|
56 Eridani
This is the list of notable stars in the constellation Eridanus, sorted by decreasing brightness. See also *List of stars by constellation All stars but one can be associated with an IAU constellation. IAU constellations are areas of the sky. Although there are only 88 IAU constellations, the sky is actually divided into 89 irregularly shaped boxes as the constellation Serpens is spli ... References * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:List of stars in Eridanus *List Eridanus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sky, night, but their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed stars, fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterism (astronomy), asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye, all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life star formation, begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Its stellar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achernar
Achernar is the brightest star in the constellation of Eridanus, and the ninth-brightest in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation Alpha Eridani, which is Latinized from α Eridani and abbreviated Alpha Eri or α Eri. The name Achernar applies to the primary component of a binary system. The two components are designated Alpha Eridani A (the primary) and B (the secondary), with the latter known informally as Achernar B. As determined by the ''Hipparcos'' astrometry satellite, this system is located at a distance of approximately from the Sun. Of the ten apparent brightest stars in the night-time sky, Alpha Eridani is the hottest and bluest in color, due to Achernar being of spectral type B. Achernar has an unusually rapid rotational velocity, causing it to become oblate in shape. The secondary is smaller, of spectral type A, and orbits Achernar at a distance of . Nomenclature ''α Eridani'' ( Latinised to ''Alpha Eridani'') is the system's Bayer designation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon Eridani
Epsilon Eridani ( Latinized from ε Eridani), formally named Ran, is a star in the southern constellation of Eridanus, at a declination of 9.46° south of the celestial equator. This allows it to be visible from most of Earth's surface. At a distance of from the Sun, it has an apparent magnitude of 3.73. It is the third-closest individual star or star system visible to the unaided eye. The star is estimated to be less than a billion years old. Because of its relative youth, Epsilon Eridani has a higher level of magnetic activity than the present-day Sun, with a stellar wind 30 times as strong. Its rotation period is 11.2 days at the equator. Epsilon Eridani is smaller and less massive than the Sun, and has a comparatively lower level of elements heavier than helium. It is a main-sequence star of spectral class K2, which means that energy generated at the core through nuclear fusion of hydrogen is emitted from the surface at a temperature of about , giving it an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tau4 Eridani
Tau4 Eridani (τ4 Eridani, τ4 Eri) is a binary star system in the constellation Eridanus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.65. The distance to this star can be estimated using the parallax method, which yields a value of roughly 300 light years. This is an evolved red giant star currently on the asymptotic giant branch with a stellar classification of M3/4 III. It is a slow irregular variable star of type Lb, undergoing changes in magnitude over the range 3.57−3.72 with a periodicity of 23.8 d. The measured angular diameter of Tau4 Eridani is . At its estimated distance, this yields a physical size of about 106 times the radius of the Sun. It shines with 1,537 times the luminosity of the Sun from an outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 3,712 K. This is most likely a binary star system. The companion is a magnitude 9.5 star at an angular separation of 5.7 ″ along a position angle of 291°, as of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chi Eridani
χ Eridani (Latinised as Chi Eridani) is a binary star system in the constellation Eridanus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.70. The distance to this system, as determined using the parallax method, is around 58 light years. The pair had an angular separation of 5.0 arcseconds as of 1994. This corresponds to a projected separation of around 128 AU. The primary component is an evolving G-type subgiant star with a stellar classification of G8 IV. It is about 1.6 times the mass of the Sun and has 4 times the Sun's radius. The star shines with 10 times the solar luminosity The solar luminosity (), is a unit of radiant flux ( power emitted in the form of photons) conventionally used by astronomers to measure the luminosity of stars, galaxies and other celestial objects in terms of the output of the Sun. One nominal ... from its outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 5,115 K. Unusually for a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phi Eridani
φ Eridani (Latinised as Phi Eridani) is a star in the constellation Eridanus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.55. The distance to this star, as determined using the parallax method, is around 154 light-years. This is a B-type star with a stellar classification of B8IV-V, suggesting it shows traits of a main-sequence star and a subgiant. It is spinning rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 250 km/s. This rotation is giving the star an oblate shape with an equator that is 17% larger than the polar radius. The estimated angular size is 0.68 milliarcseconds. Since the distance is known, this yields a physical size of around 3.4 times the radius of the Sun. It has 3.55 times the mass of the Sun and radiates 255 times the solar luminosity The solar luminosity (), is a unit of radiant flux ( power emitted in the form of photons) conventionally used by astronomers to measure the luminosity of stars, galaxies an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upsilon4 Eridani
Upsilon4 Eridani is a close binary star system in the constellation Eridanus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.56. Based upon parallax measurements, the pair are located around from the Sun. This is a double-lined spectroscopic binary star system, which means that the Doppler-shifted spectral lines of both components can be distinguished. The pair have a circular orbit with a period of five days. The system is composed of two B-type main-sequence star A B-type main-sequence star (B V) is a main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type B and luminosity class V. These stars have from 2 to 16 times the mass of the Sun and surface temperatures between 10,000 and 30,000 K. B-type star ...s: one has a stellar classification of B8V and the other B9.5V. Both stars show HgMn peculiarities in their spectrum, and their properties are nearly identical. The spin rate of the two stars is synchronized to their orbital period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
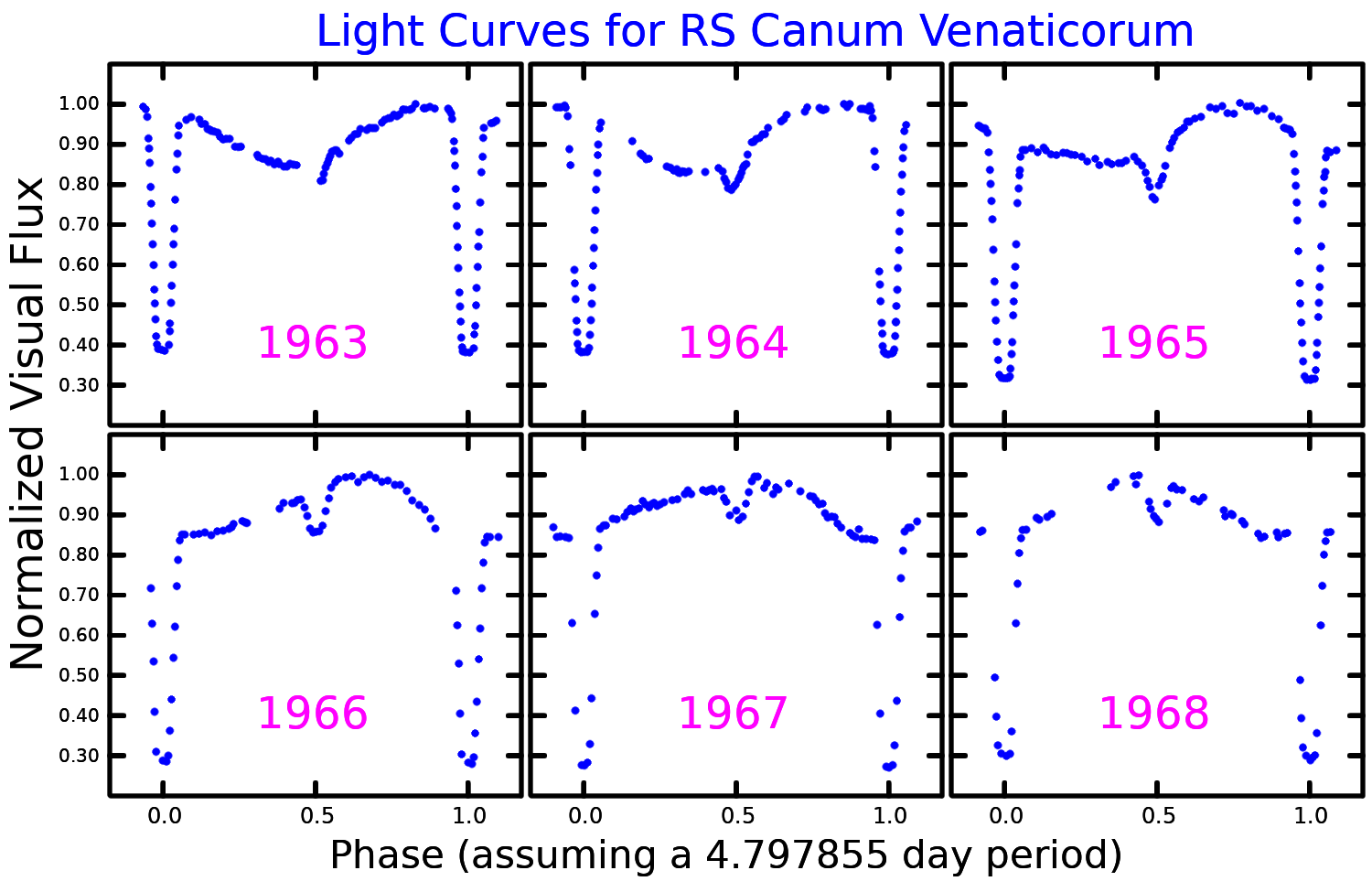
RS Canum Venaticorum Variable
An RS Canum Venaticorum variable is a type of variable star. The variable type consists of close binary stars having active chromospheres which can cause large stellar spots. These spots are believed to cause variations in their observed luminosity. Systems can exhibit variations on timescales of years due to variation in the spot surface coverage fraction, as well as periodic variations which are, in general, close to the orbital period of the binary system. Some systems exhibit variations in luminosity due to their being eclipsing binaries. Typical brightness fluctuation is around 0.2 magnitudes. They take their name from the star RS Canum Venaticorum (abbreviated RS CVn). Otto Struve (1946) first called attention to the group, but it was Oliver (1974) who was the first to formally propose a set of observational characteristics to define the RS CVn criteria. The working definition, as it is used today, was that set down by Hall (1976). Berdyuginabr>2.4 RS CVn stars/ref> The RS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Eridani
Delta Eridani, which is Latinized from δ Eridani, is a star in the equatorial constellation of Eridanus. The star is visible to the naked eye and has been observed to vary in slightly brightness between magnitudes 3.51 and 3.56, although subsequent observations did not bear this out. It is relatively near to the Sun, with a distance of about 29.5 light years as determined from parallax. The star is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −6 km/s. Delta Eridani is sometimes called Rana: ''Rana'' means "the frog" in Latin, but derivation of this name is uncertain. The name was approved by the International Astronomic Union on 4 April 2022. Structure The stellar classification of this star is K0 IV, matching a subgiant star that has exhausted its core hydrogen. This has caused the star to expand and become cooler than a comparable main sequence star. Stellar modelling indicates it is near the end of the subgiant stage and about to transition in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Eridani
Gamma Eridani (γ Eridani, abbreviated Gamma Eri, γ Eri), formally named Zaurak , is a variable star in the constellation of Eridanus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that varies around 2.9, and lies at a distance of about 203 light years from the Sun, as determined by the Hipparcos astrometry satellite. Description Gamma Eridani has been defined as a standard star for the spectral class M0III-IIIb. It is a red giant on the asymptotic giant branch, fusing hydrogen and helium in separate shells outside its core. Observations published in 1960 showed it to vary in brightness by a few hundredths of a magnitude. In 1977, it was officially listed as a variable star in the General Catalogue of Variable Stars although the class of variable is uncertain. Nomenclature ''Gamma Eridani'' is the star's Bayer designation. It has the traditional name ''Zaurak'', alternatively spelled Zaurac, which is Arabic for 'boat'. In 2016, the In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Star
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in which case they are called ''visual binaries''. Many visual binaries have long orbital periods of several centuries or millennia and therefore have orbits which are uncertain or poorly known. They may also be detected by indirect techniques, such as spectroscopy (''spectroscopic binaries'') or astrometry (''astrometric binaries''). If a binary star happens to orbit in a plane along our line of sight, its components will eclipse and transit each other; these pairs are called ''eclipsing binaries'', or, together with other binaries that change brightness as they orbit, ''photometric binaries''. If components in binary star systems are close enough they can gravitationally distort their mutual outer stellar atmospheres. In some cases, thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theta Eridani
Theta Eridani, Latinized from θ Eridani, is a binary system in the constellation of Eridanus with a combined apparent magnitude of 2.88. Its two components are designated θ1 Eridani, formally named Acamar (the traditional name of the system), and θ2 Eridani. The system's distance from the Sun based on parallax measurements is approximately 165 light-years. Nomenclature Theta Eridani is the system's Bayer designation; θ1 and θ2 Eridani those of its two components. The system bore the traditional name Acamar, derived from the Arabic آخِر النَّهْر ''Ākhir an-nahr'', which means "the end of the river", via a Roman-alphabet handwriting misread "rn" to "m". In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN decided to attribute proper names to individual stars rather than entire multiple systems. It approved the name "Acamar" for θ1 Eridani on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |