|
448 Births
__NOTOC__ Year 448 ( CDXLVIII) was a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Praetextatus and Zeno (or, less frequently, year 1201 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 448 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantium * Emperor Theodosius II sends an embassy to Attila the Hun; Anatolius, an Eastern Roman general (''magister militum'') responsible for the security of the Eastern frontier, achieves a peace treaty with the Huns, in exchange for an annual tribute of of gold per year. * Attila demands in the treaty the evacuation of the territory running from ''Singidunum'' (Belgrade, in Serbia) east along the Danube to ''Novae'' (Svishtov, in Bulgaria). This depopulated buffer zone deprives the Romans of their natural defensiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singidunum
Singidunum ( sr, Сингидунум/''Singidunum'') was an ancient city which later evolved into modern Belgrade, the capital of Serbia. The name is of Celts, Celtic origin, going back to the time when Celtic tribe Scordisci settled the area in the 3rd century BC, following the Gallic invasion of the Balkans. Later on, the Roman Republic conquered the area in 75 BC and incorporated it into the province of Moesia. It was an important fort of the Danubian Limes and Roman Legio IV Flavia Felix was garrisoned there since 86 AD. Singidunum was the birthplace of the Roman Emperor Jovian (Emperor), Jovian. It was sacked by Huns in 441, and by Pannonian Avars, Avars and South Slavs, Slavs in 584. At the beginning of the 7th century, the Singidunum fort was finally destroyed. A large part of Belgrade's downtown belongs to the "Archaeological Site of Singidunum", which was declared a protected zone on 30 June 1964. Celtic period Origin The Scythian and Thracian-Cimmerian tribes tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
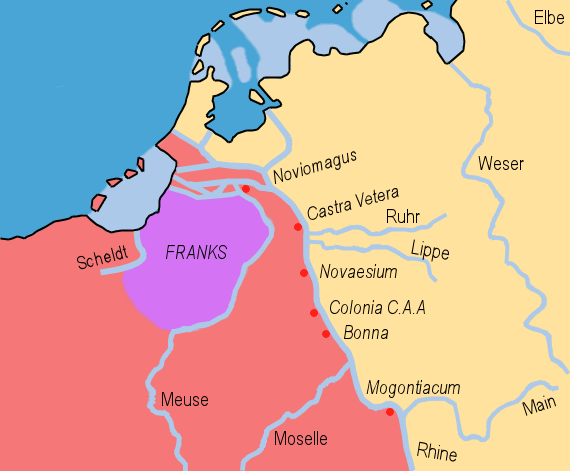
Salian Franks
The Salian Franks, also called the Salians (Latin: ''Salii''; Greek: Σάλιοι, ''Salioi''), were a northwestern subgroup of the early Franks who appear in the historical record in the fourth and fifth centuries. They lived west of the Lower Rhine in what was then the Roman Empire and today the Netherlands and Belgium. The traditional historiography sees the Salians as one of the main divisions of the Franks alongside the Ribuarians. Recent scholarship, however, has often questioned the ethnic significance of both these terms. Etymology Various etymologies are proposed. The ethnonym is unrelated to the name for the dancing priests of Mars, who were also called Salii. In line with theories that the Salians already existed as a tribe outside the Roman Empire, the name may have derived from the name of the IJssel river, formerly called ''Hisloa'' or ''Hisla'', and in ancient times, ''Sala'', which may be the Salians' original residence. Today this area is called Salland. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during Republican era, Cisalpina was annexed in 42 BC to Roman Italy), and Germany west of the Rhine. It covered an area of . According to Julius Caesar, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Belgica, and Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture, which extended across all of Gaul, as well as east to Raetia, Noricum, Pannonia, and southwestern Germania during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. During the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, Gaul fell under Roman rule: Gallia Cisalpina was conquered in 204 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri and the Teutons, who were in turn defeated by the Romans by 103 BC. Julius Caesar finally subdued the remaining parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armorica
Armorica or Aremorica (Gaulish: ; br, Arvorig, ) is the name given in ancient times to the part of Gaul between the Seine and the Loire that includes the Brittany Peninsula, extending inland to an indeterminate point and down the Atlantic Coast. Name The name ''Armorica'' is a Latinized form of the Gaulish toponym , which literally means 'place in front of the sea'. It is formed with the prefix ''are''- ('in front of') attached to -''mori''- ('sea') and the feminine suffix ''-(i)cā'', denoting the localization (or provenance). The inhabitants of the region were called ''Aremorici'' (sing. ''Aremoricos''), formed with the stem ''are-mori''- extended by the determinative suffix -''cos''. It is glossed by the Latin ''antemarini'' in Endlicher's Glossary. The Slavs use a similar formation, ''Po-mor-jane'' ('those in front of the sea'), to designate the inhabitants of Pomerania. The Latin adjective ''Armoricani'' was an administrative term designating in particular a sector of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagaudae
Bagaudae (also spelled bacaudae) were groups of peasant insurgents in the later Roman Empire who arose during the Crisis of the Third Century, and persisted until the very end of the Western Empire, particularly in the less-Romanised areas of Gallia and Hispania, where they were "exposed to the depredations of the late Roman state, and the great landowners and clerics who were its servants". The invasions, military anarchy, and disorders of the third century provided a chaotic and ongoing degradation of the regional power structure within a declining Empire into which the ''bagaudae'' achieved some temporary and scattered successes, under the leadership of members of the underclass as well as former members of local ruling elites. Etymology The name probably means "fighters" in Gaulish. C.E.V. Nixon assesses the ''bagaudae'', from the official Imperial viewpoint, as "bands of brigands who roamed the countryside looting and pillaging". J.C.S. Léon interprets the most compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavius Aetius
Aetius (also spelled Aëtius; ; 390 – 454) was a Roman general and statesman of the closing period of the Western Roman Empire. He was a military commander and the most influential man in the Empire for two decades (433454). He managed policy in regard to the attacks of barbarian federates settled throughout the West. Notably, he mustered a large Roman and allied (''foederati'') army in the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains, ending a devastating invasion of Gaul by Attila in 451, though the Hun and his subjugated allies still managed to invade Italy the following year, an incursion best remembered for the ruthless Sack of Aquileia and the intercession of Pope Leo I. Aetius has often been called, "Last of the Romans". Edward Gibbon refers to him as "the man universally celebrated as the terror of Barbarians and the support of the Republic" for his victory at the Catalaunian Plains. J.B Bury notes, "That he was the one prop and stay of the Western Empire during his life time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buffer Zone
A buffer zone is a neutral zonal area that lies between two or more bodies of land, usually pertaining to countries. Depending on the type of buffer zone, it may serve to separate regions or conjoin them. Common types of buffer zones are demilitarized zones, border zones and certain restrictive easement zones and green belts. Such zones may be comprised by a sovereign state, forming a buffer state. Buffer zones have various purposes, politically or otherwise. They can be set up for a multitude of reasons, such as to prevent violence, protect the environment, shield residential and commercial zones from industrial accidents or natural disasters, or even isolate prisons. Buffer zones often result in large uninhabited regions that are themselves noteworthy in many increasingly developed or crowded parts of the world. Conservation For use in nature conservation, a buffer zone is often created to enhance the protection of areas under management for their biodiversity importance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. Bulgaria covers a territory of , and is the sixteenth-largest country in Europe. Sofia is the nation's capital and largest city; other major cities are Plovdiv, Varna and Burgas. One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Neolithic Karanovo culture, which dates back to 6,500 BC. In the 6th to 3rd century BC the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians, Persians, Celts and Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, tribal invasions in the region resumed. Around the 6th century, these territories were settled by the early Slavs. The Bulgars, led by Asp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svishtov
Svishtov ( bg, Свищов ) is a town in northern Bulgaria, located in Veliko Tarnovo Province on the right bank of the Danube river opposite the Romanian town of Zimnicea. It is the administrative centre of the homonymous Svishtov Municipality. The town is the second-largest in the province after the city of Veliko Tarnovo and before Gorna Oryahovitsa. Name The origins of the name Svishtov can be found in its old Bulgarian variation Sveshtniy (Свѣщний), deriving from the word ''svesht'' or ''svyasht'' (свѣщ), meaning "candle". This was due to the existence of a lighthouse in the city. The previous name Sistova was first mentioned in the peace treaty that ended the Austro-Turkish War in 1791, when Bulgaria was still under Ottoman rule. This name was chosen instead of the Turkish word ''Zigit''. During the Ottoman rule of Bulgaria the town was also known as Ziștovi and in Romanian as Șiștova. Geography Svishtov is situated in northern central Bulgaria on the ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novae (fortress)
Novae was initially one of the few great Roman legionary fortresses along the empire's border, forming part of the defences (limes Moesiae) along the Danube in northern Bulgaria. The settlement later expanded into a town in the Roman province of Moesia Inferior, later Moesia Secunda. It lies about 4 km east of the modern town of Svishtov. The fortress is one of the few along the ''limes'' to have been excavated and now open to the public. Localisation and topography The site of Novae is situated on the southern bank of the Danube at Pametnicite near Svishtov (a memorial site where the Russian army entered Bulgaria during the Turkish-Russian war in 1877) or Stǎklen (a place rich in glass – Bulg. stǎklo), as many ancient glass fragments are visible on the site (the production of glass is attested in late Roman Novae). The ''castra legionis'' covering an area of 18 hectares is situated on a slope with its lowest point at the river-bank and its highest point 30m higher i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |