie, 1st Baron Seaforth, Francis Humberston MacKenzie, Chiefs of Clan Mackenzie, Chief of the Clan Mackenzie and later Earl of Seaforth, Lord Seaforth, as the 78th (Highlanders) Regiment of Foot (or The Ross-shire Buffs) on 8 March 1793. First assembled at Fort George, Highland, Fort George in July 1793, the regiment moved to the Channel Islands in August 1893, and embarked for Holland in September 1794 for service in the French Revolutionary Wars. It saw action at the defence of Nijmegen in November 1794. In a bayonet attack there the regiment lost one officer and seven men; a further four officers and 60 men were wounded. The regiment moved to England in Apri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine infantry. Although disused in modern times, heavy infantry also commonly made up the bulk of many historic armies. Infantry, cavalry, and artillery have traditionally made up the core of the combat arms professions of various armies, with the infantry almost always comprising the largest portion of these forces. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets ''infant''. The individual-soldier te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Humberston Mackenzie
Lieutenant-General Francis Humberston Mackenzie, 1st Baron Seaforth, (9 June 1754 – 11 January 1815) was a British politician, soldier, and botanist. He was Chief of the Highland Clan Mackenzie, as which he raised the renowned 78th (Highlanders) Regiment of Foot. Early life Mackenzie was the second son of Major William Mackenzie (d. 12 March 1770), who was the son of the Hon. Alexander Mackenzie, and the grandson of Kenneth Mackenzie, 4th Earl of Seaforth. Francis's mother was Mary, the daughter and heiress of Matthew Humberston of Humberston, Lincolnshire. On the death of his elder brother Colonel Thomas Frederick Mackenzie Humberston in 1783, Francis Mackenzie became the last male heir of the attainted Earls of Seaforth.Sir James Balfour Paul, ''The Scots Peerage'', volume VII (Edinburgh, David Douglas, 1910), at pages 513–514 When he was about twelve years of age, Francis contracted scarlet fever, which incurred the loss of his ability to hear and almost all of his abil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
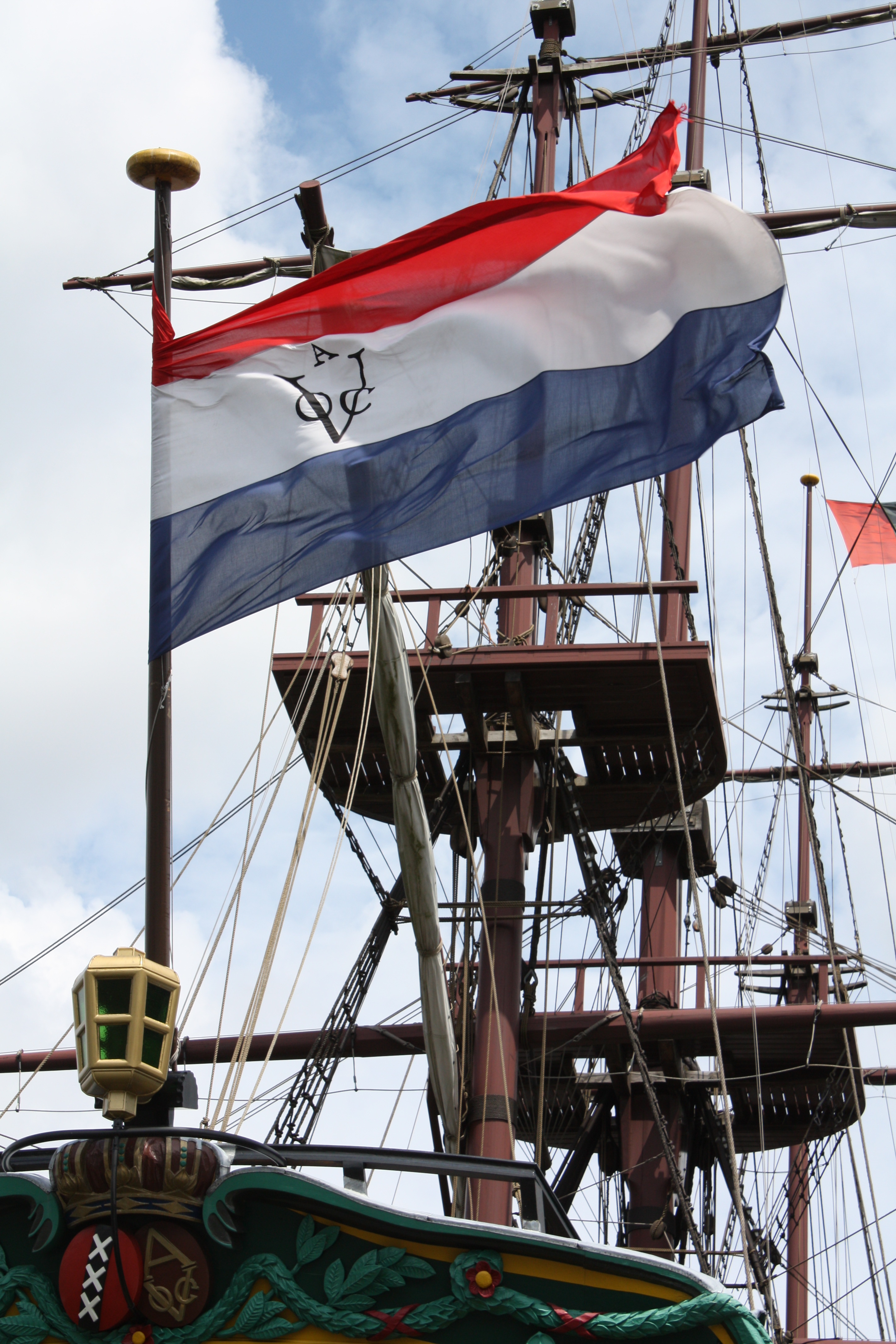
Batavian Republic
The Batavian Republic ( nl, Bataafse Republiek; french: République Batave) was the successor state to the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands. It was proclaimed on 19 January 1795 and ended on 5 June 1806, with the accession of Louis Bonaparte to the Dutch throne. From October 1801 onward, it was known as the Batavian Commonwealth ( nl, Bataafs Gemenebest). Both names refer to the Germanic tribe of the ''Batavi'', representing both the Dutch ancestry and their ancient quest for liberty in their nationalistic lore. In early 1795, intervention by the French Republic led to the downfall of the old Dutch Republic. The new Republic enjoyed widespread support from the Dutch populace and was the product of a genuine popular revolution. However, it was founded with the armed support of the French revolutionary forces. The Batavian Republic became a client state, the first of the " sister-republics", and later part of the French Empire of Napoleon. Its politics were deepl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Cape Colony
The Cape Colony ( nl, Kaapkolonie) was a Dutch United East India Company (VOC) colony in Southern Africa, centered on the Cape of Good Hope, from where it derived its name. The original colony and its successive states that the colony was incorporated into occupied much of modern South Africa. Between 1652 and 1691 it was a Commandment, and between 1691 and 1795 a Governorate of the United East India Company (VOC). Jan van Riebeeck established the colony as a re-supply and layover port for vessels of the VOC trading with Asia. The Cape came under VOC rule from 1652 to 1795 and from 1803 to 1806 was ruled by the Batavian Republic. Much to the dismay of the shareholders of the VOC, who focused primarily on making profits from the Asian trade, the colony rapidly expanded into a settler colony in the years after its founding. As the only permanent settlement of the Dutch United East India Company not serving as a trading post, it proved an ideal retirement place for employees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Elphinstone, 1st Viscount Keith
George Keith Elphinstone, 1st Viscount Keith (7 January 1746 – 10 March 1823), was a British naval officer active throughout the Napoleonic Wars. Career Early service George Elphinstone was the fourth son of Charles Elphinstone, 10th Lord Elphinstone, and his wife Lady Clementina Fleming, the daughter and heiress of John Fleming, 6th Earl of Wigtown. Elphinstone was born on 7 January 1746 at Elphinstone Tower, Scotland. Of his three elder brothers, two joined the British Army while the third, William Fullerton Elphinstone, initially served in the Royal Navy before joining the East India Company. Elphinstone followed his third brother into the navy, joining the 100-gun ship of the line on 4 November 1761. He stayed in her only briefly, transferring to the 44-gun frigate , commanded by Captain John Jervis, on 1 January of the following year. Serving in ''Gosport'' on the North American Station, Elphinstone saw action in the campaign that culminated in the removal o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period of Roman occupation. It became an independent kingdom and then a duchy before being united with the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a province governed as a separate nation under the crown. Brittany has also been referred to as Little Britain (as opposed to Great Britain, with which it shares an etymology). It is bordered by the English Channel to the north, Normandy to the northeast, eastern Pays de la Loire to the southeast, the Bay of Biscay to the south, and the Celtic Sea and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Its land area is 34,023 km2 . Brittany is the site of some of the world's oldest standing architecture, home to the Barnenez, the Tumulus Saint-Michel and others, which date to the early 5th millennium BC. Today, the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
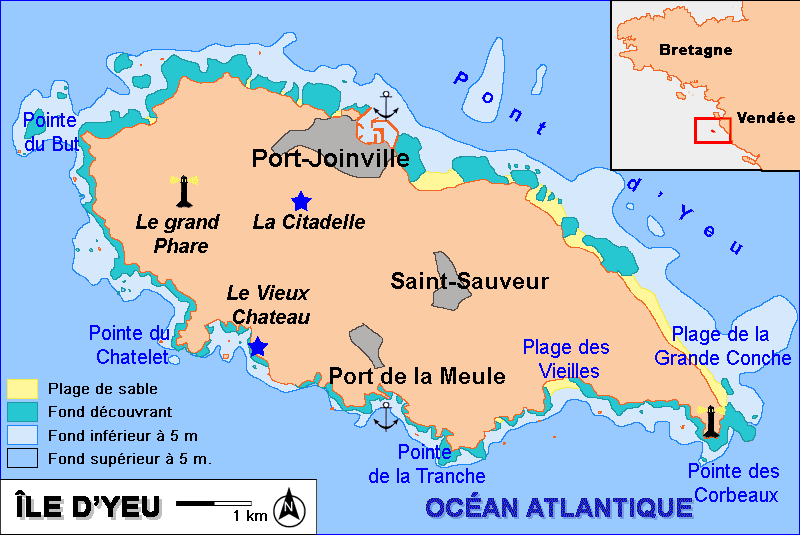
Île D'Yeu
Île d'Yeu () or L'Île-d'Yeu, is an island and commune just off the Vendée coast of western France. The island's two harbors, Port-Joinville in the north and Port de la Meule to the south, in a rocky inlet of the southern granite coast, are famous for tuna and lobster fishing, respectively. Administratively, the commune of L'Île-d'Yeu is part of the Vendée department and the Pays de la Loire region of France. History Neolithic markings in the native stone and an unusual concentration of megalithic dolmens and menhirs attest to the island's early sanctity. Irish monks from Bangor, County Down, dedicated their monastery on the Île d'Yeu to Hilaire; Saint Amand from Poitou received early training there, but it was destroyed by Viking raiders in the ninth century. During the tenth century, monks from Marmoutier near Tours and monks of Saint-Cyprien at Poitiers built a new monastery and dedicated it to Saint Stephen. The castle built on an islet linked to the coast by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of France (1795)
The invasion of France in 1795 or the Battle of Quiberon was a major landing on the Quiberon peninsula by émigré, counter-revolutionary troops in support of the Chouannerie and Vendée Revolt, beginning on 23 June and finally definitively repulsed on 21 July. It aimed to raise the whole of western France in revolt, bring an end to the French Revolution and restore the French monarchy. The invasion failed; it had a major negative impact, dealing a disastrous blow to the royalist cause. Preparations Louis XVIII and the comte d’Artois (the future Charles X of France) divided the counter-revolutionary activities and theatres between them - to Louis went political generalities and the region from the Alps to the Pyrénées (including Lyon), and to the comte the western provinces (Vendée, Brittany, Normandy). The comte named Joseph de Puisaye général en chef of Brittany, a good choice since de Puisaye had military talent and political and diplomatic experience. Playin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayonet
A bayonet (from French ) is a knife, dagger, sword, or spike-shaped weapon designed to fit on the end of the muzzle of a rifle, musket or similar firearm, allowing it to be used as a spear-like weapon.Brayley, Martin, ''Bayonets: An Illustrated History'', Iola, WI: Krause Publications, , (2004), pp. 9–10, 83–85. From the 17th century to World War I, it was a weapon for infantry attacks. Today it is considered an ancillary weapon or a weapon of last resort. History The term ''bayonette'' itself dates back to the mid-to-late 16th century, but it is not clear whether bayonets at the time were knives that could be fitted to the ends of firearms, or simply a type of knife. For example, Cotgrave's 1611 ''Dictionarie'' describes the bayonet as "a kind of small flat pocket dagger, furnished with knives; or a great knife to hang at the girdle". Likewise, Pierre Borel wrote in 1655 that a kind of long-knife called a ''bayonette'' was made in Bayonne but does not give any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nijmegen
Nijmegen (;; Spanish and it, Nimega. Nijmeegs: ''Nimwèège'' ) is the largest city in the Dutch province of Gelderland and tenth largest of the Netherlands as a whole, located on the Waal river close to the German border. It is about 60 km south east of Utrecht and 50 km north east of Eindhoven. Nijmegen is the oldest city in the Netherlands, the second to be recognized as such in Roman times, and in 2005 celebrated 2,000 years of existence. Nijmegen became a free imperial city in 1230 and in 1402 a Hanseatic city. Since 1923 it has been a university city with the opening of a Catholic institution now known as the Radboud University Nijmegen. The city is well known for the International Four Days Marches Nijmegen event. Its population in 2022 was 179,000; the municipality is part of the Arnhem–Nijmegen metropolitan area, with 736,107 inhabitants in 2011. Population centres The municipality is formed by the city of Nijmegen, incorporating the former villages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former province on the western coast of the Netherlands. From the 10th to the 16th century, Holland proper was a unified political region within the Holy Roman Empire as a county ruled by the counts of Holland. By the 17th century, the province of Holland had risen to become a maritime and economic power, dominating the other provinces of the newly independent Dutch Republic. The area of the former County of Holland roughly coincides with the two current Dutch provinces of North Holland and South Holland into which it was divided, and which together include the Netherlands' three largest cities: the capital city (Amsterdam), the home of Europe's largest port ( Rotterdam), and the seat of government (The Hague). Holland has a population of 6,583,534 as of November 2019, and a population density of 1203/km2. The name ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channel Islands
The Channel Islands ( nrf, Îles d'la Manche; french: îles Anglo-Normandes or ''îles de la Manche'') are an archipelago in the English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. They include two Crown Dependencies: the Bailiwick of Jersey, which is the largest of the islands; and the Bailiwick of Guernsey, consisting of Guernsey, Alderney, Sark, Herm and some smaller islands. They are considered the remnants of the Duchy of Normandy and, although they are not part of the United Kingdom, the UK is responsible for the defence and international relations of the islands. The Crown dependencies are not members of the Commonwealth of Nations, nor have they ever been in the European Union. They have a total population of about , and the bailiwicks' capitals, Saint Helier and Saint Peter Port, have populations of 33,500 and 18,207, respectively. "Channel Islands" is a geographical term, not a political unit. The two bailiwicks have been administered separately since the lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |