|
3 Ft Gauge Rail Modelling
3' Gauge rail modelling is a specialisation in rail transport modelling. Specifically it relates to the modelling of narrow gauge prototypes of gauge. This gauge was the most common narrow gauge in the United States and in Ireland. Apart from some other lines in North, Central and South America, gauge was uncommon elsewhere. Therefore, most 3' gauge modellers model either United States or Irish prototypes. United States gauge railroads were widespread in the United States in the period 1880-90. While most of these railroads were converted to standard gauge by the start of the 20th century, a number of lines survived till the Second World War and later, and became popular subjects for modelling. Probably the most popular prototype is the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad, followed by other Colorado railroads such as the Rio Grande Southern and Colorado and Southern. Other railroads from California and the eastern states are also popular. Scale and gauge combinations u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
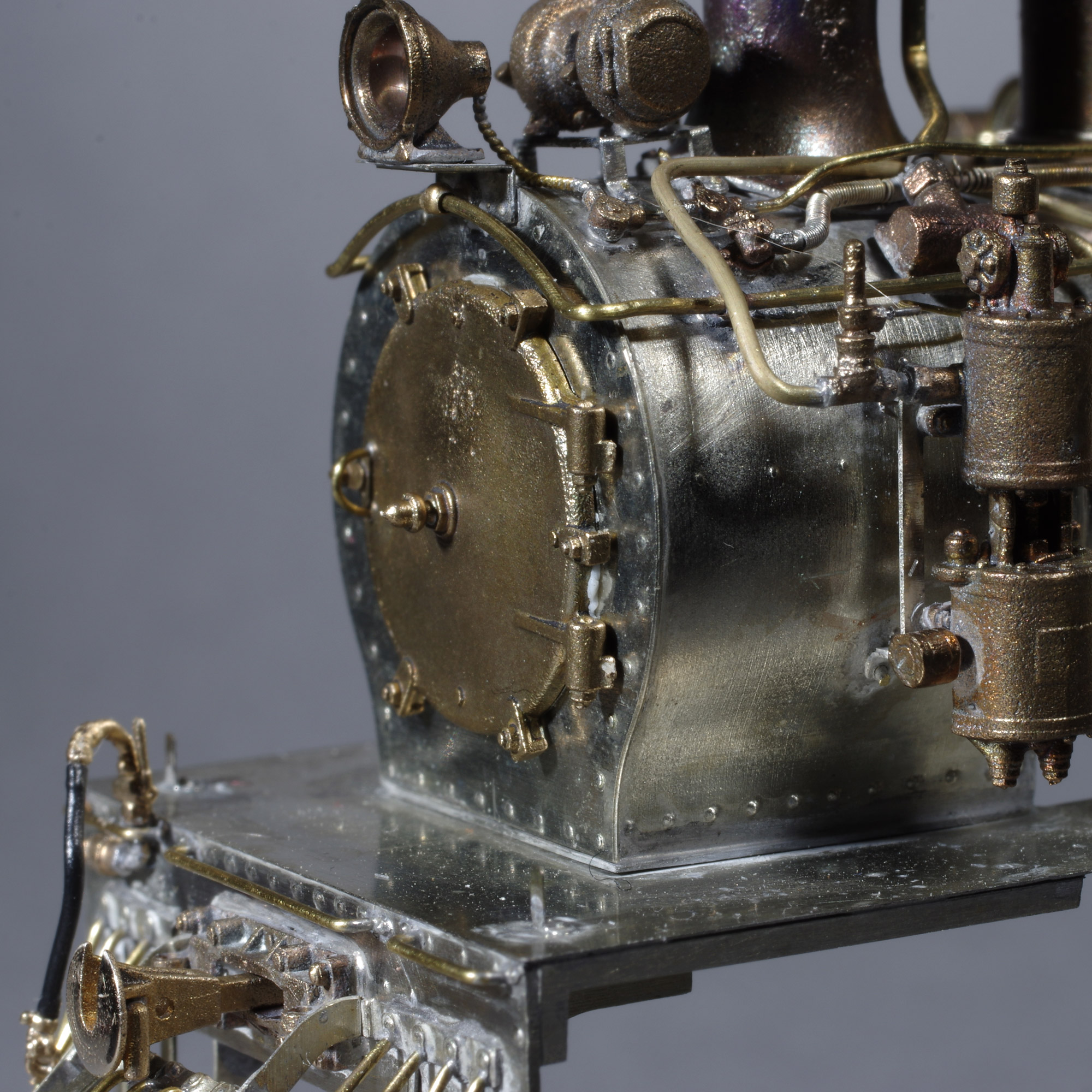
Rail Transport Modelling
Railway modelling (UK, Australia, New Zealand, and Ireland) or model railroading (US and Canada) is a hobby in which rail transport systems are modelled at a reduced scale. The scale models include locomotives, rolling stock, streetcars, tracks, signalling, cranes, and landscapes including: countryside, roads, bridges, buildings, vehicles, harbors, urban landscape, model figures, lights, and features such as rivers, hills, tunnels, and canyons. The earliest model railways were the 'carpet railways' in the 1840s. The first documented model railway was the Railway of the Prince Imperial (French: Chemin de fer du Prince impérial) built in 1859 by emperor Napoleon III for his then 3-year-old son, also Napoleon, in the grounds of the Château de Saint-Cloud in Paris. It was powered by clockwork and ran in a figure-of-eight. Electric trains appeared around the start of the 20th century, but these were crude likenesses. Model trains today are more realistic, in addition t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O Scale
O scale (or O gauge) is a scale commonly used for toy trains and rail transport modelling. Introduced by German toy manufacturer Märklin around 1900, by the 1930s three-rail alternating current O gauge was the most common model railroad scale in the United States and remained so until the early 1960s. In Europe, its popularity declined before World War II due to the introduction of smaller scales. O gauge had its heyday when model railroads were considered toys, with more emphasis placed on cost, durability, and the ability to be easily handled and operated by pre-adult hands. Detail and realism were secondary concerns, at best. It still remains a popular choice for those hobbyists who enjoy running trains more than they enjoy other aspects of modeling, but developments in recent years have addressed the concerns of scale model railroaders making O scale popular among fine-scale modellers who value the detail that can be achieved. The size of O is larger than OO/HO layouts, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport Modelling Scales
Rail transport modelling uses a variety of scales (ratio between the real world and the model) to ensure scale models look correct when placed next to each other. Model railway scales are standardized worldwide by many organizations and hobbyist groups. Some of the scales are recognized globally, while others are less widespread and, in many cases, virtually unknown outside their circle of origin. Scales may be expressed as a numeric ratio (e.g. 1/87 or 1:87) or as letters defined in rail transport modelling standards (e.g. HO, OO, N, O, G, TT and Z.) The majority of commercial model railway equipment manufacturers base their offerings on ''Normen Europäischer Modellbahnen'' (NEM) or National Model Railroad Association (NMRA) standards in most popular scales. Terminology Although '' scale'' and ''gauge'' are often confused, ''scale'' means the ratio between a unit of measurement on a model compared with a unit of measurement in corresponding full size prototype, while ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
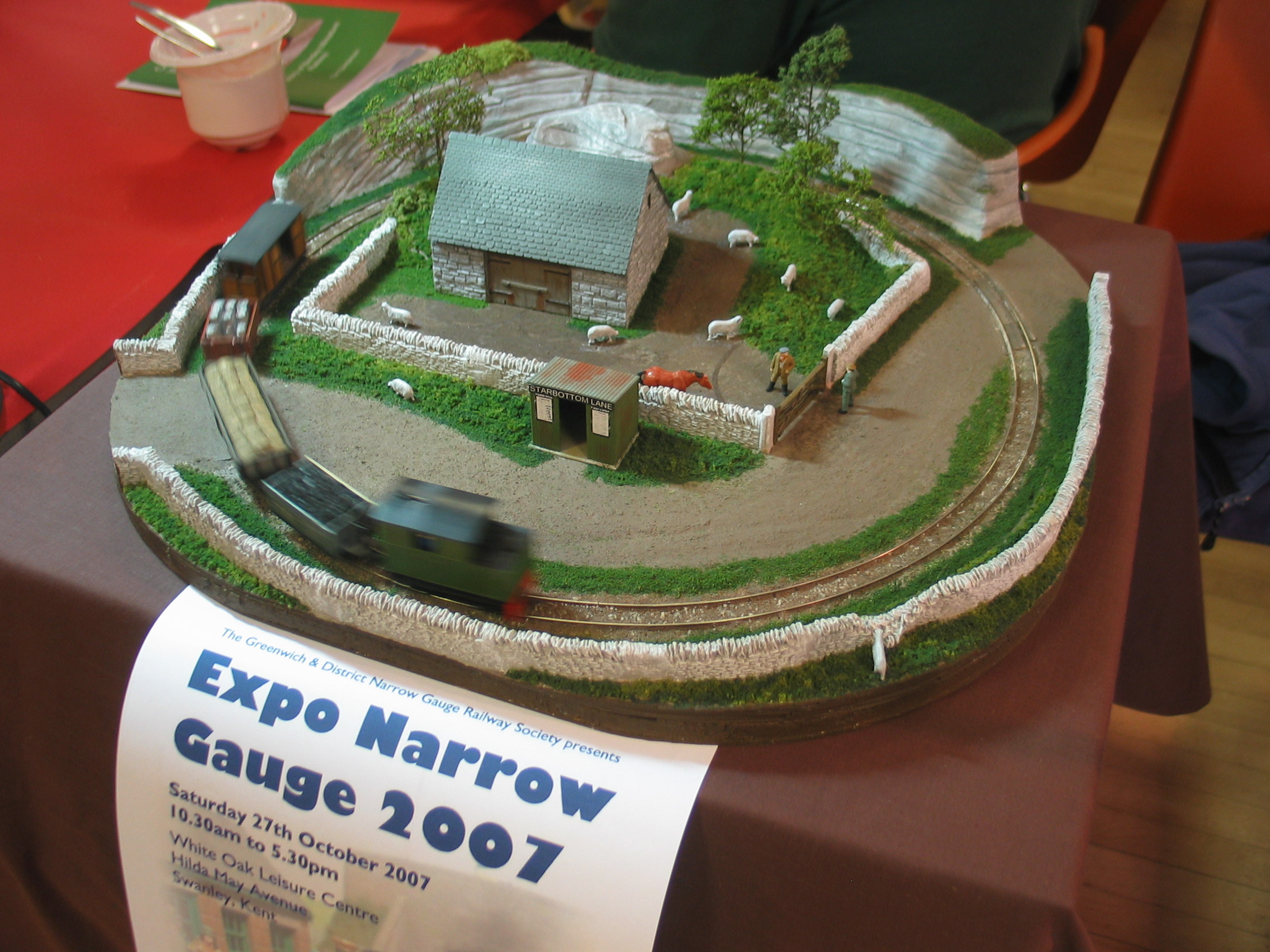
List Of Narrow-gauge Model Railway Scales
__FORCETOC__ Railway modelling has long used a variety of scales and gauges to represent its models of real subjects. In most cases, gauge and scale are chosen together, so as to represent Stephenson standard gauge. By choosing a smaller gauge than this for a particular scale, the model represents a narrow-gauge example. Such gauge and scale combinations are of course used for the deliberate modelling of particular narrow-gauge subjects, where the choice of subject is behind the choice of combination. Narrow-gauge modelling has also become especially popular from the purely modelling aspects: it combines a conveniently visible large scale that is easier to work on, with a narrow model gauge that allows tighter radius curves and so fits layouts into smaller spaces. This has been a particular reason in Europe where, houses being generally smaller than in the US, there is rarely space for 0 gauge and even 00 gauge is restricted in the size of curves. At times, particularly in the ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sn3½
In rail transport modelling, Sn3½ is a scale/gauge combination derived from S scale to represent narrow gauge track by using gauge track (the same as HO gauge). The scale is 1:64. Sn3½ is popular in South Africa, Australia (particularly Western Australia, Queensland and Tasmania where narrow gauge systems exist) and New Zealand. Sn3½ is very rarely or never used for modelling in other countries with 3 foot 6 (1067mm) gauge railways such as Japan, Taiwan, Indonesia etc. Track As track scales down to 16.5mm at 1:64, modelers use HO gauge track (which represents Standard gauge at 1:87 scale) on Sn3½ layouts. New Zealand Sn3½ is the primary scale for modeling New Zealand's narrow gauge 3 ft 6 in railways. The majority of rolling stock available, are white-metal kits, making them considerably more expensive and heavier than other scales and countries. Many of these kits are highly detailed. Buildings are generally hand-made and track (HO gauge track) can either be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Railway Scales
Rail transport modelling uses a variety of scales (ratio between the real world and the model) to ensure scale models look correct when placed next to each other. Model railway scales are standardized worldwide by many organizations and hobbyist groups. Some of the scales are recognized globally, while others are less widespread and, in many cases, virtually unknown outside their circle of origin. Scales may be expressed as a numeric ratio (e.g. 1/87 or 1:87) or as letters defined in rail transport modelling standards (e.g. HO, OO, N, O, G, TT and Z.) The majority of commercial model railway equipment manufacturers base their offerings on ''Normen Europäischer Modellbahnen'' (NEM) or National Model Railroad Association (NMRA) standards in most popular scales. Terminology Although '' scale'' and ''gauge'' are often confused, ''scale'' means the ratio between a unit of measurement on a model compared with a unit of measurement in corresponding full size prototype, while ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
00n3
00n3 is the description given to modelling narrow gauge railways in 4 mm scale with gauge track. prototypes were common in Ireland and the Isle of Man, but the scale is not generally used outside the British Isles. gauge track is the same as that used in TT scale and HOm, so some components used for those scales can be used. There is no ready-to-run support, so everything must be either built from scratch or made from kits from Worsley Works(C&LR, T&DLR, WCR & others), Branchlines (IoMR, CVR, T&DLR), Backwoods Miniatures* (CDJR, CVR, L&BER, C&LR), Dundas Models (T&DLR & WCR], Model Engine Works (CVR & CDJR), Ninelines (CDJR & SR) and Alphagraphix (CDJR, L&LSR, L&BER) amongst others. *The Backwoods kits are slowly being reintroduced by N-Drive Productions. Kits are available in etched brass and nickel-silver (locos, railcars and some rolling stock), plastic, resin, white metal and card (rolling stock). There are now some 3D printed items of stock available, for example from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Worsley Works
Worsley Works, is a manufacturer of kits for model railway carriages and locomotives, owned and run from Worsley, near Manchester, England UK, by Allen Doherty. Worsley Works is well known in the finescale modelling world, especially in less-popular scales, including British HO scale and 3mm-scale models along with various kits for Narrow Gauge railways, particularly OO9 and OOn3. Assembly of Worsley Works kits, like for most other kits that comprise only etched components, is challenging. Worsley specialises in what are described as 'scratch aid' kits, indicating that the kits are not intended to build complete models in themselves, but rather to provide the essential components to assist the process of scratch building. By manufacturing only the etched brass Brass is an alloy of copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn), in proportions which can be varied to achieve different mechanical, electrical, and chemical properties. It is a substitutional alloy: atoms of the two const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OO Gauge
OO gauge or OO scale (also, 00 gauge and 00 scale) is the most popular standard-gauge model railway standard in the United Kingdom, outside of which it is virtually unknown. OO gauge is one of several 4 mm-scale standards (4 mm to 1 foot, or 1:76.2), and the only one to be marketed by major manufacturers. The OO track gauge of (same as H0 scale) corresponds to prototypical gauge of , rather than standard gauge. However, since the 1960s, other gauges in the same scale have arisen—18.2 mm (EM) and 18.83 mm (Scalefour)—to reflect the desire of some modellers for greater scale accuracy. Origin Double-0 scale model railways were launched by Bing in 1921 as "The Table Railway", running on track and scaled at 4 mm-to-the-foot. In 1922, the first models of British prototypes appeared. Initially all locomotives were powered by clockwork, but the first electric power appeared in autumn 1923. OO describes models with a scale of 4 mm = 1 foot (1:76) running ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OOn3
00n3 is the description given to modelling narrow gauge railways in 4 mm scale with gauge track. prototypes were common in Ireland and the Isle of Man, but the scale is not generally used outside the British Isles. gauge track is the same as that used in TT scale and HOm, so some components used for those scales can be used. There is no ready-to-run support, so everything must be either built from scratch building, scratch or made from kits from Worsley Works(C&LR, T&DLR, WCR & others), Branchlines (IoMR, CVR, T&DLR), Backwoods Miniatures* (CDJR, CVR, L&BER, C&LR), Dundas Models (T&DLR & WCR], Model Engine Works (CVR & CDJR), Ninelines (CDJR & SR) and Alphagraphix (CDJR, L&LSR, L&BER) amongst others. *The Backwoods kits are slowly being reintroduced by N-Drive Productions. Kits are available in etched brass and nickel-silver (locos, railcars and some rolling stock), plastic, resin, white metal and card (rolling stock). There are now some 3D printed items of stock available, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4 Mm Scale
4 mm scale is the most popular model railway scale used in the United Kingdom. The term refers to the use of 4 millimeters on the model equating to a distance of 1 foot (305 mm) on the prototype (1:76.2). It is also used for military modelling. For historical reasons, a number of different standards are employed. Standard gauge Three different gauges are used for modelling standard gauge railways in the United Kingdom. OO gauge OO gauge uses 4 mm scale with 16.5 mm gauge track, which is inaccurately narrow since it is correct for HO scale (1:87.1). It is the most popular standard in the UK for 4 mm scale trains and is produced by the two main manufacturers in the UK. The traditional standard for wheels and track is a very coarse one with extremely oversize rails and flanges; in recent years, some manufacturers have switched to using the American National Model Railroad Association HO standard S-4 instead. EM gauge EM was originally defined to use 18mm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TT Scale
TT scale is a model railroading scale, whose name stands for ''table top''. Its 1:120 scale (from a common engineering scale where one inch equals ten feet) and gauge are roughly halfway between HO scale (1:87) and N scale (1:160). Its original purpose, like the name suggests, was to make a train set small enough to assemble and operate on a tabletop. The scale originated in the USA, but is today widespread mainly in Central Europe, thanks to "Berliner Bahnen", a defunct East German manufacturer of train sets in TT. It is the second-most popular scale in Central Europe and Russia, after HO, and adherents to TT maintain it is the smallest practical scale, especially for those who like to build models from scratch. In other parts of the world it is less spread, and can be described as a niche scale in the United States and the United Kingdom. In wargaming, the TT scale equals the 15 mm scale where the height of "standard" soldier height is . For British 3mm-scale, se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |