|
604 (New Jersey Bus)
__NOTOC__ Year 604 ( DCIV) was a leap year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 604 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * The Avars regroup after they are almost destroyed; together with the Slavs they start pillaging through the Byzantine provinces, west and south of the Danube. Due to the new Persian war, Emperor Phocas has few imperial troops available to defend the Balkan Peninsula. * Byzantine–Persian War: King Khosrau II captures the Byzantine positions east of the Euphrates; the Persians destroy many cities in the Levant region, after prolonged sieges such as the Byzantine fortress of Dara (modern Turkey). Europe * Queen Brunhilda of Austrasia conspires to have Berthoald, Mayor of the Palace, assassinated. She convinces King Theuderic II to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sui Yangdi Tang
Sui or SUI may refer to: Places * Sui County, Henan, China * Sui County, Hubei in western Suizhou, Hubei in central China * Suizhou, Hubei, China, formerly Sui County * Sui, Bhiwani, Haryana, India * Sui, Rajasthan, India * Sui, Balochistan, Pakistan ** Sui gas field, near Sui, Balochistan * Switzerland (SUI is its International Olympic Committee code or FIFA country code, based on the French name suisse) * Suisun–Fairfield station, Amtrak station code SUI * State University of Iowa, the legal name of the University of Iowa * Sukhumi Babushara Airport, IATA code SUI People * Sui (surname), a transcription of two Chinese surnames * Sui people, one of the Kam–Sui peoples, an ethnic group of China and Vietnam ** Sui language spoken by the Shui * Sui dynasty, a Chinese dynasty that ruled the country in 581–618 * Sui (state), a Zhou-dynasty Chinese state Other * ''Sui'', meaning "years of age" in Chinese age reckoning * ''Sui'' or ''mizu'', 水, meaning "Water" in Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean in South-western Asia,Gasiorowski, Mark (2016). ''The Government and Politics of the Middle East and North Africa''. }, ), meaning "the eastern place, where the Sun rises". In the 13th and 14th centuries, the term ''levante'' was used for Italian maritime commerce in the Eastern Mediterranean, including Greece, Anatolia, Syria-Palestine, and Egypt, that is, the lands east of Venice. Eventually the term was restricted to the Muslim countries of Syria-Palestine and Egypt. In 1581, England set up the Levant Company to monopolize commerce with the Ottoman Empire. The name ''Levant States'' was used to refer to the French mandate over Syria and Lebanon after World War I. This is probab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
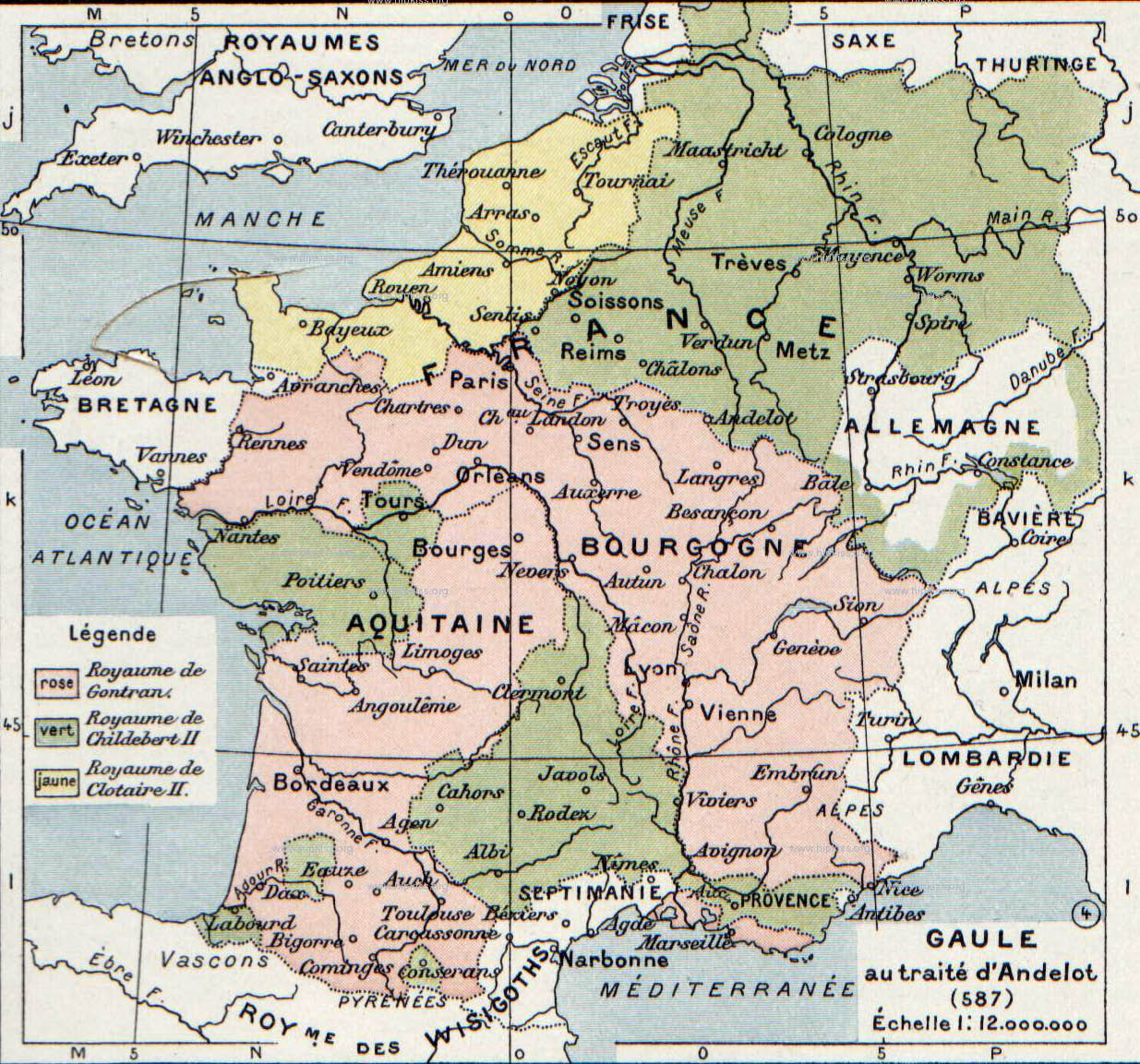
Chlothar II
Chlothar II, sometime called "the Young" (French language, French: le Jeune), (May/June 584 – 18 October 629), was king of Neustria and king of the Franks, and the son of Chilperic I and his third wife, Fredegund. He started his reign as an infant under the regency of his mother, who was in an uneasy alliance with Chlothar's uncle King Guntram of Burgundy, who died in 592. Chlothar took power upon the death of his mother in 597; though rich, Neustria was one of the smallest portions of Francia. He continued his mother's feud with Queen Brunhilda of Austrasia, Brunhilda with equal viciousness and bloodshed, finally achieving her execution in an especially brutal manner in 613, after winning the battle that enabled Chlothar to unite Francia under his rule. Like his father, he built up his territories by seizing lands after the deaths of other kings. His reign was long by contemporary standards, but saw the continuing erosion of royal power to the French nobility and the church ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, Weapons and Ornaments: Germanic Material Culture in Pre-Carolingian Central Europe, 400-750. BRILL, 2001, p.42. Later the term was associated with Romanized Germanic dynasties within the collapsing Western Roman Empire, who eventually commanded the whole region between the rivers Loire and Rhine. They imposed power over many other post-Roman kingdoms and Germanic peoples. Beginning with Charlemagne in 800, Frankish rulers were given recognition by the Catholic Church as successors to the old rulers of the Western Roman Empire. Although the Frankish name does not appear until the 3rd century, at least some of the original Frankish tribes had long been known to the Romans under their own names, both as allies providing soldiers, and as e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Étampes
Étampes () is a commune in the metropolitan area of Paris, France. It is located south-southwest from the center of Paris (as the crow flies). Étampes is a sub-prefecture of the Essonne department. Étampes, together with the neighboring communes of Morigny-Champigny and Brières-les-Scellés, form an urban area of 30,881 inhabitants (2018). This urban area is a "satellite city" of Paris. History Étampes () existed at the beginning of the 7th century and in the early Middle Ages belonged to the crown domain. During the Middle Ages it was the scene of several councils, the most notable of which took place in 1130 and resulted in the recognition of Innocent II as the legitimate pope. In 1652, during the war of the Fronde it suffered severely at the hands of the royal troops under Turenne. Geography Étampes lies on the river Chalouette, a tributary of the Juine, which borders the eastern outskirts of the serene town. Inhabitants of Étampes are known as ''Étampois''. Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
December 25
Events Pre-1600 * 36 – Forces of Emperor Guangwu of the Eastern Han, under the command of Wu Han, conquer the separatist Chengjia empire, reuniting China. * 274 – A temple to Sol Invictus is dedicated in Rome by Emperor Aurelian. * 333 – Roman Emperor Constantine the Great elevates his youngest son Constans to the rank of ''Caesar''. * 336 – First documentary sign of Christmas celebration in Rome. * 350 – Vetranio meets Constantius II at Naissus (Serbia) and is forced to abdicate his imperial title. Constantius allows him to live as a private citizen on a state pension. * 508 – Clovis I, king of the Franks, is baptized into the Catholic faith at Reims, by Saint Remigius. * 597 – Augustine of Canterbury and his fellow-labourers baptise in Kent more than 10,000 Anglo-Saxons. * 800 – The coronation of Charlemagne as Holy Roman Emperor, in Rome. * 820 – Eastern Emperor Leo V is murdered in a church of the Great Palace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seine
) , mouth_location = Le Havre/Honfleur , mouth_coordinates = , mouth_elevation = , progression = , river_system = Seine basin , basin_size = , tributaries_left = Yonne, Loing, Eure, Risle , tributaries_right = Ource, Aube, Marne, Oise, Epte The Seine ( , ) is a river in northern France. Its drainage basin is in the Paris Basin (a geological relative lowland) covering most of northern France. It rises at Source-Seine, northwest of Dijon in northeastern France in the Langres plateau, flowing through Paris and into the English Channel at Le Havre (and Honfleur on the left bank). It is navigable by ocean-going vessels as far as Rouen, from the sea. Over 60 percent of its length, as far as Burgundy, is negotiable by large barges and most tour boats, and nearly its whole length is available for recreational boating; excursion boats offer sightseeing tours of the river banks in the capital city, Paris. There are 37 bridges in P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villa
A villa is a type of house that was originally an ancient Roman upper class country house. Since its origins in the Roman villa, the idea and function of a villa have evolved considerably. After the fall of the Roman Republic, villas became small farming compounds, which were increasingly fortified in Late Antiquity, sometimes transferred to the Church for reuse as a monastery. Then they gradually re-evolved through the Middle Ages into elegant upper-class country homes. In the Early Modern period, any comfortable detached house with a garden near a city or town was likely to be described as a villa; most survivals have now been engulfed by suburbia. In modern parlance, "villa" can refer to various types and sizes of residences, ranging from the suburban semi-detached double villa to, in some countries, especially around the Mediterranean, residences of above average size in the countryside. Roman Roman villas included: * the ''villa urbana'', a suburban or country seat t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theuderic II
Theuderic II (also spelled Theuderich, Theoderic or Theodoric; in French, ''Thierry'') (587–613), king of Burgundy (595–613) and Austrasia (612–613), was the second son of Childebert II. At his father's death in 595, he received Guntram's kingdom of Burgundy, with its capital at Orléans, while his elder brother, Theudebert II, received their father's kingdom of Austrasia, with its capital at Metz. He also received the lordship of the cities (''civitates'') of Toulouse, Agen, Nantes, Angers, Saintes, Angoulême, Périgueux, Blois, Chartres, and Le Mans. During his minority, and later, he reigned under the guidance of his grandmother Brunhilda, evicted from Austrasia by his brother Theudebert II. In 596, Clotaire II, king of Neustria, and Fredegund, Clotaire's mother, took Paris, which was supposed to be held in common. Fredegund, then her son's regent, sent a force to Laffaux and the armies of Theudebert and Theuderic were defeated. In 599, Brunhilda was forced out of Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berthoald
Berthoald (or ''Bertoald'') (died 604) was the mayor of the palace of Burgundy from some time before 603 (when he is first mentioned as mayor under King Theuderic II) until his death in the next year. According to the Burgundian chronicler Fredegar, he was moderate, sensible, brave, and honest. In 604, Theuderic, at the suggestion of his grandmother Brunhilda, sent Berthoald to inspect the royal ''villae'' along the Seine, in order to have him away from court so that he might be conveniently killed. Brunhilda intended to raise her paramour Protadius to Berthoald's honours. Berthoald and three hundred men were at Arèle when King Clotaire II of Neustria—alerted by some means to his presence— sent an army under his son Merovech and his mayor Landric to assault him. Berthoald fled to Orléans, and Landric followed and besieged him, which violated a peace treaty with Theuderic. The king of Burgundy went out at Christmas to Étampes and met the forces of Merovech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brunhilda Of Austrasia
Brunhilda (c. 543–613) was queen consort of Austrasia, part of Francia, by marriage to the Merovingian king Sigebert I of Austrasia, and regent for her son, grandson and great-grandson. In her long and complicated career she ruled the eastern Frankish kingdoms of Austrasia and Burgundy for three periods as regent for her son Childebert II from 575 until 583; her grandsons Theudebert II and Theuderic II from 595 until 599; and her great-grandson Sigebert II in 613. The period was marked by tension between the royal house and the powerful nobles vying for power. Brunhilda was apparently an efficient ruler, but this and her forceful personality brought her into conflict with her nobles, the church and the other Merovingians. Her bitter feud with Fredegund, mistress of Chilperic I of Neustria, who murdered Brunhilda's sister, Queen Galswintha (c. 568) in order to replace her as queen, lasted until Fredegund's death in 597. Fredegund had Brunhilda's husband murdered and Brunhilda im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)