|
3753 Cruithne
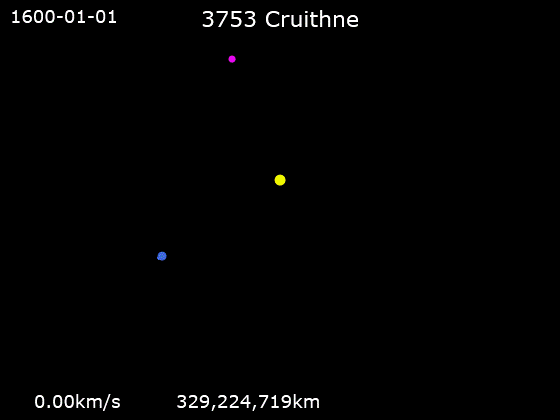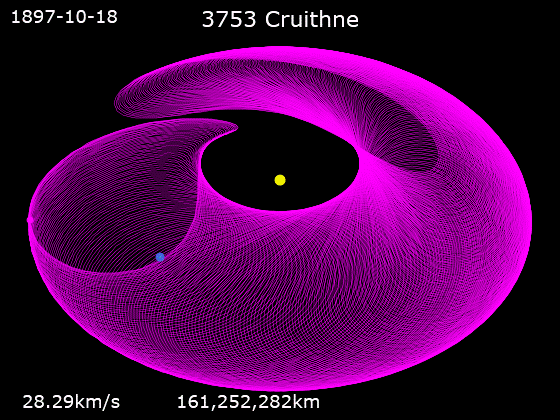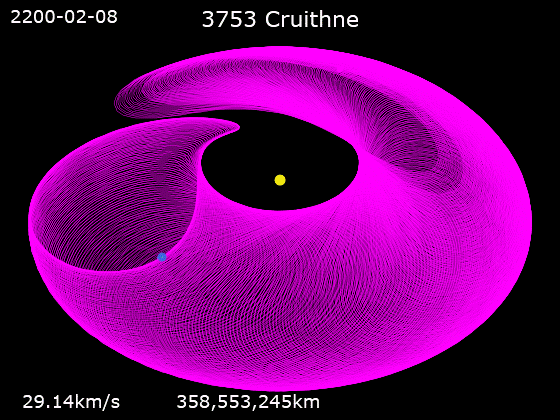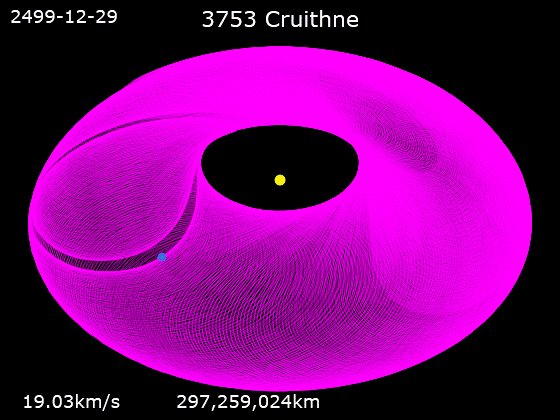
3753 Cruithne is a Q-type, Aten asteroid in orbit around the Sun in 1:1 orbital resonance with Earth, making it a co-orbital object. It is an asteroid that, relative to Earth, orbits the Sun in a bean-shaped orbit that effectively describes a horseshoe, and that can change into a quasi-satellite orbit. Cruithne does not orbit Earth and at times it is on the other side of the Sun, placing Cruithne well outside of Earth's Hill sphere. Its orbit takes it near the orbit of Mercury and outside the orbit of Mars. Cruithne orbits the Sun in about one Earth year, but it takes 770 years for the series to complete a horseshoe-shaped movement around Earth. The name ''Cruithne'' is from Irish and refers to the early Picts (Old Irish: ''Cruthin'') in the ''Annals of Ulster''Cruithne: Asteroid 3753 . Western Washington University Planetarium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duncan Waldron
J. Duncan Waldron is a Scottish planetarium astronomer, photographer, and discoverer of two minor planets. Duncan Waldron was born in Glasgow, Scotland. His first job was creating high quality reproductions of astronomical plates for the Royal Observatory in Edinburgh. On 10 October 1986 Waldron discovered the asteroid, 3753 Cruithne, while serving at the UK Schmidt Telescope at Siding Spring Observatory, and on 21 November 1986, also discovered asteroid 5577 Priestley.Schmadel, Lutz D. Dictionary of Minor Planet Names. 5th ed. Berlin and New York: Springer (2003), 317 and 474. In 1995, Waldron was first exposed to Paint Shop Pro because of the Observatory's early exploration of digital photography. This software inspired Waldron to manipulate photographs for artistic purposes, creating kaleidoscopic patterns. In 1998, Duncan Waldron and his family moved to New South Wales, Australia. Notes External links Duncan Waldron at Redbubble Discoverers of minor planets Disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monthly Notices Of The Royal Astronomical Society
''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (MNRAS) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in astronomy and astrophysics. It has been in continuous existence since 1827 and publishes letters and papers reporting original research in relevant fields. Despite the name, the journal is no longer monthly, nor does it carry the notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. History The first issue of MNRAS was published on 9 February 1827 as ''Monthly Notices of the Astronomical Society of London'' and it has been in continuous publication ever since. It took its current name from the second volume, after the Astronomical Society of London became the Royal Astronomical Society (RAS). Until 1960 it carried the monthly notices of the RAS, at which time these were transferred to the newly established ''Quarterly Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (1960–1996) and then to its successor journal ''Astronomy & Geophysics'' (since 1997). Until 1965, MNRAS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni De Sanctis
Giovanni de Sanctis (born 1949) is an Italian astronomer and discoverer of minor planets at the Osservatorio Astronomico di Torino (Astronomical Observatory of Turin) in Turin, Italy. His name is sometimes spelt DeSanctis, particularly in the Minor Planet Circulars. The Minor Planet Center credits him with the discovery of 42 numbered minor planets, most of which he discovered at ESO's La Silla site in northern Chile in the early 1980s. The Vestian asteroid 3268 De Sanctis was named by Henri Debehogne Henri Debehogne (30 December 1928 – 9 December 2007) was a Belgian astronomer and a prolific discoverer of minor planets. Biography He was born at Maillen. Debehogne worked at the Royal Observatory of Belgium (french: Observatoire Royal de ... in honor of his co-discoverer. Naming citation was published on 22 June 1986 (). List of discovered minor planets References * Piero Bianucci''Alba il 13 novembre sarà gemellata con un pianetino'' La Stampa: Il Cielo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precovery
In astronomy, precovery (short for pre-discovery recovery) is the process of finding the image of an object in images or photographic plates predating its discovery, typically for the purpose of calculating a more accurate orbit. This happens most often with minor planets, but sometimes a comet, a dwarf planet, a natural satellite, or a star is found in old archived images; even exoplanet precovery observations have been obtained. "Precovery" refers to a pre-discovery image; "recovery" refers to imaging of a body which was lost to our view (as behind the Sun), but is now visible again ''(also see lost minor planet and lost comet)''. Orbit determination requires measuring an object's position on multiple occasions. The longer the interval between observations, the more accurately the orbit can be calculated; however, for a newly discovered object, only a few days' or weeks' worth of measured positions may be available, sufficient only for a preliminary (imprecise) orbit calculatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a Megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with Deserts of Australia, deserts in the centre, tropical Forests of Australia, rainforests in the north-east, and List of mountains in Australia, mountain ranges in the south-east. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south east Asia approximately Early human migrations#Nearby Oceania, 65,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Period, last i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coonabarabran
Coonabarabran is a town in Warrumbungle Shire that sits on the divide between the Central West and North West Slopes regions of New South Wales, Australia. At the 2016 census, the town had a population of 2,537, Material was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.and as of 2021, the population of Coonabarabran and its surrounding area is 3,477. Local and district residents refer to the town as 'Coona'. History and description In 1817 the area was opened up by a Government-sponsored expedition. In 1818 John Oxley found Aboriginal people living here — later identified as the western language reach of the Kamilaroi clans (Gamilaraay is the spelling used by linguists). Kamilaroi people are still well represented in the region, having occupied Coonabarabran for approximately 7,500 years. In 1859 Lewis Gordon first proposed a town plan survey for Coonabarabran. The origin of the name ''Coonabarabran'' is unconfirme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siding Spring Observatory
Siding Spring Observatory near Coonabarabran, New South Wales, Australia, part of the Research School of Astronomy & Astrophysics (RSAA) at the Australian National University (ANU), incorporates the Anglo-Australian Telescope along with a collection of other telescopes owned by the Australian National University, the University of New South Wales, and other institutions. The observatory is situated above sea level in the Warrumbungle National Park on Mount Woorat, also known as Siding Spring Mountain. Siding Spring Observatory is owned by the Australian National University (ANU) and is part of the Mount Stromlo and Siding Spring Observatories research school. More than 100 million worth of research equipment is located at the observatory. There are over 60 telescopes on site, though not all are operational. History The original Mount Stromlo Observatory was set up by the Commonwealth Government in 1924. After duty supplying optical components to the military in World W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UK Schmidt Telescope
The UK Schmidt Telescope (UKST) is a 1.24 metre Schmidt telescope operated by the Australian Astronomical Observatory (formerly the Anglo-Australian Observatory); it is located adjacent to the 3.9 metre Anglo-Australian Telescope at Siding Spring Observatory, Australia. It is very similar to the Samuel Oschin telescope in California. The telescope can detect objects down to magnitude 21 after an hour of exposure on photographic plates. It was originally built and operated by the United Kingdom, starting from 1973, and was merged with the former Anglo-Australian Observatory in 1988. It has been wholly operated by Australia since the UK withdrew from the AAO in 2010 (though the name is unchanged). The UKST is a Schmidt camera, with a design based on the Oschin Schmidt Telescope. It is a survey telescope with a 6 ° by 6° field of view, originally imaged onto a 35 cm square glass photographic plate, and was the primary source of optical survey data in the southe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pictish Chronicle
The Pictish Chronicle is a name used to refer to a pseudo-historical account of the kings of the Picts beginning many thousand years before history was recorded in Pictavia and ending after Pictavia had been enveloped by Scotland. Version A There are actually several versions of the Pictish Chronicle. The so-called "A" text is probably the oldest, the fullest, and seems to have fewer errors than other versions. The original (albeit lost) manuscript seems to date from the early years of the reign of Kenneth II of Scotland (who ruled Scotland from 971 until 995) since he is the last king mentioned and the chronicler does not know the length of his reign. This chronicle survives only in the 14th century Poppleton Manuscript. It is in three parts: # ''Cronica de origine antiquorum Pictorum'', an account of the origins of the Picts, mostly from the Etymologies of Isidore of Seville. # A list of Pictish kings. # ''Chronicle of the Kings of Alba''. It is evident that the latter two s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of Ulster
The ''Annals of Ulster'' ( ga, Annála Uladh) are annals of medieval Ireland. The entries span the years from 431 AD to 1540 AD. The entries up to 1489 AD were compiled in the late 15th century by the scribe Ruaidhrí Ó Luinín, under his patron Cathal Óg Mac Maghnusa, on the island of ''Senadh-Mic-Maghnusa'', also known as ''Senad'' or Ballymacmanus Island (now known as Belle Isle, where Belle Isle Castle is located), near Lisbellaw, on Lough Erne in the kingdom of ''Fir Manach'' (Fermanagh). Later entries (up to AD 1540) were added by others. Entries up to the mid-6th century are retrospective, drawing on earlier annalistic and historical texts, while later entries were contemporary, based on recollection and oral history. T. M. Charles-Edwards has claimed that the main source for its records of the first millennium A.D. is a now lost Armagh continuation of the '' Chronicle of Ireland''. The Annals used the Irish language, with some entries in Latin. Becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from early medieval texts and Pictish stones. Their Latin name, , appears in written records from the 3rd to the 10th century. Early medieval sources report the existence of a distinct Pictish language, which today is believed to have been an Insular Celtic language, closely related to the Common Brittonic, Brittonic spoken by the Celtic Britons, Britons who lived to the south. Picts are assumed to have been the descendants of the Caledonians, Caledonii and other British Iron Age, Iron Age tribes that were mentioned by Roman historians or on the Ptolemy's world map, world map of Ptolemy. The Pictish kingdom, often called Pictland in modern sources, achieved a large degree of political unity in the late 7th and early 8th centuries through the expa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Language
Irish ( Standard Irish: ), also known as Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, which is a part of the Indo-European language family. Irish is indigenous to the island of Ireland and was the population's first language until the 19th century, when English gradually became dominant, particularly in the last decades of the century. Irish is still spoken as a first language in a small number of areas of certain counties such as Cork, Donegal, Galway, and Kerry, as well as smaller areas of counties Mayo, Meath, and Waterford. It is also spoken by a larger group of habitual but non-traditional speakers, mostly in urban areas where the majority are second-language speakers. Daily users in Ireland outside the education system number around 73,000 (1.5%), and the total number of persons (aged 3 and over) who claimed they could speak Irish in April 2016 was 1,761,420, representing 39.8% of respondents. For most of recorded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |