|
413 BC
__NOTOC__ Year 413 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Cossus and Medullinus (or, less frequently, year 341 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 413 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Greece * After suffering a defeat in which the Athenian commander Lamachus is killed, Demosthenes suggests that they immediately give up the siege of Syracuse and return to Athens, where they are needed to defend against a Spartan invasion of Attica. Nicias refuses, but the Syracusans and Spartans under Hermocrates are able to trap the Athenians in the harbour and the Athenians sustain heavy losses in the Battle of Syracuse. Demosthenes is ambushed by the Syracusans and is forced to surrender. Nicias is soon captured as well, and both are executed, with most of the surviving Athenian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Calendar
The Roman calendar was the calendar used by the Roman Kingdom and Roman Republic. The term often includes the Julian calendar established by the reforms of the Roman dictator, dictator Julius Caesar and Roman emperor, emperor Augustus in the late 1stcenturyBC and sometimes includes any system dated by inclusive counting towards months' kalends, nones (calendar), nones, and ides (calendar), ides in the Roman manner. The term usually excludes the Alexandrian calendar of Roman Egypt, which continued the unique months of that land's Egyptian calendar, former calendar; the Byzantine calendar of the Byzantine Empire, later Roman Empire, which usually dated the Roman months in the simple count of the ancient Greek calendars; and the Gregorian calendar, which refined the Julian system to bring it into still closer alignment with the tropical year. Roman dates were counted inclusively forward to the next of three principal days: the first of the month (the kalends), a day shortly befor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest empire in history, spanning a total of from the Balkans and Egypt in the west to Central Asia and the Indus Valley in the east. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the formal establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognized for its imposition of a successful model of centralized, bureaucratic administration; its multicultural policy; building complex infrastructure, such as road systems and an organized postal system; the use of official languages across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
470 BC
__NOTOC__ Year 470 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Potitus and Mamercus (or, less frequently, year 284 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 470 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Greece * Suspected of plotting to seize power in Sparta by instigating a helot uprising, Pausanias takes refuge in the Temple of Athena of the Brazen House to escape arrest. The sanctuary is respected, but the Spartans wall in the sanctuary and starve Pausanias to death. By topic Architecture * The construction of the Temple of Zeus, begins at Olympia, Greece. This includes the relief sculpture (of which fragments now remain at the Archaeological Museum of Olympia) of ''Apollo with battling Lapiths and centaurs'' (approximate date). Art * The ''Charioteer'', in the Sanctuary of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electra (Euripides Play)
Euripides' ''Electra'' ( grc, Ἠλέκτρα, ''Ēlektra'') is a play probably written in the mid 410s BC, likely before 413 BC. It is unclear whether it was first produced before or after Sophocles' version of the Electra story. Background Years before the start of the play, near the start of the Trojan War, the Greek general Agamemnon sacrificed his daughter Iphigeneia in order to appease the goddess Artemis. While his sacrifice allowed the Greek army to set sail for Troy, it led to a deep resentment in his wife, Clytemnestra. Upon Agamemnon's return from the Trojan War ten years later, Clytemnestra and her lover Aegisthus murdered him. Plot The play begins with the introduction of Electra, the daughter of Clytemnestra and the late Agamemnon. Several years after Agamemnon's death suitors began requesting Electra's hand in marriage. Out of fear that Electra's child might seek revenge, Clytemnestra and Aegisthus married her off to a peasant of Mycenae. The peasant is kind to h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
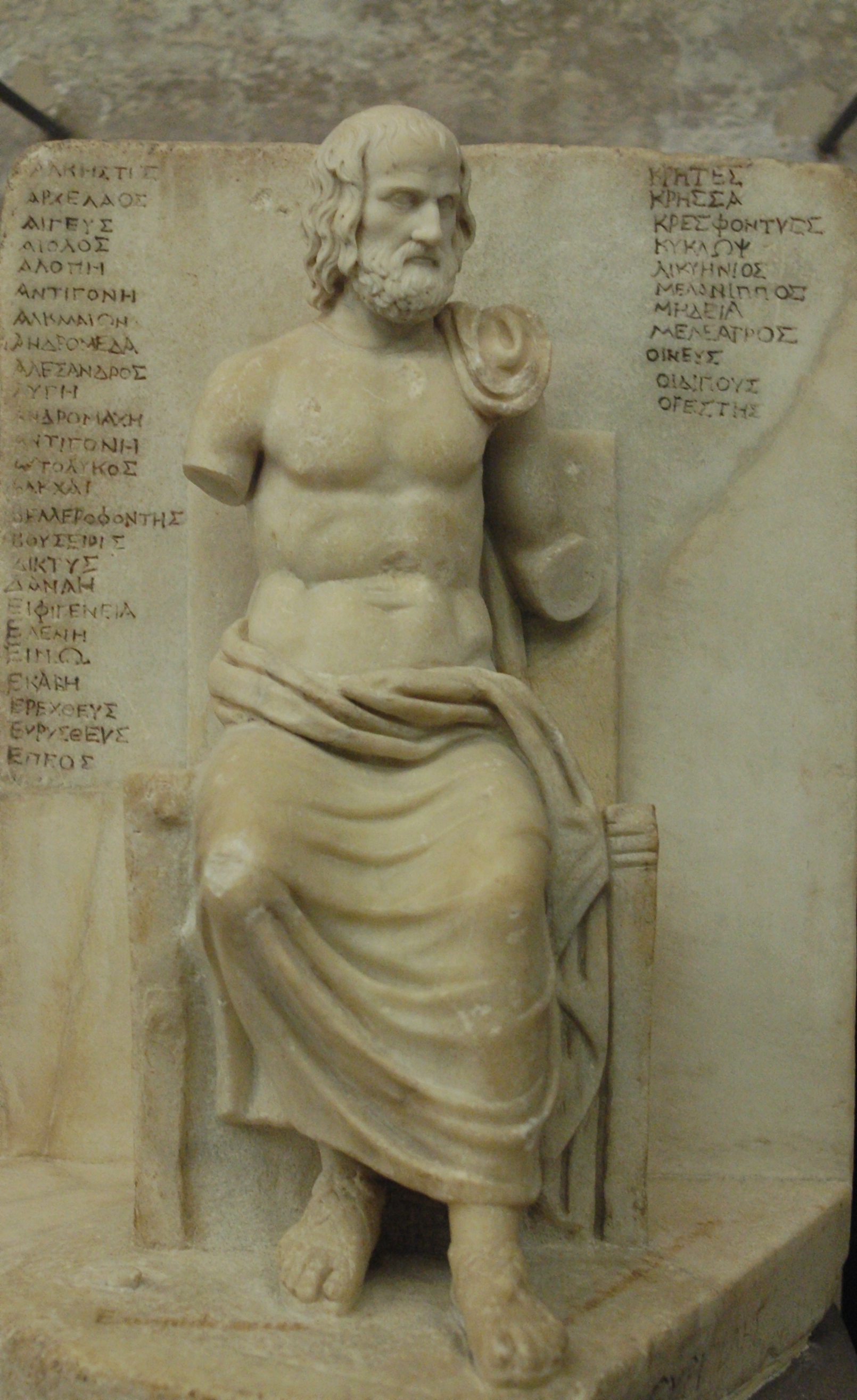
Euripides
Euripides (; grc, Εὐριπίδης, Eurīpídēs, ; ) was a tragedian Tragedy (from the grc-gre, τραγῳδία, ''tragōidia'', ''tragōidia'') is a genre of drama based on human suffering and, mainly, the terrible or sorrowful events that befall a main character. Traditionally, the intention of tragedy i ... of classical Athens. Along with Aeschylus and Sophocles, he is one of the three ancient Greek tragedians for whom any plays have survived in full. Some ancient scholars attributed ninety-five plays to him, but the ''Suda'' says it was ninety-two at most. Of these, eighteen or nineteen have survived more or less complete (''Rhesus (play), Rhesus'' is suspect). There are many fragments (some substantial) of most of his other plays. More of his plays have survived intact than those of Aeschylus and Sophocles together, partly because his popularity grew as theirs declinedMoses Hadas, ''Ten Plays by Euripides'', Bantam Classic (2006), Introduction, p. ixhe became, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perdiccas II
Perdiccas II ( gr, Περδίκκας, Perdíkkas) was a king of Macedonia from c. 448 BC to c. 413 BC. During the Peloponnesian War, he frequently switched sides between Sparta and Athens. Family Perdiccas II was the son of Alexander I, he had four brothers, Alcetas II, Philip, Menelaus and Amyntas, and a sister, Stratonice. Alcetas II preceded him on the throne until his murder at the hands of Perdiccas' son Archelaus I resulted in Perdiccas' elevation. Philip was the father of king Amyntas II, while Amyntas' grandson was king Amyntas III. Around 429 - 428 BC, Perdiccas arranged the marriage of his sister Stratonice to Seuthes II of Thrace. Perdiccas II first married a woman called Symache or Simiche. While some consider her a woman of unknown lineage, she was probably part of the Macedonian nobility, other sources call her a slave. By her, he had two sons, Archelaus I and Aeropus II. He later married a woman named Cleopatra, by whom he had another son. Cleopatra's son, acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal Argead dynasty, which was followed by the Antipatrid and Antigonid dynasties. Home to the ancient Macedonians, the earliest kingdom was centered on the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula,. and bordered by Epirus to the west, Paeonia to the north, Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south. Before the 4th century BC, Macedonia was a small kingdom outside of the area dominated by the great city-states of Athens, Sparta and Thebes, and briefly subordinate to Achaemenid Persia. During the reign of the Argead king PhilipII (359–336 BC), Macedonia subdued mainland Greece and the Thracian Odrysian kingdom through conquest and diplomacy. With a reformed army containing phalanxes wielding the ''sarissa'' pike, PhilipII d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archelaus I Of Macedon
Archelaus I (; grc-gre, Ἀρχέλαος ) was a king of the kingdom of Macedonia from 413 to 399 BC. He was a capable and beneficent ruler, known for the sweeping changes he made in state administration, the military, and commerce. By the time that he died, Archelaus had succeeded in converting Macedon into a significantly stronger power. The Ancient Greek Thucydides credited Archelaus with doing more for his kingdom's military infrastructure than all of his predecessors together. Biography Family Archelaus was a son of Perdiccas II by a slave woman. He obtained the throne by murdering his own uncle Alcetas II and cousin Alexander, such that his father became king, and his half-brother, a child of seven years, the legitimate heir. It is speculated that his mother might be the descendant of Gygaea of Macedon and the Persian general Bubares furthermore that she was enslaved and sent back to Macedonia to marry the Macedonian king Perdiccas II of Macedon as a Gesture of go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decelea
Decelea ( grc, Δεκέλεια, ), ''Dekéleia''), was a deme and ancient village in northern Attica serving as a trade route connecting Euboea with Athens, Greece. It was situated near the entrance of the eastern pass across Mount Parnes, which leads from the northeastern part of the Athenian plain to Oropus, and from thence both to Tanagra on the one hand, and to Delium and Chalcis on the other. It was situated about 120 stadia from Athens, and the same distance from the frontiers of Boeotia: it was visible from Athens, and from its heights also might be seen the ships entering the harbour of Peiraeeus. History It was originally one of the twelve cities of Attica. The historian Herodotus reports that Decelea's citizens enjoyed a special relationship with Sparta. The Spartans took control of Decelea around 413 BCE. With advice from Alcibiades in 415 BCE, the former Athenian general wanted on Athenian charges of religious crimes, the Spartans and their allies, under king Agis II, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agis II
Agis II ( grc-gre, Ἄγις; died c. 399 BC) was the 18th Eurypontid king of Sparta, the eldest son of Archidamus II by his first wife, and half-brother of Agesilaus II. He ruled with his Agiad co-monarch Pausanias.Agis II fro Livius.Org Life Agis succeeded his father in 427 BC, and reigned a little more than 26 years. In the summer of 426 BC, he led an army of Peloponnesians and their allies as far as the |
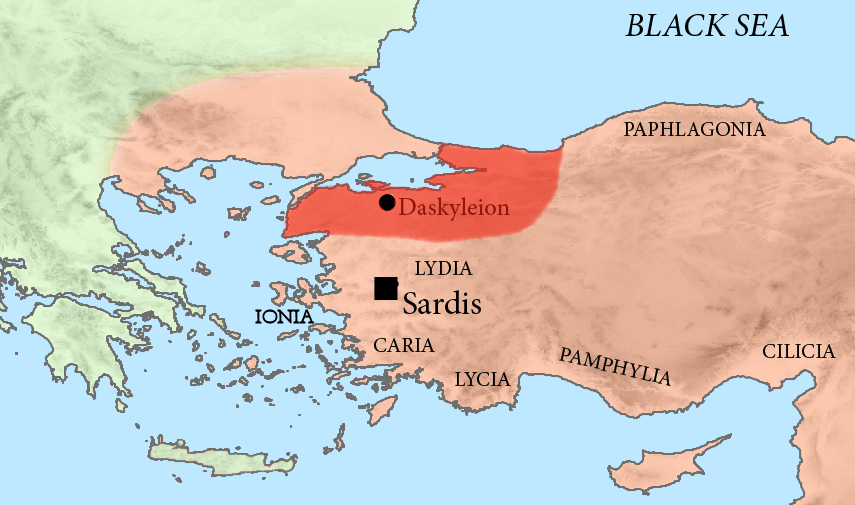
Pharnabazus (5th Century BC)
Pharnabazus II (Old Iranian: ''Farnabāzu'', grc-gre, Φαρνάβαζος ; ruled 413-374 BC) was a Persian soldier and statesman, and Satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia. He was the son of Pharnaces II of Phrygia and grandson of Pharnabazus I, and great-grandson of Artabazus I. He and his male ancestors, forming the Pharnacid dynasty, had governed the satrapy of Hellespontine Phrygia from its headquarters at Dascylium since 478 BC. He married Apama, daughter of Artaxerxes II of Persia, and their son Artabazus also became a satrap of Phrygia. According to some accounts, his granddaughter Barsine may have become Alexander the Great's concubine. According to research by Theodor Nöldeke, he was descended from Otanes, one of the associates of Darius in the murder of Smerdis. Satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia War with Sparta against Athens (c.413-404 BC) Athens was the dominant power in the Aegean in the 5th century BC, following the Greeks' victories over the Achaemenids in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcibiades
Alcibiades ( ; grc-gre, Ἀλκιβιάδης; 450 – 404 BC) was a prominent Athenian statesman, orator, and general. He was the last of the Alcmaeonidae, which fell from prominence after the Peloponnesian War. He played a major role in the second half of that conflict as a strategic advisor, military commander, and politician. During the course of the Peloponnesian War, Alcibiades changed his political allegiance several times. In his native Athens in the early 410s BC, he advocated an aggressive foreign policy and was a prominent proponent of the Sicilian Expedition. After his political enemies brought charges of sacrilege against him, he fled to Sparta, where he served as a strategic adviser, proposing or supervising several major campaigns against Athens. However, Alcibiades made powerful enemies in Sparta too, and defected to Persia. There he served as an adviser to the satrap Tissaphernes until Athenian political allies brought about his recall. He served as an Ath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |