|
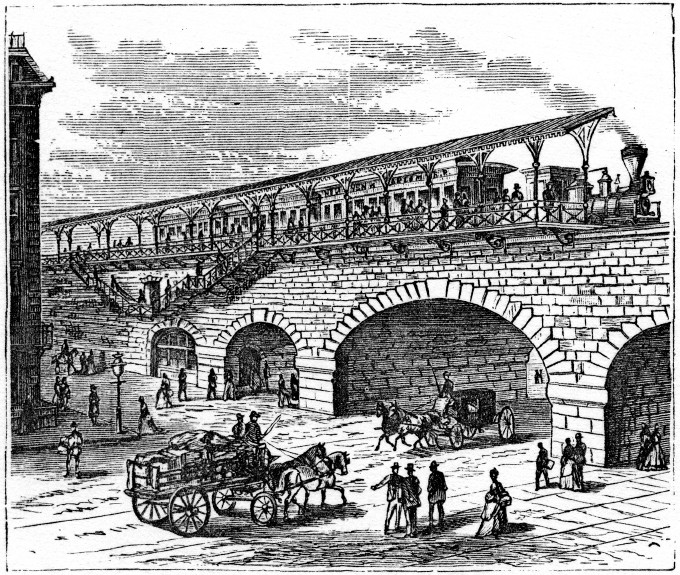
59th Street Station (New York Central Railroad)
The 59th Street station is a never-opened station in the Park Avenue Tunnel used by the Metro-North Railroad for all of its trains. The station was built by the New York Central & Hudson River Railroad as part of an agreement with the government of New York City during the late 1870s, although trains never stopped here. The station is used as an emergency exit for the Metro-North Railroad. History The New York State Legislature passed legislation in 1872, requiring that of New York and Harlem Railroad tracks between Grand Central and the Harlem River be placed underground. The confluence of tracks to the north of Grand Central was considered to be the city's "most fearful death-trap" by ''The New York Times'' in 1872, and large meetings were held to protest the deaths caused by collisions between trains and pedestrians. The law set up a Board of Engineers to manage the project, which was known as the Fourth Avenue Improvement. The law stated that the authorization for two add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Park Avenue
Park Avenue is a wide New York City boulevard which carries north and southbound traffic in the boroughs of Manhattan and the Bronx. For most of the road's length in Manhattan, it runs parallel to Madison Avenue to the west and Lexington Avenue to the east. Park Avenue's entire length was formerly called Fourth Avenue; the title still applies to the section between Cooper Square and 14th Street. The avenue is called Union Square East between 14th and 17th Streets, and Park Avenue South between 17th and 32nd Streets. History Early years and railroad construction The entirety of Park Avenue was originally known as Fourth Avenue and carried the tracks of the New York and Harlem Railroad starting in the 1830s. The railroad originally ran through an open cut through Murray Hill, which was covered with grates and grass between 34th and 40th Street in the early 1850s. A section of this "park" was later renamed Park Avenue in 1860. Park Avenue's original southern terminus was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornelius Vanderbilt
Cornelius Vanderbilt (May 27, 1794 – January 4, 1877), nicknamed "the Commodore", was an American business magnate who built his wealth in railroads and shipping. After working with his father's business, Vanderbilt worked his way into leadership positions in the inland water trade and invested in the rapidly growing railroad industry, effectively transforming the geography of the United States. As one of the richest Americans in history and wealthiest figures overall, Vanderbilt was the patriarch of the wealthy and influential Vanderbilt family. He provided the initial gift to found Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tennessee. According to historian H. Roger Grant: "Contemporaries, too, often hated or feared Vanderbilt or at least considered him an unmannered brute. While Vanderbilt could be a rascal, combative and cunning, he was much more a builder than a wrecker ..being honorable, shrewd, and hard-working." Ancestry Cornelius Vanderbilt's great-great-great-grandf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former New York Central Railroad Stations
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Railway Stations In New York (state)
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midtown Manhattan
Midtown Manhattan is the central portion of the New York City borough of Manhattan and serves as the city's primary central business district. Midtown is home to some of the city's most prominent buildings, including the Empire State Building, the Chrysler Building, the Hudson Yards Redevelopment Project, the headquarters of the United Nations, Grand Central Terminal, and Rockefeller Center, as well as tourist destinations such as Broadway, Times Square, and Koreatown. Penn Station in Midtown Manhattan is the busiest transportation hub in the Western Hemisphere. Midtown Manhattan is the largest central business district in the world and ranks among the most expensive locations for real estate; Fifth Avenue in Midtown Manhattan commands the world's highest retail rents, with average annual rents at US in 2017. However, due to the high price of retail spaces in Midtown, there are also many vacant storefronts in the neighborhood. Midtown is the country's largest commercia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Avenue (Manhattan)
Second Avenue is located on the East Side of the New York City borough of Manhattan extending from Houston Street at its south end to the Harlem River Drive at 128th Street at its north end. A one-way street, vehicular traffic on Second Avenue runs southbound (downtown) only, except for a one-block segment of the avenue in Harlem. South of Houston Street, the roadway continues as Chrystie Street south to Canal Street. A bicycle lane runs in the leftmost lane of Second Avenue from 125th to Houston Streets. The section from 55th to 34th Streets closes a gap in the Manhattan Waterfront Greenway. Second Avenue passes through a number of Manhattan neighborhoods including (from south to north) the Lower East Side, the East Village, Stuyvesant Square, Kips Bay, Tudor City, Turtle Bay, East Midtown, Lenox Hill, Yorkville and Spanish Harlem. History Downtown Second Avenue in the Lower East Side was the home to many Yiddish theatre productions during the early part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Williams Bridge Station
Williams Bridge station (also known as Williams Bridge–East 210th Street station) is a commuter rail stop on the Metro-North Railroad's Harlem Line, serving the Williamsbridge and Norwood sections of the Bronx, New York City. It is from Grand Central Terminal and travel time there is approximately 24 minutes. The station is located at the intersection of Gun Hill Road and Webster Avenue. Due to its short platform length, only the doors of four cars can open for passengers. The station is located in the Zone 2 Metro-North fare zone. History Rail service in Williams Bridge can be traced as far back as 1842 with the establishment of the New York and Harlem Railroad, which became part of the New York Central and Hudson River Railroad in 1864 and eventually taken over by the New York Central Railroad. Williams Bridge Station itself, which was originally built sometime in the 19th century, originally had a station house on the southeast corner of the Gun Hill Road bridge an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harlem–125th Street Station
The Harlem–125th Street station is a commuter rail stop serving the Metro-North Railroad's Hudson, Harlem, and New Haven Lines. It is located at East 125th Street and Park Avenue in East Harlem, Manhattan, New York City. The station also serves as an important transfer point between the Metro-North trains and the New York City Subway's IRT Lexington Avenue Line () for access to the Upper East Side of Manhattan. It is the only station besides Grand Central Terminal that serves all three lines east of the Hudson River. Trains leave for Grand Central Terminal, as well as to the Bronx and the northern suburbs, regularly. History The current station was built in 1896–97 and designed by Morgan O'Brien, New York Central and Hudson River Railroad principal architect. It replaced an earlier one that was built in 1874 when the New York Central and the New York, New Haven & Hartford Railroad, the ancestors of today's Metro-North, moved the tracks from an open cut to the present-day ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
110th Street Station (New York Central Railroad)
The 110th Street station was a station located on the Metro-North Railroad's Park Avenue Viaduct in East Harlem, Manhattan, New York City. The station was built by the New York Central & Hudson River Railroad as part of an agreement with the New York City government. It was located at Park Avenue and 110th Street. History This station opened on May 15, 1876 with the introduction of partial rapid transit on the Harlem Line, with sixteen trains a day running between Grand Central Depot Grand Central Terminal is a major commuter rail terminal in Midtown Manhattan, New York City, serving the Metro-North Railroad's Harlem, Hudson and New Haven Lines. It is the most recent of three functionally similar buildings on the same s ... and William's Bridge. On the same date, the 86th Street station opened, and while that station was exclusively served by the rapid transit service, some trains expresses to Golden's Bridge stopped here. By 1904, this station was only served by l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
86th Street Station (New York Central Railroad)
The 86th Street station is an abandoned station located in the Park Avenue Tunnel used by Metro-North Railroad for all of its trains. The station was built by the New York Central & Hudson River Railroad as part of an agreement with New York City. The station was built during the late 19th century. It was located at Park Avenue and 86th Street on the Upper East Side of Manhattan. History Construction The New York State Legislature passed legislation in 1872, requiring that of New York and Harlem Railroad tracks between Grand Central and the Harlem River be placed underground. The confluence of tracks to the north of Grand Central was considered to be the city's "most fearful death-trap" by ''The New York Times'' in 1872, and large meetings were held to protest the deaths caused by collisions between trains and pedestrians. The law set up a Board of Engineers to manage the project, which was known as the Fourth Avenue Improvement. The law stated that the authorization for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
72nd Street Station (New York Central Railroad)
The 72nd Street station is an abandoned station located in the Park Avenue Tunnel used by Metro-North Railroad for all of its trains. The station has two side platforms and is located in between 72nd Street and 73rd Street underneath Park Avenue on the Upper East Side of Manhattan. The station was built by the New York Central & Hudson River Railroad as part of an agreement with New York City. History Construction The New York State Legislature passed legislation in 1872, requiring that of New York and Harlem Railroad tracks between Grand Central and the Harlem River be placed underground. The confluence of tracks to the north of Grand Central was considered to be the city's "most fearful death-trap" by '' The New York Times'' in 1872, and large meetings were held to protest the deaths caused by collisions between trains and pedestrians. The law set up a Board of Engineers to manage the project, which was known as the Fourth Avenue Improvement. The law stated that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Track Ballast
Track ballast forms the trackbed upon which railroad ties (sleepers) are laid. It is packed between, below, and around the ties. It is used to bear the load from the railroad ties, to facilitate drainage of water, and also to keep down vegetation that might interfere with the track structure. Ballast also holds the track in place as the trains roll over it. A variety of materials have been used as track ballast, including crushed stone, washed gravel, bank run (unwashed) gravel, torpedo gravel (a mixture of coarse sand and small gravel), slag, chats, coal cinders, sand, and burnt clay. The term "ballast" comes from a nautical term for the stones used to stabilize a ship. Construction The appropriate thickness of a layer of track ballast depends on the size and spacing of the ties, the amount of traffic on the line, and various other factors. Track ballast should never be laid down less than thick, and high-speed railway lines may require ballast up to thick.Bell 2004, p. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)