|
6708 Bobbievaile
6708 Bobbievaile, provisional designation ', is a stony background asteroid and asynchronous binary system from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately in diameter. It was discovered on 4 January 1989, by Australian astronomer Robert McNaught at the Siding Spring Observatory in New South Wales, Australia. It is named after Bobbie Vaile. Orbit and classification ''Bobbievaile'' is a stony, non-family asteroid from the main belt's background population. It orbits the Sun in the inner main-belt at a distance of 2.0–2.9 AU once every 3 years and 10 months (1,397 days). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.18 and an inclination of 12 ° with respect to the ecliptic. It was first observed as ' at El Leoncito in 1979, extending the body's observation arc by 10 years prior to its official discovery observation at Siding Spring. Binary asteroid On 7 May 2009, it was announced that ''Bobbievaile'' was determined to be a binary asteroid based on a series of ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert McNaught
Robert H. McNaught (born in Scotland in 1956) is a Scottish-Australian astronomer at the Research School of Astronomy and Astrophysics of the Australian National University (ANU). He has collaborated with David J. Asher of the Armagh Observatory. The inner main-belt asteroid 3173 McNaught, discovered by Edward Bowell at Anderson Mesa Station in 1981, was named after him by its discoverer, following a suggestion by David Seargent. Work McNaught is a prolific discoverer of asteroids and comets, described as "the world's greatest comet discoverer" and he participated in the Siding Spring Survey (SSS) using the ANU's Uppsala Southern Schmidt Telescope. He discovered the Great Comet C/2006 P1 on 7 August 2006, the brightest comet in several decades, which became easily visible to the naked eye for observers in the Southern Hemisphere. The SSS was the only active professional Near Earth Object survey in the Southern Hemisphere. The survey ended in 2013 after funding dried up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object. For a satellite orbiting the Earth directly above the Equator, the plane of the satellite's orbit is the same as the Earth's equatorial plane, and the satellite's orbital inclination is 0°. The general case for a circular orbit is that it is tilted, spending half an orbit over the northern hemisphere and half over the southern. If the orbit swung between 20° north latitude and 20° south latitude, then its orbital inclination would be 20°. Orbits The inclination is one of the six orbital elements describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit. It is the angle between the orbital plane and the plane of reference, normally stated in degrees. For a satellite orbiting a planet, the plane of reference is usually the plane containing the planet's equator. For pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Planet Circulars
The Minor Planet Center (MPC) is the official body for observing and reporting on minor planets under the auspices of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Founded in 1947, it operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. Function The Minor Planet Center is the official worldwide organization in charge of collecting observational data for minor planets (such as asteroids), calculating their orbits and publishing this information via the '' Minor Planet Circulars''. Under the auspices of the International Astronomical Union (IAU), it operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, which is part of the Center for Astrophysics along with the Harvard College Observatory. The MPC runs a number of free online services for observers to assist them in observing minor planets and comets. The complete catalogue of minor planet orbits (sometimes referred to as the "Minor Planet Catalogue") may also be freely downloaded. In addition to astrometric data, the MPC collect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Planet Center
The Minor Planet Center (MPC) is the official body for observing and reporting on minor planets under the auspices of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Founded in 1947, it operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. Function The Minor Planet Center is the official worldwide organization in charge of collecting observational data for minor planets (such as asteroids), calculating their orbits and publishing this information via the '' Minor Planet Circulars''. Under the auspices of the International Astronomical Union (IAU), it operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, which is part of the Center for Astrophysics along with the Harvard College Observatory. The MPC runs a number of free online services for observers to assist them in observing minor planets and comets. The complete catalogue of minor planet orbits (sometimes referred to as the "Minor Planet Catalogue") may also be freely downloaded. In addition to astrometric data, the MPC collect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Phoenix (SETI)
Project Phoenix was a SETI project to search for extraterrestrial intelligence by analyzing patterns in radio signals. It was run by the independently funded SETI Institute of Mountain View, California, U.S. Project Phoenix started work in February 1995 with the Parkes radio telescope located in New South Wales, Australia, the largest telescope in the Southern Hemisphere. Between September 1996 and April 1998, the Project used the National Radio Astronomy Observatory, Green Bank in Green Bank, West Virginia, U.S. Rather than attempting to scan the whole sky for messages, the Project concentrated on nearby systems that are similar to our own. Project Phoenix's targets comprised about 800 stars with a 200 light-year range. The Project searched for radio signals as narrow as 1 Hz between 1,000 and 3,000 MHz: a broad bandwidth compared with most SETI searches. In March 2004 the Project announced that after checking the 800 stars on its list, it had failed to find any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SETI
The search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI) is a collective term for scientific searches for intelligent extraterrestrial life, for example, monitoring electromagnetic radiation for signs of transmissions from civilizations on other planets. Scientific investigation began shortly after the advent of radio in the early 1900s, and focused international efforts have been ongoing since the 1980s. In 2015, Stephen Hawking and Israeli billionaire Yuri Milner announced a project called Breakthrough Listen. History Early work There have been many earlier searches for extraterrestrial intelligence within the Solar System. In 1896, Nikola Tesla suggested that an extreme version of his wireless electrical transmission system could be used to contact beings on Mars. In 1899, while conducting experiments at his Colorado Springs experimental station, he thought he had detected a signal from Mars since an odd repetitive static signal seemed to cut off when Mars set in the night ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Sydney University
Western Sydney University, formerly the University of Western Sydney, is an Australian multi-campus university in the Greater Western region of Sydney, Australia. The university in its current form was founded in 1989 as a federated network university with an amalgamation between the Nepean College of Advanced Education and the Hawkesbury Agricultural College. The Macarthur Institute of Higher Education was incorporated in the university in 1989. In 2001, the University of Western Sydney was restructured as a single multi-campus university rather than as a federation. In 2015, the university underwent a rebranding which resulted in a change in name from the University of Western Sydney to Western Sydney University. It is a provider of undergraduate, postgraduate, and higher research degrees with campuses in Bankstown, Blacktown, Campbelltown, Hawkesbury, Liverpool, Parramatta, and Penrith. In 2022, it was ranked in the top 201–250 in the world and jointly 11th in Austral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Planet
According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a minor planet is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the Sun that is exclusively classified as neither a planet nor a comet. Before 2006, the IAU officially used the term ''minor planet'', but that year's meeting reclassified minor planets and comets into dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies (SSSBs).Press release, IAU 2006 General Assembly: Result of the IAU Resolution votes International Astronomical Union, August 24, 2006. Accessed May 5, 2008. Minor planets include asteroids ( |
Spherical
A sphere () is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the centre of the sphere, and is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental object in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres roll smoothly in any direction, so most balls used in sports and toys are spherical, as are ball bearings. Basic terminology As mentioned earlier is the sphere's r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
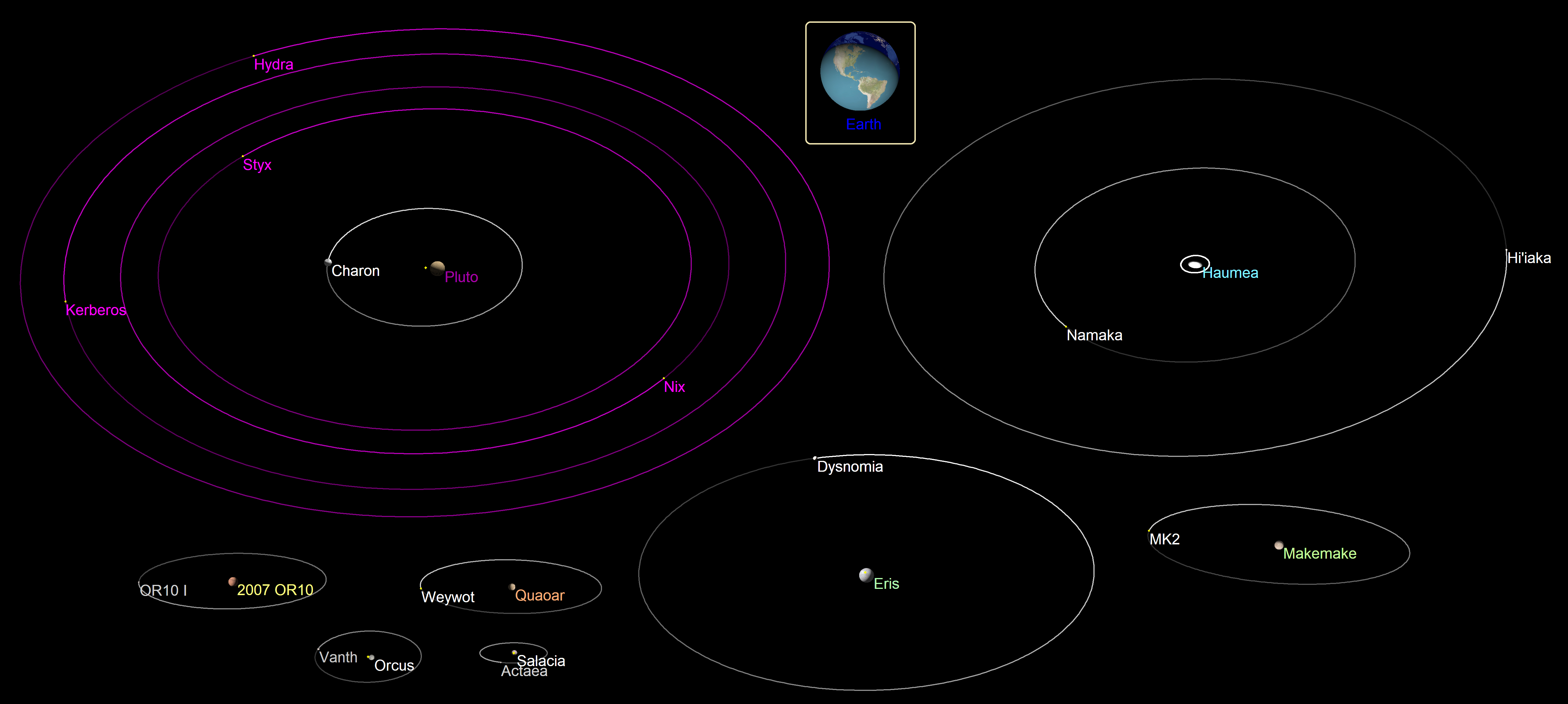
Minor-planet Moon
A minor-planet moon is an astronomical object that orbits a minor planet as its natural satellite. , there are 457 minor planets known or suspected to have moons. Discoveries of minor-planet moons (and binary objects, in general) are important because the determination of their orbits provides estimates on the mass and density of the primary, allowing insights into their physical properties that are generally not otherwise accessible. Several of the moons are quite large compared to their primaries: 90 Antiope, Mors–Somnus and Sila–Nunam (95%), Patroclus–Menoetius, Altjira and Lempo–Hiisi (90%, with Lempo–Paha at 50%). The largest known minor-planet moon in ''absolute'' size is Pluto's largest moon Charon, which itself has about half the diameter of Pluto. The first modern era mention of the possibility of an asteroid satellite was in connection with an occultation of the bright star Gamma Ceti by the asteroid 6 Hebe in 1977. The observer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary (astronomy)
A primary (also called a gravitational primary, primary body, or central body) is the main physical body of a gravitationally bound, multi-object system. This object constitutes most of that system's mass and will generally be located near the system's barycenter. In the Solar System, the Sun is the primary for all objects that orbit the star. In the same way, the primary of all satellites (be they natural satellites (moons) or artificial ones) is the planet they orbit. The term ''primary'' is often used to avoid specifying whether the object near the barycenter is a planet, a star, or any other astronomical object. In this sense, the word ''primary'' is always used as a noun. The center of mass is the average position of all the objects weighed by mass. The Sun is so massive that the Solar System's barycenter frequently lies very near the Sun's center but owing to the mass and distance of the gas giant planets, the Solar System's barycenter occasionally lies outside the Sun as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lightcurve
In astronomy, a light curve is a graph of light intensity of a celestial object or region as a function of time, typically with the magnitude of light received on the y axis and with time on the x axis. The light is usually in a particular frequency interval or band. Light curves can be periodic, as in the case of eclipsing binaries, Cepheid variables, other periodic variables, and transiting extrasolar planets, or aperiodic, like the light curve of a nova, a cataclysmic variable star, a supernova or a microlensing event or binary as observed during occultation events. The study of the light curve, together with other observations, can yield considerable information about the physical process that produces it or constrain the physical theories about it. Variable stars Graphs of the apparent magnitude of a variable star over time are commonly used to visualise and analyse their behaviour. Although the categorisation of variable star types is increasingly done from their spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |