|
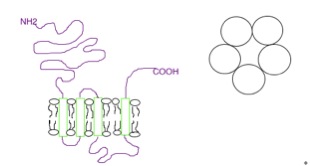
5-HT5 Receptor
5-Hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 5A, also known as HTR5A, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HTR5A'' gene. Agonists and antagonists for 5-HT receptors, as well as serotonin uptake inhibitors, present promnesic (memory-promoting) and/or anti-amnesic effects under different conditions, and 5-HT receptors are also associated with neural changes. Function The gene described in this record is a member of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor family and encodes a multi-pass membrane protein that functions as a receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine and couples to G proteins, negatively influencing cAMP levels via Gi and Go. This protein has been shown to function in part through the regulation of intracellular Ca2+ mobilization. The 5-HT5A receptor has been shown to be functional in a native expression system. Rodents have been shown to possess two functional 5-HT5 receptor subtypes, 5-HT5A and 5-HT5B, however while humans possess a gene coding for the 5-HT5B subtype, its co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atypical Antipsychotic
The atypical antipsychotics (AAP), also known as second generation antipsychotics (SGAs) and serotonin–dopamine antagonists (SDAs), are a group of antipsychotic drugs (antipsychotic drugs in general are also known as major tranquilizers and neuroleptics, although the latter is usually reserved for the ''typical antipsychotics'') largely introduced after the 1970s and used to treat psychiatric conditions. Some atypical antipsychotics have received regulatory approval (e.g. by the Food and Drug Administration, FDA of the United States of America, US, the Therapeutic Goods Administration, TGA of Australia, the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency, MHRA of the United Kingdom, UK) for schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, irritability in autism, and as an adjuvant therapy, adjunct in major depressive disorder. Both generations of medication tend to block receptors in the brain's dopamine pathways. Atypicals are less likely than haloperidol — the most widely used typi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT6 Receptor
The 5HT6 receptor is a subtype of 5HT receptor that binds the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5HT). It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is coupled to Gs and mediates excitatory neurotransmission. ''HTR6'' denotes the human gene encoding for the receptor. Distribution The 5HT6 receptor is expressed almost exclusively in the brain. It is distributed in various areas including, but not limited to, the olfactory tubercle, cerebral cortex (frontal and entorhinal regions), nucleus accumbens, striatum, caudate nucleus, hippocampus, and the molecular layer of the cerebellum. Based on its abundance in extrapyramidal, limbic, and cortical regions it can be suggested that the 5HT6 receptor plays a role in functions like motor control, emotionality, cognition, and memory. Function Blockade of central 5HT6 receptors has been shown to increase glutamatergic and cholinergic neurotransmission in various brain areas, whereas activation enhances GA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT4 Receptor
5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HTR4'' gene. Function This gene is a member of the family of human serotonin receptors, which are G protein-coupled receptors that stimulate cAMP production in response to serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine). The gene product is a glycosylated transmembrane protein that functions in both the peripheral and central nervous system to modulate the release of various neurotransmitters. Multiple transcript variants encoding proteins with distinct C-terminal sequences have been described, but the full-length nature of some transcript variants has not been determined. Location The receptor is located in the alimentary tract, urinary bladder, heart and adrenal gland as well as the central nervous system (CNS). In the CNS the receptor appears in the putamen, caudate nucleus, nucleus accumbens, globus pallidus, and substantia nigra, and to a lesser extent in the neocortex, raphe, pontine nuclei, and some area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT3 Receptor
The 5-HT3 receptor belongs to the Cys-loop superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs) and therefore differs structurally and functionally from all other 5-HT receptors (5-hydroxytryptamine, or serotonin receptors) which are G protein-coupled receptors. This ion channel is cation-selective and mediates neuronal depolarization and excitation within the central and peripheral nervous systems. As with other ligand gated ion channels, the 5-HT3 receptor consists of five subunits arranged around a central ion conducting pore, which is permeable to sodium (Na), potassium (K), and calcium (Ca) ions. Binding of the neurotransmitter 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) to the 5-HT3 receptor opens the channel, which, in turn, leads to an excitatory response in neurons. The rapidly activating, desensitizing, inward current is predominantly carried by sodium and potassium ions. 5-HT3 receptors have a negligible permeability to anions. They are most closely related by homology to the nicotinic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT2 Receptor
The 5-HT2 receptors are a subfamily of 5-HT receptors that bind the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT). The 5-HT2 subfamily consists of three G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) which are coupled to Gq/G11 and mediate excitatory neurotransmission Neurotransmission (Latin: ''transmissio'' "passage, crossing" from ''transmittere'' "send, let through") is the process by which signaling molecules called neurotransmitters are released by the axon terminal of a neuron (the presynaptic neuron), ..., including 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C. For more information, please see the respective main articles of the individual subtypes: * 5-HT2A receptor * 5-HT2B receptor * 5-HT2C receptor See also * 5-HT1 receptor * 5-HT3 receptor * 5-HT4 receptor * 5-HT5 receptor * 5-HT6 receptor * 5-HT7 receptor * 5-HT2 antagonists References {{Serotonergics Serotonin receptors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SB-699,551
SB-699551 is a drug which was the first compound developed to act as a selective antagonist for the serotonin receptor 5-HT5A, with selectivity of around 100x over other serotonin receptor subtypes. Multiple therapeutic roles have been suggested for 5-HT5A ligands due to the presence of this receptor in several areas of the brain, but research is still at an early stage, In animal studies, SB-699551 was found to block cue-mediated responding to LSD, again suggesting an antipsychotic type of activity. It also reduces the viability of certain types of cancer Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ... cells ''in vitro'', suggesting the 5-HT5A receptor as a possible target for novel chemotherapy drugs. References 5-HT5 antagonists Dimethylamino compounds Carboxamides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risperidone
Risperidone, sold under the brand name Risperdal among others, is an atypical antipsychotic used to treat schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. It is taken either by mouth or by injection (subcutaneous or intramuscular). The injectable versions are long-acting and last for 2–4 weeks. Common side effects include extrapyramidal symptoms, movement problems, sedation, sleepiness, dizziness, trouble seeing, constipation, and increased weight. Serious side effects may include the potentially permanent movement disorder tardive dyskinesia, as well as neuroleptic malignant syndrome, an increased risk of suicide, and hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels. In older people with psychosis as a result of dementia, it may increase the risk of death. It is unknown if it is safe for use in pregnancy. Its mechanism of action is not entirely clear, but is believed to be related to its action as a dopamine antagonist, dopamine and serotonin antagonist. Study of risperidone began in the late 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latrepirdine
Latrepirdine (INN, also known as dimebolin and sold as Dimebon) is an antihistamine drug which has been used clinically in Russia since 1983. Research was conducted in both Russia and western nations into potential applications as a neuroprotective drug to treat Alzheimer's disease and, possibly, as a nootropic, as well. After a major phase III clinical trial for Alzheimer's disease (AD) treatment failed to show any benefit, three other AD trials continued.Novel Alzheimer's Drug Flops ''MedPage Today'', March 03, 2010 Major industry-based development in this indication essentially stopped after another Phase III trial suffered the same fate in 2012.Sweetlove M: Phase III CONCERT Trial of Latrepirdine. Negative results. Pharm Med 2012;26(2):113-115 Latrepirdine failed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astellas Pharma
is a Japanese multinational pharmaceutical company, formed on 1 April 2005 from the merger of and . On February 5, 2020, the company announced management changes effective from April 1, 2020. Astellas is a member of the Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group (MUFJ) keiretsu. History Early foundations Fujisawa Shoten was started in 1894 by Tomokichi Fujisawa in Osaka, and was renamed Fujisawa Pharmaceutical Co. in 1943. Yamanouchi Yakuhin Shokai was started in 1923 by Kenji Yamanouchi in Osaka. The company was renamed Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical Co. in 1940 and moved to Tokyo in 1942. Both companies started their overseas expansion at about the same time, opening offices in Taiwan in 1962 and 1963, respectively, and in the United States and Europe from 1977 onwards. Recent times and mergers Fujisawa acquired Lyphomed in 1990 and thereafter established its US R&D center in Deerfield, Illinois. Yamanouchi's R&D center in Leiderdorp was established with the acquisition of the pharmaceut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |