|
64th Rifle Division (Soviet Union)
The 64th Rifle Division was an infantry division of the Soviet Union's Red Army which existed between 1942 and 1945. History There was a previous 64th Rifle Division active between July 1925 and 26 September 1941, which it was renamed the 7th Guards Rifle Division. A new 64th Rifle Division was formed in early 1942, which took part in hostilities from 5 March 1942 to 9 May 1945. Until June 1942, the division was part of the Moscow Military District. Then it was included in the 8th Reserve Army which became the 66th Army on 27 August 1942. On 16 August, the division was moved to the front and took up defensive positions in the area of the settlement of Spartak, on the northern outskirts of Pichuga with the task of preventing the enemy from moving north along the right bank of the Volga River. In stubborn and bloody battles, the division suffered heavy losses, but stopped the enemy's advance. Over the next 4,5 months, its units, as part of the 66th Army of the Don Front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after 1922, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. The army was established in January 1918. The Bolsheviks raised an army to oppose the military confederations (especially the various groups collectively known as the White Army) of their adversaries during the Russian Civil War. Starting in February 1946, the Red Army, along with the Soviet Navy, embodied the main component of the Soviet Armed Forces; taking the official name of "Soviet Army", until its dissolution in 1991. The Red Army provided the largest land force in the Allied victory in the European theatre of World War II, and its invasion of Manchuria assisted the unconditional surrender of Imperial Japan. During operations on the Eastern Front, it accounted for 75–80% of casual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
50th Army (Soviet Union)
The 50th Army was a Soviet field army during World War II. It was formed in mid-August, 1941 and deployed on the southwest approaches to Moscow. Partly encircled and destroyed by German Second Panzer Army in the opening stages of Operation Typhoon, enough of the army escaped that it could be reinforced to successfully defend the city of Tula in November. It was at this time that the 50th came under the command of Lt. Gen. Ivan Boldin, who continued in command until February, 1945. During most of its career the army was relatively small and accordingly served in secondary roles. It finished the war in East Prussia, under the command of Lt. Gen. Fyodor Ozerov, as part of 3rd Belorussian Front. Formation The Army became active on August 16, 1941, along the Desna River as part of the newly-forming Bryansk Front. The Army's first commander, Major General Mikhail Petrov, issued his Combat Order No. 1 on that date. In it, he recorded the composition of the 50th Army as follows: * 217th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
33rd Army (Soviet Union)
The Red Army's 33rd Army was a Soviet field army during the Second World War. It was disbanded by being redesignated HQ Smolensk Military District in 1945. Initial Operations It was initially formed in the Moscow Military District in July 1941, consisting of the 1st, 5th, 9th, 17th, and 21st Moscow Narodnoe Opolcheniye, People's Militia divisions, plus artillery and other support units. Kombrig Dmitry Onuprienko (July — on October, 25th 1941) took command. It conducted defensive operations as a part of the Mozhaisk Defence Line and the Soviet Reserve Front. It was at Naro-Fominsk under General Lieutenant Mikhail Grigoryevich Yefremov, Mikhail Yefremov in October 1941. With the arrival of the German 2nd Panzer Army to Kashira and its 4th Panzer Group to the Moskva-Volga Canal, the conditions for the German capture of Moscow were created. But on December 1, the Germans hit the centre of the Soviet front. Two German divisions with 70 tanks broke through in the 33rd Army's sector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osowiec Fortress
Osowiec Fortress (Polish: ''Twierdza Osowiec'', Russian: ''Крепость Осовец'') is a 19th-century fortress built by the Russian Empire, located in what is now north-eastern Poland. It saw heavy fighting during World War I when it was defended for several months by its Russian garrison against German attacks. The fortress was built in the years 1882–1892 as one of the defensive works to protect the western borders of Russia against Germany, and continuously modernised afterwards to cope with advances in heavy siege artillery. In 1889–1893, military engineer Nestor Buinitsky took an important part in the creation of the fortress. It was located on the river Biebrza about 50 km from the border with the German province of East Prussia, in the one place where the marshlands of the river could be crossed, hence controlling a vital chokepoint. The extensive marshlands and bogs that surrounded it made attacks upon it difficult. The strategic Belostok– Lyck– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neman
The Neman, Nioman, Nemunas or MemelTo bankside nations of the present: Lithuanian: be, Нёман, , ; russian: Неман, ''Neman''; past: ger, Memel (where touching Prussia only, otherwise Nieman); lv, Nemuna; et, Neemen; pl, Niemen; ; uk, Німан, ''Niman'' is a river in Europe that rises in central Belarus and flows through Lithuania then forms the northern border of Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia's western exclave, which specifically follows its southern channel. It drains into the Curonian Lagoon, narrowly connected to the Baltic Sea. It flows about , so is considered a major Eastern European river. It flows generally west to Grodno within of the Polish border, north to Kaunas, then westward again to the sea. The largest river in Lithuania, and the third-largest in Belarus, it is navigable for most of its length. It starts from two small headwaters merging about southwest of the town of Uzda – about southwest of capital city Minsk. Only , an eastward me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
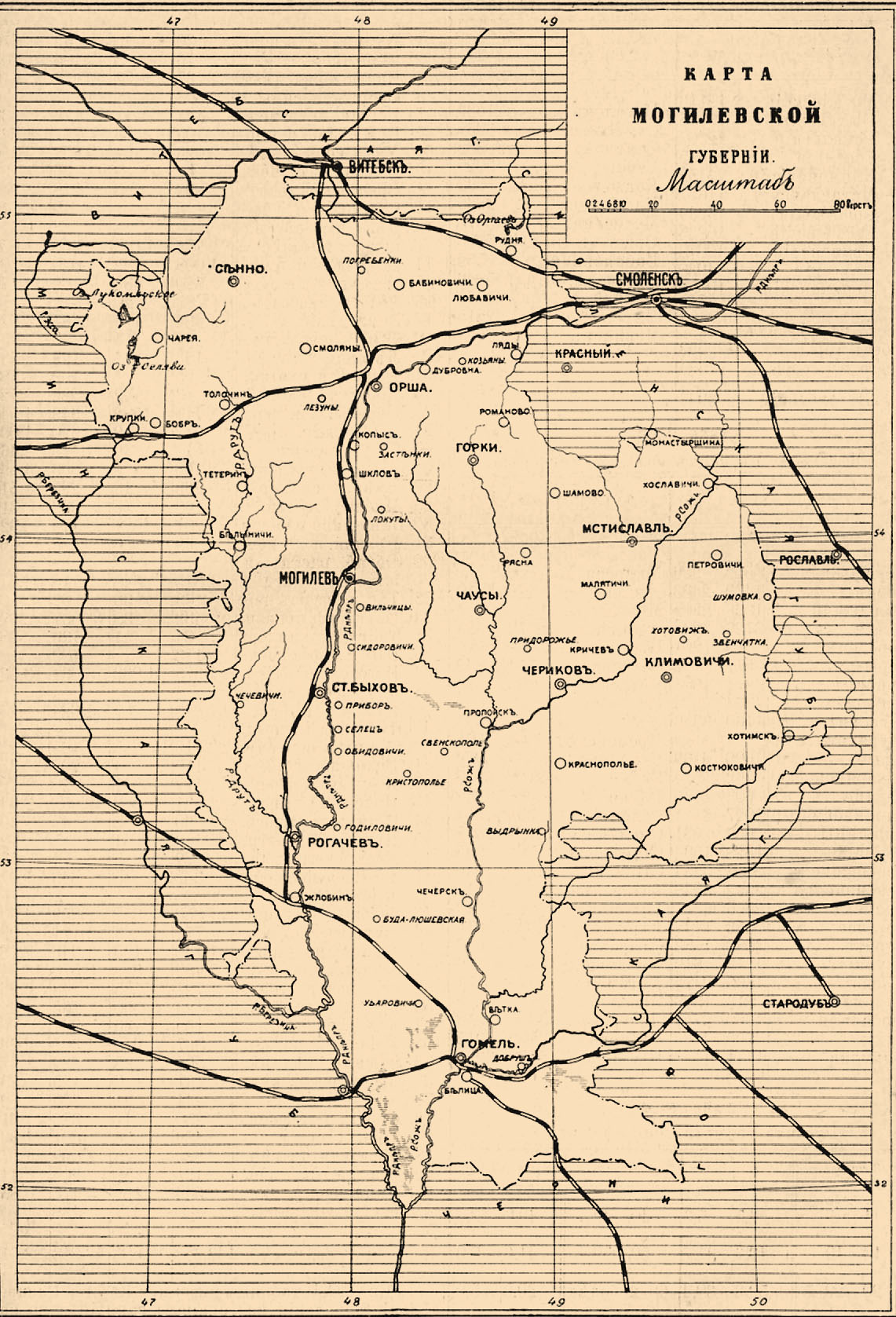
Mogilev Oblast
Mogilev Region or Mogilev Oblast or Mahiliow Voblasts ( be, link=no, Магілёўская вобласць; ''Mahiloŭskaja voblasć''; russian: link=no, Могилёвская область; ''Mogilyovskaya Oblast''), is a region (''oblast'') of Belarus with its administrative center at Mogilev (Mahilyow). Both Mogilev and Gomel Regions suffered severely after the Chernobyl nuclear radioactive reactor catastrophe in April 1986. Important cities within the region include Mogilev, Asipovichy and Babruysk. Geography The Mogilev Region covers a total area of , about 14% of the national total. The oblast's greatest extent from north to south is , from east to west - , while the highest point is above sea level and the lowest at above sea level. Many rivers flow through the Mogilev Region including the Dnieper (Dniapro), Berezina, Sozh, Druts, Pronya and Ptsich. The oblast' also has small lakes, the largest being the Zaozerye Lake with a surface area of . The Chigirin R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kastsyukovichy District
Kastsyukovichy' District ( be, Касцюковіцкі раён, russian: Костюковичский район, Kostyukovichsky raion) is a raion (district) in Mogilev Region, Belarus, the administrative center is the town of Kastsyukovichy. As of 2009, its population was 26,410. Population of Kastsyukovichy accounts for 60.6% of the district's population. Notable residents Masiej Siadnioŭ (1915 (1913?), Mokraje village - 2001), Belarusian poet and novelist, victim of the Gulag The Gulag, an acronym for , , "chief administration of the camps". The original name given to the system of camps controlled by the GPU was the Main Administration of Corrective Labor Camps (, )., name=, group= was the government agency in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Belorussian Front
The 2nd Belorussian Front (Russian: Второй Белорусский фронт, alternative spellings are 2nd Byelorussian Front) was a military formation, of Army group size, of the Soviet Army during the Second World War. Soviet army groups were known as Fronts. The 2nd Belorussian Front was created in February 1944 as the Soviets pushed the Germans back towards Byelorussia. General Colonel Pavel Kurochkin became its first commander. In hiatus in April 1944, its headquarters was reformed from the army headquarters of the disbanding 10th Army. Operations On 2 January 1944 2BF entered the former Polish territories. On 26 June 1944 the Front's forces captured Mogilev in the Mogilev Offensive. On 4 July, 2BF was tasked with mopping up the remains of Army Group Centre's Fourth Army under the command of General von Tippelskirch and the remains of the Ninth Army in a large pocket southeast of Minsk. On 9 July The 2BF attacks northwest from Vitebsk as part of a major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
49th Army (Soviet Union)
The 49th Combined Arms Army (russian: 49-я общевойсковая армия) is a combined arms (field) army (CAA) of the Russian Ground Forces, formed in 2010 and headquartered in Stavropol. Part of the Southern Military District, the army traces its heritage back to the Soviet Red Army's 49th Army, formed in 1941 after the German invasion of the Soviet Union in World War II. The 49th Army served through the entire war and was disbanded postwar in the summer of 1945. History Red Army On 6 August 1941, a Stavka directive ordered the formation of the 49th Army. One day later the army was formed as part of the Reserve Front, based on the 35th Rifle Corps, commanded by Lieutenant General Ivan Zakharkin. The army initially comprised 194th Mountain Rifle Division, 220th, 248th, 298th Rifle Divisions, the 4th People's Militia Division, 396th Corps Artillery Regiment, and other units. By 17 August 1941 the army was deployed in the rear of the Western Front, concentrated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mogilev
Mogilev (russian: Могилёв, Mogilyov, ; yi, מאָלעוו, Molev, ) or Mahilyow ( be, Магілёў, Mahilioŭ, ) is a city in eastern Belarus, on the Dnieper River, about from the border with Russia's Smolensk Oblast and from the border with Russia's Bryansk Oblast. , its population was 360,918, up from an estimated 106,000 in 1956. It is the administrative centre of Mogilev Region and the third-largest city in Belarus. History The city was first mentioned in historical records in 1267. From the 14th century, it was part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and since the Union of Lublin (1569), part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, where it became known as ''Mohylew''. In the 16th-17th centuries, the city flourished as one of the main nodes of the east–west and north–south trading routes. In 1577, Polish King Stefan Batory granted it city rights under Magdeburg law. In 1654, the townsmen negotiated a treaty of surrender to the Russians peacefully, if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roslavl
Roslavl (russian: Ро́славль, ) is a town and the administrative center of Roslavlsky District in Smolensk Oblast, Russia. It is a road and rail junction and a market town. Population: Climate Roslavl has a warm-summer humid continental climate (''Dfb'' in the Köppen climate classification). History Roslavl was founded as Rostislavl in the 1130s or 1140s. The name is likely due to Prince Rostislav of Smolensk, who was the founder of the fortress. It belonged to the Principality of Smolensk. The area belonged intermittently to the Principality of Smolensk and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. In 1376, Roslavl was transferred to Lithuania and became the center of a principality. It was chartered under Lithuanian rule in 1408. In 1515, it was conquered by the Grand Duchy of Moscow, but in 1618 transferred to Poland. Under Polish-Lithuanian rule Roslavl was part of the Smolensk Voivodeship. In 1667, according to the Truce of Andrusovo, Roslavl was transferred back to Russi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Army (Soviet Union)
The 10th Army of the Soviet Union's Red Army was a field army active from 1939 to 1944. History The Army was formed in September 1939, in the Moscow Military District, and then deployed to the Western Special Military District. During the Soviet invasion of Poland it consisted, according to Steven Zaloga, of the 11th Rifle Corps ( 6th, 33rd, and 121st RD); the 16th Rifle Corps (8th, 52nd, and 55th Rifle Divisions); and the 3rd Rifle Corps (in reserve) (33 and 113 RDs), under General Ivan Zakharkin. On 22 June 1941, at the onset of Operation Barbarossa, the Army was part of the Soviet Western Front. It consisted of the 1st Rifle Corps ( 2nd and 8th Rifle Divisions); 5th Rifle Corps (including 13th, 86th, and 113th Rifle Divisions); 6th Cavalry Corps ( 6th and 36th Cavalry Divisions) and 6th and 13th Mechanised Corps, under General K.D. Golubev. It was encircled by German forces in June 1941 and largely destroyed. By late June, the German Army Group Centre surrounded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |