|
4',7-Dihydroxyflavone
4âē,7-Dihydroxyflavone is a flavone. It is found in ''Medicago truncatula'' in relation with the root nodulation symbiont ''Sinorhizobium meliloti'' or in seeds of '' Sophora viciifolia''. Like many other flavonoids, 4âē,7-dihydroxyflavone has been found to possess activity at opioid receptors ''in vitro''. Specifically, it acts as an antagonist of the Ξ-opioid receptor and, with lower affinity, of the Κ- and Îī-opioid receptor The Îī-opioid receptor, also known as delta opioid receptor or simply delta receptor, abbreviated DOR or DOP, is an inhibitory 7-transmembrane G-protein coupled receptor coupled to the G protein Gi/G0 and has enkephalins as its endogenous lig ...s. See also * Pratol (7-hydroxy-4âē-methoxyflavone) is the ''O''-methylated form of the molecule. References Flavones Kappa-opioid receptor antagonists Mu-opioid receptor antagonists {{aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pratol
Pratol is a flavonoid, 4âē-''O''-methylated 4âē,7-dihydroxyflavone. It can be found in ''Trifolium pratense ''Trifolium pratense'', the red clover, is a herbaceous species of flowering plant in the bean family Fabaceae, native to Europe, Western Asia, and northwest Africa, but planted and naturalized in many other regions. Description Red clove ...''. References O-methylated flavones {{aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavone
Flavone is an organic compound with the formula . A white solid, flavone is a derivative of chromone with a phenyl (Ph) substituent adjacent to the ether group. The compound is of little direct practical importance, but susbstituted derivatives, the flavones and flavonoids are a large class of nutritionally important natural products. Flavone can be prepared in the laboratory by cyclization of 2-hydroxacetophenone. Isomeric with flavone is isoflavone, where the phenyl group is adjacent to the ketone In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure RâC(=O)âR', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group âC(=O)â (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bo .... References {{Flavones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicago Truncatula
''Medicago truncatula'', the barrelclover, strong-spined medick, barrel medic, or barrel medick, is a small annual legume native to the Mediterranean region that is used in genomic research. It is a low-growing, clover-like plant tall with trifoliate leaves. Each leaflet is rounded, long, often with a dark spot in the center. The flowers are yellow, produced singly or in a small inflorescence of two to five together; the fruit is a small, spiny pod. This species is studied as a model organism for legume biology because it has a small diploid genome, is self-fertile, has a rapid generation time and prolific seed production, is amenable to genetic transformation, and its genome has been sequenced. It forms symbioses with nitrogen-fixing rhizobia (''Sinorhizobium meliloti'' and '' Sinorhizobium medicae'') and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi including ''Rhizophagus irregularis'' (previously known as ''Glomus intraradices''). The model plant ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' does not form eithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinorhizobium Meliloti
''Ensifer meliloti'' (formerly ''Rhizobium meliloti'' and ''Sinorhizobium meliloti'') are an aerobic, Gram-negative, and diazotrophic species of bacteria. ''S. meliloti'' are motile and possess a cluster of peritrichous flagella. ''S. meliloti'' fix atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia for their legume symbionts, such as alfalfa. ''S. meliloti'' forms a symbiotic relationship with legumes from the genera ''Medicago'', ''Melilotus'' and ''Trigonella'', including the model legume ''Medicago truncatula''. This symbiosis promotes the development of a plant organ, termed a root nodule. Because soil often contains a limited amount of nitrogen for plant use, the symbiotic relationship between ''S. meliloti'' and their legume hosts has agricultural applications. These techniques reduce the need for inorganic nitrogenous fertilizers. Symbiosis Symbiosis between ''S. meliloti'' and its legume hosts begins when the plant secretes an array of betaines and flavonoids into the rhizosphere: 4,4â ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sophora Viciifolia
''Sophora'' is a genus of about 45 species of small trees and shrubs in the pea family Fabaceae. The species have a pantropical distribution. The generic name is derived from ''sophera'', an Arabic name for a pea-flowered tree. The genus formerly had a broader interpretation including many other species now treated in other genera, notably ''Styphnolobium'' (pagoda tree genus), which differs in lacking nitrogen fixing bacteria (rhizobia) on the roots, and ''Dermatophyllum'' (the mescalbeans). ''Styphnolobium'' has galactomannans as seed polysaccharide reserve, in contrast ''Sophora'' contains arabinogalactans, and ''Dermatophyllum'' amylose. The New Zealand ''Sophora'' species are known as kowhai. The seeds of species such as ''Sophora affinis'' and ''Sophora chrysophylla'' are reported to be poisonous. Fossil record One ''Sophora'' fossil seed pod from the middle Eocene epoch has been described from the Miller clay pit in Henry County, Tennessee, United States. Species ''Sop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opioid Receptor
Opioid receptors are a group of inhibitory G protein-coupled receptors with opioids as ligands. The endogenous opioids are dynorphins, enkephalins, endorphins, endomorphins and nociceptin. The opioid receptors are ~40% identical to somatostatin receptors (SSTRs). Opioid receptors are distributed widely in the brain, in the spinal cord, on peripheral neurons, and digestive tract. Discovery By the mid-1960s, it had become apparent from pharmacologic studies that opiate drugs were likely to exert their actions at specific receptor sites, and that there were likely to be multiple such sites. Early studies had indicated that opiates appeared to accumulate in the brain. The receptors were first identified as specific molecules through the use of binding studies, in which opiates that had been labeled with radioisotopes were found to bind to brain membrane homogenates. The first such study was published in 1971, using 3H-levorphanol. In 1973, Candace Pert and Solomon H. Snyder publis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, ''in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' ( la, in glass; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins.Pharmacology Guide: In vitro pharmacology: concentration-response curves " '' GlaxoWellcome.'' Retrieved on December 6, 2007. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, |
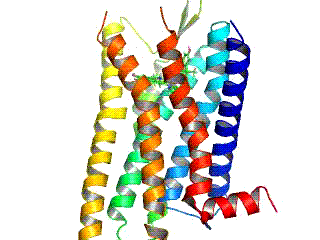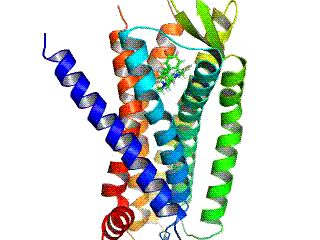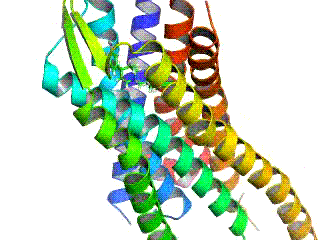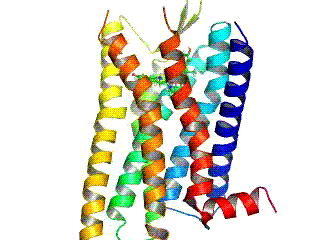
Ξ-opioid Receptor
The Ξ-opioid receptors (MOR) are a class of opioid receptors with a high affinity for enkephalins and beta-endorphin, but a low affinity for dynorphins. They are also referred to as Ξ(''mu'')-opioid peptide (MOP) receptors. The prototypical Ξ-opioid receptor agonist is morphine, the primary psychoactive alkaloid in opium. It is an inhibitory G-protein coupled receptor that activates the Gi alpha subunit, inhibiting adenylate cyclase activity, lowering cAMP levels. Structure The structure of the Ξ-opioid receptor has been determined with the antagonist Îē-FNA, the agonist BU72, and in a complex with DAMGO and Gi protein. Splice variants Three variants of the Ξ-opioid receptor are well characterized, though RT-PCR has identified up to 10 total splice variants in humans. Location They can exist either presynaptically or postsynaptically depending upon cell types. The Ξ-opioid receptors exist mostly presynaptically in the periaqueductal gray region, and in the superfi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affinity (pharmacology)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a molecule which produces a signal by binding to a site on a target protein. The binding typically results in a change of conformational isomerism (conformation) of the target protein. In DNA-ligand binding studies, the ligand can be a small molecule, ion, or protein which binds to the DNA double helix. The relationship between ligand and binding partner is a function of charge, hydrophobicity, and molecular structure. Binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals forces. The association or docking is actually reversible through dissociation. Measurably irreversible covalent bonding between a ligand and target molecule is atypical in biological systems. In contrast to the definition of liga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Κ-opioid Receptor
The Κ-opioid receptor or kappa opioid receptor, abbreviated KOR or KOP, is a G protein-coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''OPRK1'' gene. The KOR is coupled to the G protein Gi/G0 and is one of four related receptors that bind opioid-like compounds in the brain and are responsible for mediating the effects of these compounds. These effects include altering nociception, consciousness, motor control, and mood. Dysregulation of this receptor system has been implicated in alcohol and drug addiction. The KOR is a type of opioid receptor that binds the opioid peptide dynorphin as the primary endogenous ligand (substrate naturally occurring in the body). In addition to dynorphin, a variety of natural alkaloids, terpenes and synthetic ligands bind to the receptor. The KOR may provide a natural addiction control mechanism, and therefore, drugs that target this receptor may have therapeutic potential in the treatment of addiction. There is evidence that distribution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Îī-opioid Receptor
The Îī-opioid receptor, also known as delta opioid receptor or simply delta receptor, abbreviated DOR or DOP, is an inhibitory 7-transmembrane G-protein coupled receptor coupled to the G protein Gi/G0 and has enkephalins as its endogenous ligands. The regions of the brain where the Îī-opioid receptor is largely expressed vary from species model to species model. In humans, the Îī-opioid receptor is most heavily expressed in the basal ganglia and neocortical regions of the brain. Function The endogenous system of opioid receptors is well known for its analgesic potential; however, the exact role of Îī-opioid receptor activation in pain modulation is largely up for debate. This also depends on the model at hand since receptor activity is known to change from species to species. Activation of delta receptors produces analgesia, perhaps as significant potentiators of Ξ-opioid receptor agonists. However, it seems like delta agonism provides heavy potentiation to any mu agonism. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |