|
4-AcO-MET
4-Acetoxy-MET (4-Acetoxy-''N''-methyl-''N''-ethyl tryptamine), also known as metacetin or 4-AcO-MET, is a hallucinogenic tryptamine. It is the acetate ester of 4-HO-MET, and a homologue of 4-AcO-DMT. It is a novel compound with very little history of human use. It is sometimes sold as a research chemical by online retailers. It is expected that the compound is quickly hydrolyzed into the free phenolic 4-HO-MET by serum esterases, but human studies concerning the metabolic fate of this drug are lacking. Legality 4-Acetoxy-MET is unscheduled in the United States. It may be considered an analogue of Psilocin, a Schedule I drug under the Controlled Substances Act The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) is the statute establishing federal government of the United States, federal drug policy of the United States, U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture, importation, possession, use, and distribution of .... As such, the sale for human consumption or the use for illicit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-AcO-DMT
''O''-Acetylpsilocin (also known as psilacetin, 4-acetoxy-DMT, 4-AcO-DMT, or synthetic shrooms) is a semi-synthetic psychoactive drug that has been suggested by David Nichols to be a potentially useful alternative to psilocybin for pharmacological studies, as they are both believed to be prodrugs of psilocin. However, some users report that ''O''-acetylpsilocin's subjective effects differ from those of psilocybin and psilocin. Additionally, some users prefer 4-AcO-DMT to natural psilocybin mushrooms due to feeling fewer adverse side effects such as nausea and heavy body load, which are more frequently reported in experiences involving natural mushrooms. It is the acetylated form of the psilocybin mushroom alkaloid psilocin and is a lower homolog of 4-AcO-MET, 4-AcO-DET, 4-AcO-MiPT and 4-AcO-DiPT. History ''O''-Acetylpsilocin (psilacetin) and several other esters of psilocin were patented on January 16, 1963 by Sandoz Ltd via Albert Hofmann & Franz Troxler. Despite this, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psilocin
Psilocin (also known as 4-HO-DMT, 4-hydroxy DMT, psilocine, psilocyn, or psilotsin) is a substituted tryptamine alkaloid and a serotonergic psychedelic substance. It is present in most psychedelic mushrooms together with its phosphorylated counterpart psilocybin. Psilocin is a Schedule I drug under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances. Acting on the 5-HT2A receptors, psilocin modulates the production and reuptake of serotonin. The mind-altering effects of psilocin are highly variable and subjective and resemble those of LSD and DMT. Chemistry Psilocin and its phosphorylated cousin, psilocybin, were first isolated and named in 1958 by Swiss chemist Albert Hofmann. Hofmann obtained the chemicals from laboratory-grown specimens of the entheogenic mushroom ''Psilocybe mexicana''. Hofmann also succeeded in finding synthetic routes to these chemicals. Psilocin can be obtained by dephosphorylation of natural psilocybin under strongly acidic or under alkaline conditions (hyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula . In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many organic compounds. It is a very stable group in most molecules. While the methyl group is usually part of a larger molecule, bounded to the rest of the molecule by a single covalent bond (), it can be found on its own in any of three forms: methanide anion (), methylium cation () or methyl radical (). The anion has eight valence electrons, the radical seven and the cation six. All three forms are highly reactive and rarely observed. Methyl cation, anion, and radical Methyl cation The methylium cation () exists in the gas phase, but is otherwise not encountered. Some compounds are considered to be sources of the cation, and this simplification is used pervasively in organic chemistry. For example, protonation of methanol gives an elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Group
In organic chemistry, an ethyl group (abbr. Et) is an alkyl substituent with the formula , derived from ethane (). ''Ethyl'' is used in the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry's nomenclature of organic chemistry for a saturated two-carbon moiety in a molecule, while the prefix "''eth-''" is used to indicate the presence of two carbon atoms in the molecule. Ethylation Ethylation is the formation of a compound by introduction of the ethyl group. The most widely practiced example of this reaction is the ethylation of benzene with ethylene to yield ethylbenzene, a precursor to styrene, which is a precursor to polystyrene. Approximately 24.7 million tons of ethylbenzene were produced in 1999. :: Many ethyl-containing compounds are generated by electrophilic ethylation, i.e. treatment of nucleophiles with sources of Et+. Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate t3OF4 is such a reagent. For good nucleophiles, less electrophilic reagents are employed, such as ethyl h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
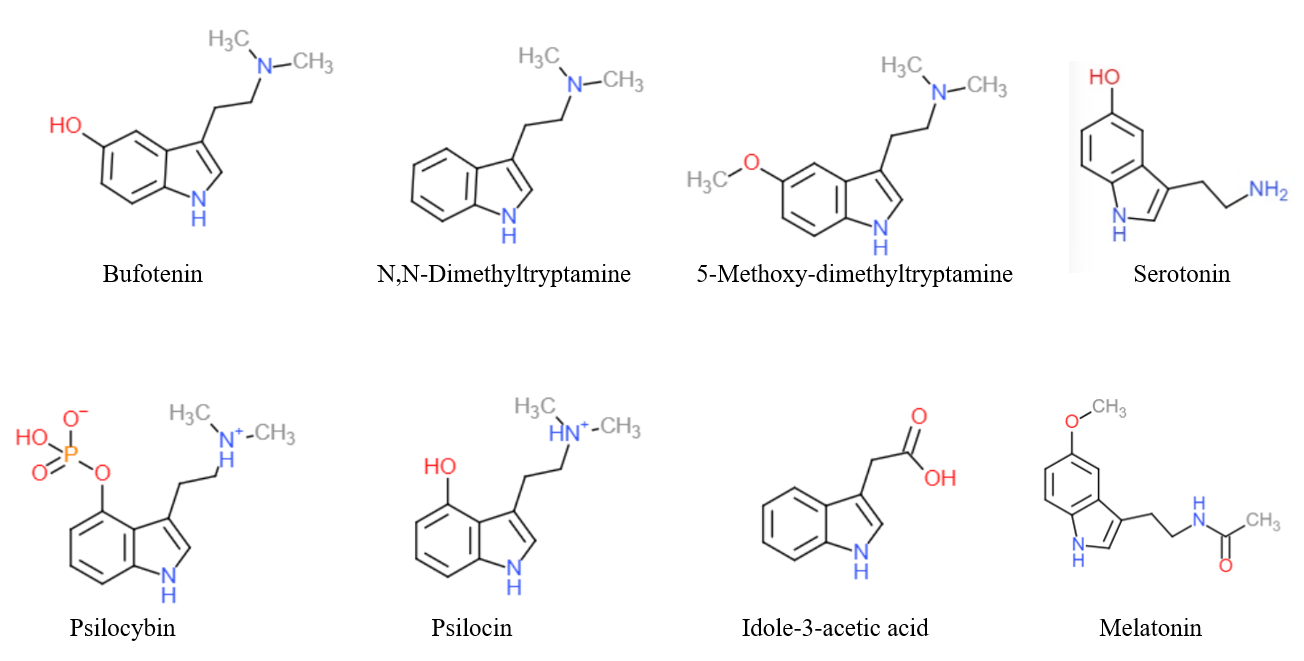
Tryptamine
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid, tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole ─ a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the first one being the heterocyclic nitrogen). The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and others. Tryptamine has been shown to activate trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain, and regulates the activity of dopaminergic, serotonergic and glutamatergic systems. In the human gut, symbiotic bacteria convert dietary tryptophan to tryptamine, which activates 5-HT4 receptors and regulates gastrointestinal motility. Multiple tryptamine-derived drugs have been developed to treat migraines, while trace amine-associated receptors are being explored as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychedelics, Dissociatives And Deliriants
Hallucinogens are a large, diverse class of psychoactive drugs that can produce altered states of consciousness characterized by major alterations in thought, mood, and perception as well as other changes. Most hallucinogens can be categorized as either being psychedelics, dissociatives, or deliriants. However, certain hallucinogens such as Fly agaric as well as other gabaergic hallucinogenics are more often considered to technically be hypnotics, therefore indicating another separate subcategory of drugs which can substantially alter visual perception. Etymology The word ''hallucinogen'' is derived from the word ''hallucination''. The term ''hallucinate'' dates back to around 1595–1605, and is derived from the Latin ''hallūcinātus'', the past participle of ''(h)allūcināri'', meaning "to wander in the mind." Characteristics Leo Hollister gave five criteria for classifying a drug as hallucinogenic.Glennon RA. Classical drugs: an introductory overview. In Lin GC and Gle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-HO-MET
4-HO-MET (4-hydroxy-''N''-methyl-''N''-ethyltryptamine, metocin, or methylcybin), is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is a structural− and functional analog of psilocin as well as the 4-hydroxyl analog of methylethyltryptamine (MET). 4-HO-MET was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book ''TiHKAL'' (''Tryptamines I Have Known and Loved''), the dosage is listed as 10-20 mg. 4-HO-MET produces psilocin-like distortion of color, sound, and form. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of 4-HO-MET. There have been no reports of deaths from 4-HO-MET, even though people have reported taking doses up to 150 mg, more than an order of magnitude above the effective dose. Effects Users report similar effects to psilocin, including mydriasis, closed and open eye visuals, euphoria, time dilation and general change in thought processes. These effects occur in a wavelike pattern such as that of psilocybin with near-normal per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (chemistry)
In chemistry, homology is the appearance of homologues. A homologue (also spelled as homolog) is a compound belonging to a series of compounds differing from each other by a repeating unit, such as a methylene bridge −−, a peptide residue, etc. A homolog is a special case of an analog. Examples are alkanes and compounds with alkyl side chains of different length (the repeating unit being a methylene group -CH2-). Periodic table On the periodic table, homologous elements share many electrochemical properties and appear in the same group (column) of the table. For example, all noble gases are colorless, monatomic gases with very low reactivity. These similarities are due to similar structure in their outer shells of valence electrons. Mendeleev used the prefix eka- for an unknown element below a known one in the same group. See also * Homologous series * Analog Analog or analogue may refer to: Computing and electronics * Analog signal, in which information is enco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Chemical
Research chemicals are chemical substances used by scientists for medical and scientific research purposes. One characteristic of a research chemical is that it is for laboratory research use only; a research chemical is not intended for human or veterinary use. This distinction is required on the labels of research chemicals, and is what exempts them from regulation under parts 100-740 in Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations ( 21CFR). Background Pharmacological research chemicals Research chemicals are fundamental in the development of novel pharmacotherapies. Common medical laboratory uses include ''in vivo'' and animal testing to determine therapeutic value, toxicology testing by contract research organizations to determine drug safety, and analysis by drug test and forensic toxicology labs for the purposes of evaluating human exposure. Many pharmacologically active chemicals are sold online under the guise of "research chemicals," when in reality they are untested d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serum Esterase
The enzyme cholinesterase (EC 3.1.1.8, choline esterase; systematic name acylcholine acylhydrolase) catalyses the hydrolysis of choline-based esters: : an acylcholine + H2O = choline + a carboxylate Several of these serve as neurotransmitters. Thus, it is either of two enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of these cholinergic neurotransmitters, such as breaking acetylcholine into choline and acetic acid. These reactions are necessary to allow a cholinergic neuron to return to its resting state after activation. For example, in muscle contraction, acetylcholine at a neuromuscular junction triggers a contraction; but for the muscle to relax afterward, rather than remaining locked in a tense state, the acetylcholine must be broken down by a choline esterase. The main type for that purpose is acetylcholinesterase (also called choline esterase I or erythrocyte cholinesterase); it is found mainly in chemical synapses and red blood cell membranes. The other type is butyryl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Controlled Substances Act
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) is the statute establishing federal government of the United States, federal drug policy of the United States, U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture, importation, possession, use, and distribution of certain substances is regulated. It was passed by the 91st United States Congress as Title II of the Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970 and signed into law by President Richard Nixon. The Act also served as the national implementing legislation for the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs. The legislation created five schedules (classifications), with varying qualifications for a substance to be included in each. Two federal agencies, the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), determine which substances are added to or removed from the various schedules, although the statute passed by Congress created the initial listing. Congress has sometimes scheduled other substances th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychedelic Tryptamines
Psychedelics are a subclass of hallucinogenic drugs whose primary effect is to trigger non-ordinary states of consciousness (known as psychedelic experiences or "trips").Pollan, Michael (2018). ''How to Change Your Mind: What the New Science of Psychedelics Teaches Us About Consciousness, Dying, Addiction, Depression, and Transcendence'' Sometimes, they are called classic hallucinogens, serotonergic hallucinogens, or serotonergic psychedelics, and the term ''psychedelics'' is used more broadly to include all hallucinogens; this article uses the narrower definition of ''psychedelics''. Psychedelics cause specific psychological, visual, and auditory changes, and often a substantially altered state of consciousness.Leary, Timothy; Metzner, Ralph (1964). ''The Psychedelic Experience: A Manual Based on The Tibetan Book of the Dead'' Psychedelic states are often compared to meditative, psychodynamic or transcendental types of alterations of mind. The "classical" psychedelics, the psyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |