|
4G-LTE Filter
4G-LTE filter is a low-pass filter or notch filter, to be used in OTA-reception installations (both collective and individual) if one is using an older/unfiltered TV antenna, without the risk of interference caused by the cellular transmitters on the higher channels. (See following section.) These filters are usually used for existing facilities as for new installations in urban or rural areas, antennas and amplifiers sold from the application of the new standard may be already be configured to receive, with good signal gain, only TV channels from 14 to 51 of the UHF band, the other higher channels (former TV channels 52 to 83) being attenuated. Interference between 4G LTE and DTT 4G LTE is the fourth generation mobile phone standard. In urban areas, the 4G uses a frequency band located between 1800 MHz and 2600 MHz, and therefore is quite far from the TV band for causing any type of interference problem. In rural areas, however, the major operators asked to use part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-pass Filter
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filter design. The filter is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble-cut filter in audio applications. A low-pass filter is the complement of a high-pass filter. In optics, high-pass and low-pass may have different meanings, depending on whether referring to frequency or wavelength of light, since these variables are inversely related. High-pass frequency filters would act as low-pass wavelength filters, and vice versa. For this reason it is a good practice to refer to wavelength filters as ''short-pass'' and ''long-pass'' to avoid confusion, which would correspond to ''high-pass'' and ''low-pass'' frequencies. Low-pass filters exist in many different forms, including electronic circuits such as a hiss filter used in audio, anti-aliasing fil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band-stop Filter
In signal processing, a band-stop filter or band-rejection filter is a filter that passes most frequencies unaltered, but attenuates those in a specific range to very low levels. It is the opposite of a band-pass filter. A notch filter is a band-stop filter with a narrow stopband (high Q factor). Narrow notch filters (optical) are used in Raman spectroscopy, live sound reproduction (public address systems, or PA systems) and in instrument amplifiers (especially amplifiers or preamplifiers for acoustic instruments such as acoustic guitar, mandolin, bass instrument amplifier, etc.) to reduce or prevent audio feedback, while having little noticeable effect on the rest of the frequency spectrum (electronic or software filters). Other names include "band limit filter", "T-notch filter", "band-elimination filter", and "band-reject filter". Typically, the width of the stopband is 1 to 2 decades (that is, the highest frequency attenuated is 10 to 100 times the lowest frequency atten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrestrial Television
Terrestrial television or over-the-air television (OTA) is a type of television broadcasting in which the signal transmission occurs via radio waves from the terrestrial (Earth-based) transmitter of a TV station to a TV receiver having an antenna. The term ''terrestrial'' is more common in Europe and Latin America, while in Canada and the United States it is called ''over-the-air'' or simply ''broadcast''. This type of TV broadcast is distinguished from newer technologies, such as satellite television (direct broadcast satellite or DBS television), in which the signal is transmitted to the receiver from an overhead satellite; cable television, in which the signal is carried to the receiver through a cable; and Internet Protocol television, in which the signal is received over an Internet stream or on a network utilizing the Internet Protocol. Terrestrial television stations broadcast on television channels with frequencies between about 52 and 600 MHz in the VHF and U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collective
A collective is a group of entities that share or are motivated by at least one common issue or interest, or work together to achieve a common objective. Collectives can differ from cooperatives in that they are not necessarily focused upon an economic benefit or saving, but can be that as well. The term "collective" is sometimes used to describe a species as a whole—for example, the human collective. For political purposes, a collective is defined by decentralized, or "majority-rules" decision making styles. Types of groups Collectives are sometimes characterised by attempts to share and exercise political and social power and to make decisions on a consensus-driven and egalitarian basis. A commune or intentional community, which may also be known as a "collective household", is a group of people who live together in some kind of dwelling or residence, or in some other arrangement (e.g., sharing land). Collective households may be organized for a specific purpose (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
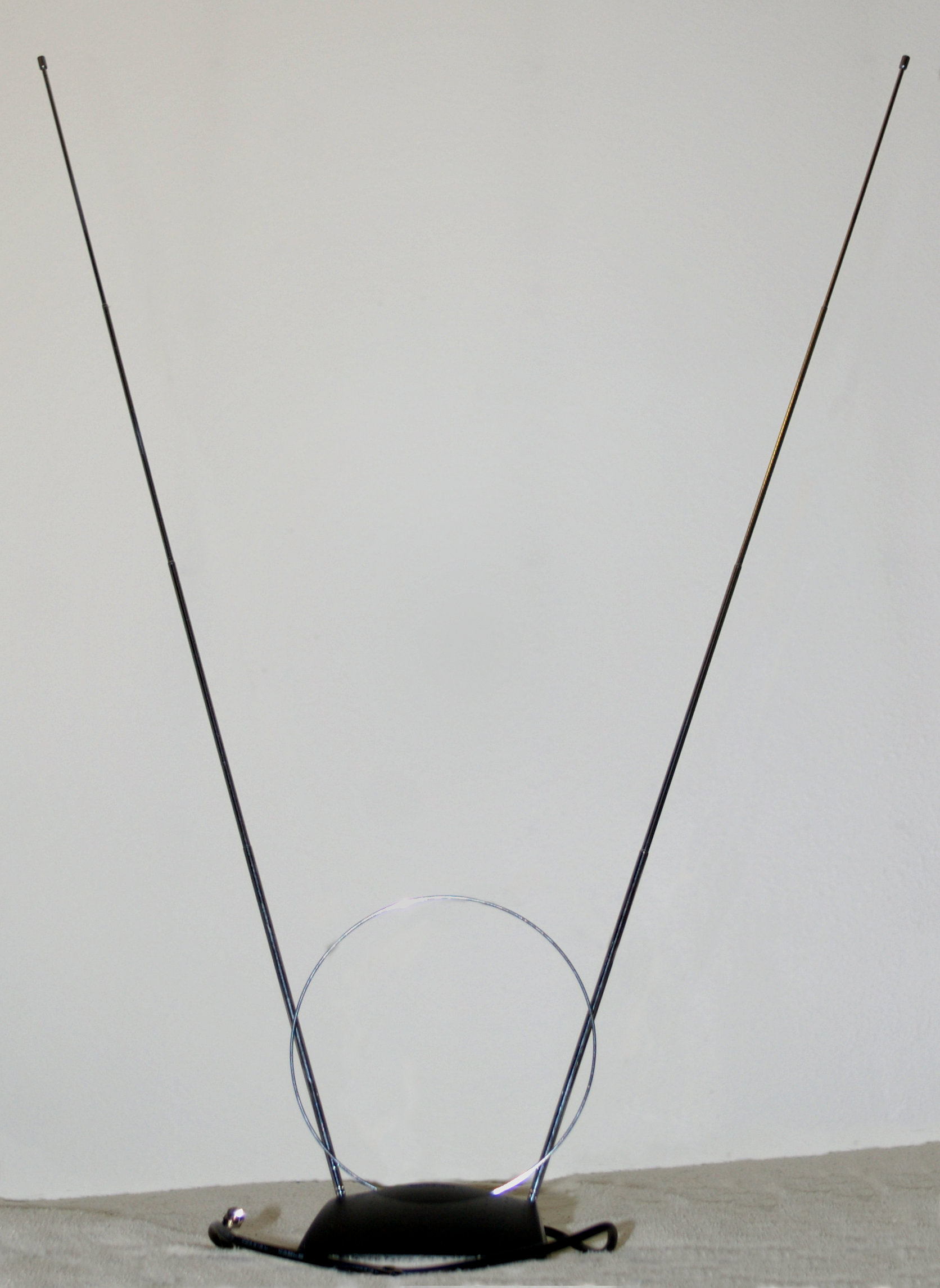
TV Antenna
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, entertainment, news, and sports. Television became available in crude experimental forms in the late 1920s, but only after several years of further development was the new technology marketed to consumers. After World War II, an improved form of black-and-white television broadcasting became popular in the United Kingdom and the United States, and television sets became commonplace in homes, businesses, and institutions. During the 1950s, television was the primary medium for influencing public opinion.Diggs-Brown, Barbara (2011''Strategic Public Relations: Audience Focused Practice''p. 48 In the mid-1960s, color broadcasting was introduced in the U.S. and most other developed countries. The availability of various types of archival stora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adjacent-channel Interference
Adjacent-channel interference (ACI) is interference caused by extraneous power from a signal in an adjacent channel. ACI may be caused by inadequate filtering (such as incomplete filtering of unwanted modulation products in FM systems), improper tuning or poor frequency control (in the reference channel, the interfering channel or both). ACI is distinguished from crosstalk.Federal Standard 1037Accessed: 2011-10-19. (Archived by WebCite at http://webcitation.org/62Z8qe0pC)/ref> Origin The adjacent-channel interference which receiver A experiences from a transmitter B is the sum of the power that B emits into A's channel—known as the "unwanted emission", and represented by the ACLR (Adjacent Channel Leakage Ratio)—and the power that A picks up from B's channel, which is represented by the ACS (Adjacent Channel Selectivity). B emitting power into A's channel is called adjacent-channel leakage (unwanted emissions). It occurs for two reasons. First, because RF filters require a rol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, entertainment, news, and sports. Television became available in crude experimental forms in the late 1920s, but only after several years of further development was the new technology marketed to consumers. After World War II, an improved form of black-and-white television broadcasting became popular in the United Kingdom and the United States, and television sets became commonplace in homes, businesses, and institutions. During the 1950s, television was the primary medium for influencing public opinion.Diggs-Brown, Barbara (2011''Strategic Public Relations: Audience Focused Practice''p. 48 In the mid-1960s, color broadcasting was introduced in the U.S. and most other developed countries. The availability of various types of archival st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Dividend
The digital dividend refers to the radio spectrum which is released in the process of digital television transition. When television broadcasters switch from analog TV to digital-only platforms, part of the electromagnetic spectrum that has been used for broadcasting will be freed-up because digital television needs less spectrum than analog television, due to lossy compression. One reason is that new digital video compression technology can transmit numerous digital subchannels using the same amount of spectrum used to transmit one analog TV channel. However, the primary reason is that digital transmissions require much less of a guard band on either side, since they are not nearly as prone to RF interference from adjacent channels. Because of this, there is no longer any need to leave empty channels to protect stations from each other, in turn allowing stations to be repacked into fewer channels, leaving more contiguous spectrum to be allocated for other wireless service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Spaces (radio)
In telecommunications, white spaces refer to radio frequencies allocated to a broadcasting service but not used locally. National and international bodies assign frequencies for specific uses and, in most cases, license the rights to broadcast over these frequencies. This frequency allocation process creates a bandplan which for technical reasons assigns white space between used radio bands or channels to avoid interference. In this case, while the frequencies are unused, they have been specifically assigned for a purpose, such as a guard band. Most commonly however, these white spaces exist naturally between used channels, since assigning nearby transmissions to immediately adjacent channels will cause destructive interference to both. In addition to white space assigned for technical reasons, there is also unused radio spectrum which has either never been used, or is becoming free as a result of technical changes. In particular, the switchover to digital television frees up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |