|
46th Battalion (South Saskatchewan), CEF
The 46th Battalion (South Saskatchewan), CEF, was an infantry battalion of the Canadian Expeditionary Force during the Great War. History The 46th Battalion was authorized on 7 November 1914 and embarked for Britain on 23 October 1915. On 11 August 1916 it disembarked in France, where it fought with the 10th Infantry Brigade, 4th Canadian Division in France and Flanders until the end of the war. The battalion was disbanded on 30 August 1920. The unit has come to be known as "The Suicide Battalion". The 46th Battalion lost 1,433 killed and 3,484 wounded – a casualty rate of 91.5 percent in 27 months. The battalion recruited throughout Saskatchewan and was mobilized at Moose Jaw, Saskatchewan.Meek, John F. ''Over the Top! The Canadian Infantry in the First World War.'' Orangeville, Ont.: The Author, 1971. The 46th Battalion had two officers commanding: *Lieutenant-Colonel H. Snell, 22 October 1915 – 29 August 1916 *Lieutenant-Colonel H.J. Dawson, CMG, DSO, 29 August 1916-D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Expeditionary Force
The Canadian Expeditionary Force (CEF) was the expeditionary field force of Canada during the First World War. It was formed following Britain’s declaration of war on Germany on 15 August 1914, with an initial strength of one infantry division. The division subsequently fought at Ypres on the Western Front, with a newly raised second division reinforcing the committed units to form the Canadian Corps. The CEF and corps was eventually expanded to four infantry divisions, which were all committed to the fighting in France and Belgium along the Western Front. A fifth division was partially raised in 1917, but was broken up in 1918 and used as reinforcements following heavy casualties. Personnel Recruitment The Canadian Expeditionary Force was mostly volunteers; a bill allowing conscription was passed in August, 1917, but not enforced until call-ups began in January 1918 (''see'' Conscription Crisis of 1917). In all, 24,132 conscripts had been sent to France to take part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
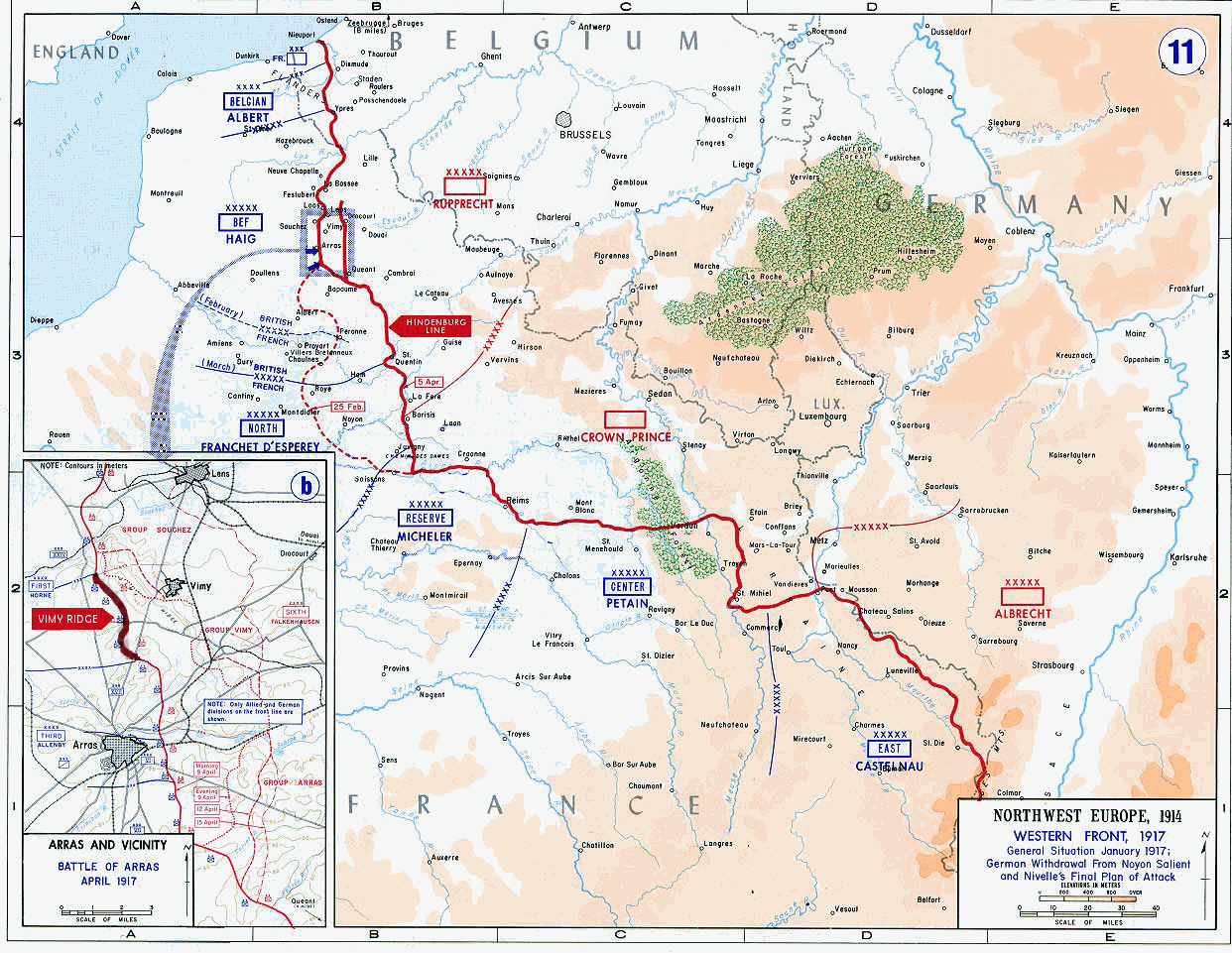
Battle Of Vimy Ridge
The Battle of Vimy Ridge was part of the Battle of Arras, in the Pas-de-Calais department of France, during the First World War. The main combatants were the four divisions of the Canadian Corps in the First Army, against three divisions of the German 6th Army. The battle took place from 9 to 12 April 1917 at the beginning of the Battle of Arras, the first attack of the Nivelle Offensive, which was intended to attract German reserves from the French, before the French attempt at a decisive offensive on the Aisne and the Chemin des Dames ridge further south, several days later. The Canadian Corps were to capture the German-held high ground of Vimy Ridge, an escarpment on the northern flank of the Arras front. This would protect the First Army and the Third Army farther south from German enfilade fire. Supported by a creeping barrage, the Canadian Corps captured most of the ridge during the first day. The village of Thélus fell during the second day, as did the crest of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Infantry Battalions In The Canadian Expeditionary Force
During the First World War, the Canadian Army authorized the formation of 260 infantry battalions to serve in the Canadian Expeditionary Force. Only fifty-three of these battalions ever reached the front lines. The remaining battalions, most often upon arrival in England, were broken up and primarily absorbed into a reserve battalion. In addition to the numbered battalions, there were two named battalions. Several regiments of Canadian Mounted Rifles (mounted infantry) were converted to regular infantry battalions and served in the Canadian Corps. Besides the infantry, there were other Canadian combat units in the CEF, including cavalry and mounted infantry regiments (in particular the Canadian Cavalry Brigade), artillery brigades and machine gun battalions. The infantry battalions in bold type served in the field. Sources * Chartrand, René, ''The Canadian Corps in World War I''. Oxford: Osprey Publishing, 2007 * ''Canadian Expeditionary Force, 1914–1919'' by G. W. L. N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Saskatchewan Dragoons
The Saskatchewan Dragoons is a Primary Reserve armoured regiment of the Canadian Army. The unit is based in Moose Jaw. Their primary job is to assist the Regular Force in meeting Canada's military commitments. Their training and equipment closely follow that of the Regular Force, which the Reserves are called upon to assist increasingly often. The Saskatchewan Dragoons are part of 3rd Canadian Division's 38 Canadian Brigade Group. Prince Edward, Earl of Wessex, became colonel-in-chief of the regiment on visiting Saskatchewan in 2003, when he congratulated the regiment on its "contribution to Canada's proud tradition of citizen-soldiers in the community". Involved in peacekeeping operations in Cyprus, the Golan Heights, Bosnia and Croatia, members of the regiment have also provided aid during floods and forest fires in the prairies. Role Their role is that of a reconnaissance squadron. They examine an area in preparation for the advance of a main body of troops. They go forw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The South Saskatchewan Regiment (1920-1924)
The South Saskatchewan Regiment was an infantry regiment of the Canadian Forces formed in 1936 by the amalgamation of The Weyburn Regiment and The Saskatchewan Border Regiment. It was reduced to nil strength and placed on the Supplementary Order of Battle (i.e., virtually disbanded) in 1968. They participated in the 1942 Dieppe Raid. History The regiment traces its lineage to July 3, 1905, when an infantry regiment was authorized in the District of Assiniboia and the District of Saskatchewan, which later that year became the province of Saskatchewan. The regiment was eventually organized as the 95th Saskatchewan Rifles, in Regina. After the First World War the 95th merged with the 60th Rifles of Canada (in Moose Jaw) to become the South Saskatchewan Regiment, which expanded to five battalions with the creation of units in Weyburn (3rd Battalion), Moosomin (4th Battalion) and Estevan (5th Battalion). In 1924, each of the battalions became a distinct regiment, and the name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Front (World War I)
The Western Front was one of the main theatres of war during the First World War. Following the outbreak of war in August 1914, the German Army opened the Western Front by invading Luxembourg and Belgium, then gaining military control of important industrial regions in France. The German advance was halted with the Battle of the Marne. Following the Race to the Sea, both sides dug in along a meandering line of fortified trenches, stretching from the North Sea to the Swiss frontier with France, which changed little except during early 1917 and in 1918. Between 1915 and 1917 there were several offensives along this front. The attacks employed massive artillery bombardments and massed infantry advances. Entrenchments, machine gun emplacements, barbed wire and artillery repeatedly inflicted severe casualties during attacks and counter-attacks and no significant advances were made. Among the most costly of these offensives were the Battle of Verdun, in 1916, with a combined 700,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pursuit To The Selle
Pursuit may refer to: Arts and entertainment Films * ''Pursuit'' (1935 film), a 1935 American action film * ''Pursuit'' (1972 American film), a made-for-TV film directed by Michael Crichton * ''Pursuit'' (1972 Hong Kong film), a Shaw Brothers film * ''Pursuit'' (1989 film), a TV miniseries directed by Ian Sharp * ''The pursuit of happyness'', a 2006 Gabriel Muccino film * ''Pursuit'' (2015 film), an Irish film * ''Pursuit'' (2022 film), an American film * ''Apache Blood'' or ''Pursuit'', a 1975 film directed by Vern Piehl Music * ''Pursuit'' (album), 2012 album by Stuck in the Sound * ''The Pursuit'' (album), a 2009 album by Jamie Cullum * "Pursuit", a 2010 song by In Fear and Faith from the album, ''Imperial'' Television * "Pursuit" (''Death Note'' episode), 2006 episode of the anime series * ''Pursuit'' (TV series), a 1950s anthology Novel and games * ''Pursuit'' (novel), a science fiction novel * ''Pursuit'' (video game), a 1975 Atari game *''Trivial Pursu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Canal Du Nord
The Battle of Canal du Nord was part of the Hundred Days Offensive of the First World War by the Allies against German positions on the Western Front. The battle took place in the Nord-Pas-de-Calais region of France, along an incomplete portion of the Canal du Nord and on the outskirts of Cambrai between 27 September and 1 October 1918. To prevent the Germans from sending reinforcements against one attack, the assault along the Canal du Nord was part of a sequence of Allied attacks at along the Western Front. The attack began the day after the Meuse-Argonne Offensive commenced, a day before an offensive in Belgian Flanders and two days before the Battle of St. Quentin Canal. The attack took place along the boundary between the British First Army and Third Army, which were to continue the advance started with the Battle of the Drocourt-Quéant Line, Battle of Havrincourt and Battle of Epehy. The First Army was to lead the crossing of the Canal du Nord and secure the northern fla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindenburg Line
The Hindenburg Line (German: , Siegfried Position) was a German defensive position built during the winter of 1916–1917 on the Western Front during the First World War. The line ran from Arras to Laffaux, near Soissons on the Aisne. In 1916, the Battle of Verdun and the Battle of the Somme left the German western armies () exhausted and on the Eastern Front, the Brusilov Offensive had inflicted huge losses on the Austro-Hungarian armies and forced the Germans to take over more of the front. The declaration of war by Romania had placed additional strain on the German army and war economy. The Hindenburg Line, built behind the Noyon Salient, was to replace the old front line as a precaution against a resumption of the Battle of the Somme in 1917. By wasting the intervening ground, the Germans could delay a spring offensive in 1917. A shortened front could be held with fewer troops and with tactical dispersal, reverse-slope positions, defence in depth and camouflage, Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Scarpe (1918)
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Amiens (1918)
The Battle of Amiens, also known as the Third Battle of Picardy (french: 3ème Bataille de Picardie), was the opening phase of the Allied offensive which began on 8 August 1918, later known as the Hundred Days Offensive, that ultimately led to the end of the First World War. Allied forces advanced over on the first day, one of the greatest advances of the war, with Gen Henry Rawlinson's British Fourth Army (with 9 of its 19 divisions supplied by the fast moving Australian Corps of Lt Gen John Monash and Canadian Corps of Lt Gen Arthur Currie) playing the decisive role. The battle is also notable for its effects on both sides' morale and the large number of surrendering German forces. This led Erich Ludendorff to later describe the first day of the battle as "the black day of the German Army". Amiens was one of the first major battles involving armoured warfare. Prelude On 21 March 1918, the German Army had launched Operation Michael, the first in a series of attacks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

