|
42nd Motor Rifle Division
The 42nd Guards "Evpatoriyskaya Red Banner" Motor Rifle Division (Military Unit Number 27777, until 1987 MUN 29410; until 2009 MUN 28320)Michael Holm42nd Guards Training Motor Rifle Division accessed February 2015. is a Russian military unit. The division was formed originally as the 111th Rifle Division in Vologda in 1940, and became the 24th Guards Rifle Division in March 1942. It was based in the North Caucasus following World War II; it became 42nd Guards MRD on 10 June 1957, while at Grozny. It became 42nd Guards Training Motor Rifle Division, part of the 12th Army Corps, on 18 October 1960. Second World War The division was formed in July 1940 in Vologda as the 111th Rifle Division on the basis of the 29th Reserve Brigade of the Arkhangelsk Military District. In the active army from June 22, 1941 to March 17, 1942. On July 16, 1940, the division was fully formed (which became the division's anniversary). Until March 1941, the 111th Rifle Division only held 3,000 personne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after Frederick Barbarossa ("red beard"), a 12th-century Holy Roman emperor and German king, put into action Nazi Germany's ideological goal of conquering the western Soviet Union to repopulate it with Germans. The German aimed to use some of the conquered people as forced labour for the Axis war effort while acquiring the oil reserves of the Caucasus as well as the agricultural resources of various Soviet territories. Their ultimate goal was to create more (living space) for Germany, and the eventual extermination of the indigenous Slavic peoples by mass deportation to Siberia, Germanisation, enslavement, and genocide. In the two years leading up to the invasion, Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union signed political and economic pacts for st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
45 Mm Anti-tank Gun M1932 (19-K)
The 45 mm anti-tank gun model 1932 (factory designation 19-K and GRAU index 52-P-243A) was a light quick-firing anti-tank gun used in the interwar period and in the first stage of the German-Soviet War. It was created by factory No. 8 which was located in now Korolyov city, under leadership of engineer V. Bering. History The gun bearing factory designation 19-K (Cyrillic ''19-К'') was a combination of a modified carriage of the 37 mm anti-tank gun model 1930 (built according to a documentation bought from Rheinmetall) with a 45 mm barrel designed in March 1932. and adopted by the Red Army on March 23, 1932. The 45 mm caliber was selected because the large reserves of the French 47 mm shells could be converted to 45 mm by milling out the driving bands. The resulting light quarter-automatic anti-tank gun was discovered to be unsatisfactory due to low mobility and reliability problems, and after a series of modifications (including the arrest of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
152 Mm Howitzer-gun M1937 (ML-20)
The 152 mm howitzer-gun M1937 (ML-20) (russian: 152-мм гаубица-пушка обр. 1937 г. (МЛ-20)), is a Soviet heavy gun-howitzer. The gun was developed by the design bureau of the plant no 172, headed by F. F. Petrov, as a deep upgrade of the 152-mm gun M1910/34, in turn based on the 152-mm siege gun M1910, a pre-World War I design by Schneider. It was in production from 1937 to 1946. The ML-20 saw action in World War II, mainly as a corps / army level artillery piece of the Soviet Army. Captured guns were employed by Wehrmacht and the Finnish Army. Post World War II, the ML-20 saw combat in numerous conflicts during the mid to late twentieth century. Description The ML-20 was officially classified as howitzer-gun, i.e. an artillery system which combines characteristics of a howitzer and (to lesser extent) of a gun and therefore can be used in both roles. This universality was achieved by wide range of elevation angles and by using separate loading with 13 d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
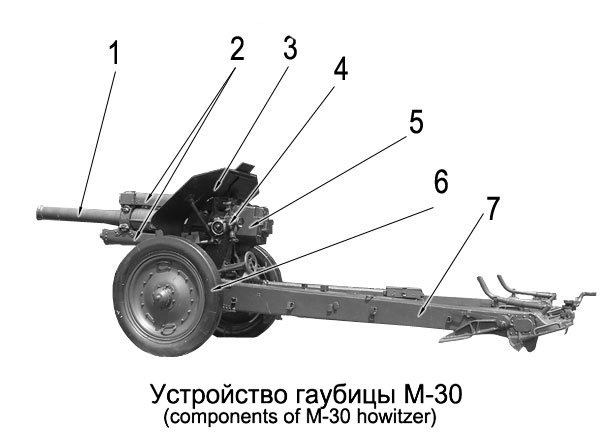
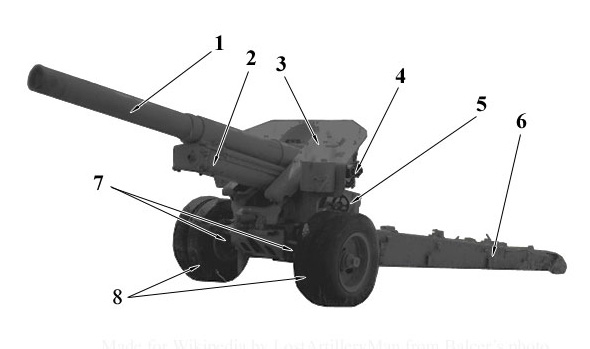
122 Mm Howitzer M1938 (M-30)
The 122 mm howitzer M1938 (M-30) (GRAU index: 52-G-463) was a Soviet 121.92 mm (4.8 inch) howitzer. The weapon was developed by the design bureau of Motovilikha Plants, headed by F. F. Petrov, in the late 1930s, and was in production from 1939 to 1955. The M-30 saw action in World War II, mainly as a divisional artillery piece of the Red Army (RKKA). Captured guns were also employed later in the conflict by the German Wehrmacht and the Finnish Army. Post World War II the M-30 saw combat in numerous conflicts of the mid- to late twentieth century in service of other countries' armies, notably in the Middle East. Development In 1930 Red Army (RKKA) authorities started to look for a new divisional-level howitzer to replace the pre-World War I 122 mm howitzer M1909 and 122 mm howitzer M1910. Although both pieces were eventually modernized, resulting in the 122-mm howitzer M1909/37 and the 122-mm howitzer M1910/30 respectively, these upgrades did not address some short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
152 Mm Howitzer M1938 (M-10)
152-mm howitzer M1938 (M-10) (russian: 152-мм гаубица обр. 1938 г. (М-10)) was a Soviet 152.4 mm (6 inch) howitzer of World War II era. It was developed in 1937–1938 at the ''Motovilikha Mechanical Plant'' by a team headed by F. F. Petrov. Although production of the gun was stopped in 1941, it saw combat with the Red Army until the end of World War II and remained in service until the 1950s. Captured pieces were used by Wehrmacht and the Finnish Army. The latter kept the M-10 in service until 2000. In a tank-mounted variant, M-10T, the gun was mounted on the KV-2 heavy tank. Development history By the early 1930s the Red Army (RKKA) started to look for a replacement for the 152-mm howitzer M1909 and the 152-mm howitzer M1910. Those pieces, developed before World War I, had unsprung fixed trail carriages and short barrels, which meant poor mobility, insufficient elevation and traverse angles and short range. Although both pieces were eventually modernized, res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
76 Mm Divisional Gun M1936 (F-22)
The 76-mm divisional gun M1936 (F-22) was a Soviet divisional semi-universal gun, adopted for Red Army service in 1936. This gun was used in conflicts between the USSR and Japan on the Far East, in the Winter War and in World War II. Many F-22s were captured by the Wehrmacht, modernized by the Germans and used against Soviet forces. Description The F-22 was a semi-universal gun which combined the capabilities of a divisional gun and - to some extent - of an anti-aircraft gun. It had a split-trail carriage with suspension and steel wheels with rubber tires. The gun was equipped with a semi-automatic vertical sliding breech block; the recoil mechanism consisted of a hydraulic recoil buffer and a hydro-pneumatic recuperator. The sights and the elevation controls were located on different sides of the barrel. The chamber fitted the standard model 1900 cartridge, which meant that the gun could use ammunition of older 76.2-mm divisional and regimental guns. Development and production h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-38 Tank
The T-38 amphibious scout tank was a Soviet amphibious light tank that saw service in World War II. Developed as a modernized version of the earlier T-37A light tank, the T-38 proved to be only a moderate improvement over its predecessor, and was eventually replaced in 1940 by the T-40. History Early trials of the T-37A revealed many deficiencies in its design, including limited range, sub-par buoyancy, and an unreliable transmission and running gear that could cause its tracks to fall off while on the move.Baryatinskiy, p. 15-19 Development of an improved version of the tank that would fix these flaws was begun in late 1934 at Factory No. 37 in Moscow, under the direction of Chief Designer N. Astrov and Chief Engineer N. Kozyrev.Zaloga, p. 77-79 The redesign proved to be so extensive that the project was given the independent designation T-38, and a prototype was completed by June 1935. The T-38 retained many design features of the T-37A, including its repurposed GAZ-AA en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FAI Armoured Car
The FAI ''(Ford-A Izhorskiy)'' armoured car was a replacement for the D-8 armoured car, used by the Soviet Union from the early 1930s to early 1940s. Description The FAI was built on the chassis of the GAZ-A car, a licensed copy of the American Ford A. This chassis was the major weakness of the FAI. Most commercial car chassis were not powerful enough to move a useful amount of armour or firepower on the battlefield. The Germans were known to get round this particular problem by designing a car chassis that was intended from the outset for both civilian and military vehicles and which was used successfully in at least one German armoured car family of this period. However, armoured cars based on commercial car chassis were, for the most part, road-bound, thinly armoured and lightly armed. The FAI was a typical example of this class of vehicle with a single 7.62 mm DT machine-gun in a revolving turret. The armour was sufficient to stop most shell fragments and small arms f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vologda Oblast
Vologda Oblast ( rus, Вологодская область, p=vəlɐˈɡotskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ, r=Vologodskaya oblast, ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is Vologda. The Oblast has a population of 1,202,444 ( 2010 Census). The largest city is Cherepovets, the home of the Severstal metallurgical plant, the largest industrial enterprise in the oblast. Vologda Oblast is rich in historic monuments, such as the Kirillo-Belozersky Monastery, Ferapontov Monastery (a World Heritage Site) with the frescoes of Dionisius, medieval towns of Velikiy Ustyug and Belozersk, and baroque churches of Totma and Ustyuzhna. Large reserves of wood and fresh water are the main natural resources. History The area of Vologda Oblast was settled by Finnic peoples in prehistory, and most of the toponyms in the region are in fact Finnic. Vepsians, who still live in the west of the oblast, are the descendants of that population. Subsequently, the area was colonized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
111th Rifle Division
111th may refer to: *111th Delaware General Assembly, a meeting of the legislative branch of the state government *111th Engineer Brigade (United States), a combat engineer brigade of the United States Army *111th Field Artillery Regiment (United States), a 155MM towed artillery unit with a General Support/Reinforcing mission *111th Fighter Escadrille (Poland) of the Polish Air Force, a fighter unit of the Polish Army * 111th Fighter Wing, an Air National Guard fighter unit located at NAS Willow Grove, Pennsylvania * 111th Indian Infantry Brigade, an Infantry formation of the Indian Army during World War II *111th Infantry Brigade (Pakistan), an infantry brigade of the Pakistan Army *111th Infantry Division (German Empire), a unit of the Imperial German Army in World War I *111th Infantry Regiment (United States), represented in the U.S. Army by 1st Battalion, 111th Infantry *111th Maneuver Enhancement Brigade (United States), an air defense artillery brigade of the United States Arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pskov Oblast
Pskov Oblast (russian: Пско́вская о́бласть, ') is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast), located in the west of the country. Its administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Pskov. As of the Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census, its population was 673,423. Geography Pskov Oblast is the westernmost federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of contiguous Russia (Kaliningrad Oblast, while located further to the west, is an enclave and exclave, exclave).1september.ru. Д. В. Заяц (D. V. Zayats).Псковская область (''Pskov Oblast''). It borders with Leningrad Oblast in the north, Novgorod Oblast in the east, Tver Oblast, Tver and Smolensk Oblasts in the southeast, Vitebsk Region, Vitebsk Oblast of Belarus in the south, and with the counties of Latvia (Alūksne Municipality, Balvi Municipality, and Ludza Municipality) and Estonia (Võru County) in the west. In the northwest, Pskov O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

_1.jpg)