|
333
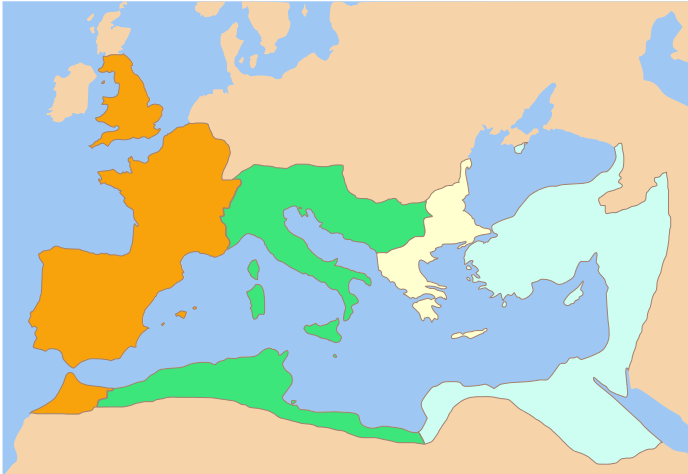
__NOTOC__ Year 333 ( CCCXXXIII) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Dalmatius and Zenophilus (or, less frequently, year 1086 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 333 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Flavius Dalmatius and Domitius Zenofilus are appointed consuls. * Emperor Constantine the Great pulls Roman troops out of Britain, and abandons work on Hadrian's Wall. * Calocaerus revolts against Constantine I and proclaims himself emperor. Flavius Dalmatius, responsible for the security of the eastern frontier, is sent to Cyprus to suppress the rebellion. * December 25 – Constantine I elevates his youngest son Constans to the rank of ''Caesar'' at Constantinople. China * Shi Hong succeeds his fathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table Of Chinese Monarchs
This list of Chinese monarchs includes rulers of China with various titles prior to the establishment of the Republic in 1912. From the Zhou dynasty until the Qin dynasty, rulers usually held the title "king" (). With the separation of China into different Warring States, this title had become so common that the unifier of China, the first Qin Emperor Qin Shihuang created a new title for himself, that of "emperor" (). The title of Emperor of China continued to be used for the remainder of China's imperial history, right down to the fall of the Qing dynasty in 1912. While many other monarchs existed in and around China throughout its history, this list covers only those with a quasi-legitimate claim to the majority of China, or those who have traditionally been named in king-lists. The following list of Chinese monarchs is in no way comprehensive. Chinese sovereigns were known by many different names, and how they should be identified is often confusing. Sometimes the same emperor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shi Hu
Shi Hu (; 295–349), courtesy name Jilong (季龍), formally Emperor Wu of (Later) Zhao ((後)趙武帝), was an emperor of the Jie-led Chinese Later Zhao dynasty. He was the founding emperor Shi Le's distant nephew, who took power in a coup after Shi Le's death from Shi Le's heir Shi Hong. Shi Hu was a talented general who rarely lost battles, and Shi Le relied on him heavily in his conquest of northern and central China. However, he was also exceedingly cruel in his military campaigns. After he became the ruler of Later Zhao under the title of "heavenly prince" (''Tian Wang''), he ruled the empire with a heavy hand, imposing heavy tax and labor burdens and spending much of his effort on constructing palaces and collecting concubines. His laws were cruel, and he applied them in a harsh manner, even killing two of his crown princes when they crossed him. While he was alive, his empire remained intact, but as soon as he died, his sons and adopted grandson Ran Min engaged i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shi Le
Shi Le (274–17 August 333), courtesy name Shilong, formally Emperor Ming of (Later) Zhao, was the founding emperor of the Jie-led Later Zhao dynasty of China. At a young age he was sold as a slave by Jin officials, but he later helped start a rebellion and eventually became a powerful general for the Xiongnu-led Han Zhao dynasty, conquering most of northern China in Han Zhao's name but holding the territory under his own control. In 319, after a dispute with the Han Zhao emperor Liu Yao, he broke away from Han Zhao and formed his own state, Later Zhao, and in 329 he captured Liu Yao and conquered Han Zhao, adding western China to his empire as well. Shi Le was known as a brilliant general, but was criticized by historians for excessive cruelty during his campaigns. He also put too much power in the hands of his ambitious and even more ferocious nephew Shi Hu who, after Shi Le's death, seized power from Shi Le's son Shi Hong. Early life Shi Le was born in 274—but was no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empress Liu (Shi Le's Wife)
Empress Liu (劉皇后, personal name unknown) (died 333) was an empress of the Chinese/ Jie state Later Zhao. Her husband was the founder of the empire, Shi Le. Life During the time that Shi Le was a Han Zhao general and later as the ruler of his own independent state, she was described as having both bravery and wisdom, often participating in Shi Le's military decisions and helpful to him. She was therefore compared to the Han Dynasty Empress Lü Zhi, who provided similar assistance her husband Emperor Gao of Han, but traditional historians praised Empress Liu for not being jealous as Empress Lü was. In 330, after Shi Le declared himself heavenly prince (''Tian Wang''), he created her princess, and later that year, after he declared himself emperor, she was created empress. In 333, after Shi Le's death, his nephew Shi Hu the Prince of Zhongshan quickly seized power in a coup d'état and controlled the government in the name of Shi Le's son and heir Shi Hong. Empress Dowager ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xu Guang (Later Zhao)
Xu Guang (died 333), courtesy name Jiwu, was a minister of Later Zhao during the Sixteen Kingdoms period. He was captured by Shi Le's general Wang Yang (王陽) and served as a servant, but after discovering his potential, he was recruited into Shi Le's army instead. Misconducts by Xu Guang angered Shi Le who had him and family imprisoned in 326. However, Xu Guang won Shi Le's favour back in 328, after his advice earned them a victory over Zhao's rival Han Zhao. As he became a prominent member of the administration, Xu Guang tried to reduce the power of Shi Le's nephew, Shi Hu but could not convince Shi Le to fully remove him. Shi Hu resented him for this, and after his coup in 333, Shi Hu had him and his ally Cheng Xia executed. Early life and background Xu Guang was from Dunqiu County in Dong Commandery. He grew up poor and his father Xu Cong (徐聰) only worked as a mere cow doctor. Despite his poor upbringing, he took a liking for studying and reciting literature. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheng Xia
Cheng Xia (died 333) was a Chinese minister of Later Zhao during the Sixteen Kingdoms period. His sister, Consort Cheng, was a wife of Shi Le and also the mother to the Crown Prince Shi Hong. Cheng Xia was thus given an important role in Shi Le's administration, although he was not very liked by Shi, as he lacked the qualities of Shi's favoured advisor Zhang Bin. Cheng Xia was a strong opposition to Shi Le's powerful nephew, Shi Hu, who he feared would usurp the throne once Shi Le passes. His attempts at diminishing Shi Hu's influence captured his scorn, and after he launched a coup in 333 following Shi Le's death, Shi Hu had Cheng Xia and his ally Xu Guang executed. Life Early career Cheng Xia joined Shi Le while the latter was raising an army in Hebei. His sister was Consort Cheng who married Shi Le and gave birth to Shi Le's soon-to-be heir, Shi Hong. Cheng Xia's first known positions in Shi Le's administration was the Prefect of Changle and Marshal of the Right. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geographically in Western Asia, its cultural ties and geopolitics are overwhelmingly Southern European. Cyprus is the third-largest and third-most populous island in the Mediterranean. It is located north of Egypt, east of Greece, south of Turkey, and west of Lebanon and Syria. Its capital and largest city is Nicosia. The northeast portion of the island is ''de facto'' governed by the self-declared Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus, which was established after the 1974 invasion and which is recognised as a country only by Turkey. The earliest known human activity on the island dates to around the 10th millennium BC. Archaeological remains include the well-preserved ruins from the Hellenistic period such as Salamis and Kourion, and Cypr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murong Hui
Murong Hui (慕容廆, 269 – 4 June 333), courtesy name Yiluo (弈洛), was an Xianbei chief, formally known as Duke Xiang of Liaodong, posthumously honored as Emperor Wuxuan (武宣皇帝). In the Book of Jin, Murong Hui was described as tall, physically strong and having a beautiful appearance. Murong Hui had initially been a Xianbei chief who fought Jin forces during the late reign of Emperor Wu of Jin, Jin's founding emperor, but he submitted as a Jin vassal in 289. Under constant attack by fellow Xianbei chief Duan Jie () of the Duan tribe, he humbly sought peace with the Duan and married one of Duan Jie's daughters. From this union came Murong Huang (in 297) and two of his younger brothers, Murong Ren () and Murong Zhao (). During Murong Hui's rule as tribal chief, the Jin Dynasty's central government was in constant turmoil and eventually collapsed due to infighting and agrarian rebellions, the strongest of which was the Xiongnu state Han Zhao. As a result, many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Later Zhao
The Later Zhao (; 319–351) was a dynasty of the Sixteen Kingdoms in northern China. It was founded by the Shi family of the Jie ethnicity. The Jie were most likely a Yeniseian people and spoke next to Chinese one of the Yeniseian languages.Vovin, Alexander. "Did the Xiongnu speak a Yeniseian language?". Central Asiatic Journal 44/1 (2000), pp. 87–104. The Later Zhao was the second in territorial size to the Former Qin dynasty that once unified northern China under Fu Jiān. When Later Zhao was founded by former Han general Shi Le, the capital was at Xiangguo (襄國, in modern Xingtai, Hebei), but in 335 Shi Hu moved the capital to Yecheng (鄴城, in modern Handan, Hebei), where it would remain for the rest of the state's history (except for Shi Zhi's brief attempt to revive the state at Xiangguo). Rulers of the Later Zhao Rulers family tree See also *Jie (ethnic group) * Wei–Jie war *List of past Chinese ethnic groups * Wu Hu * Buddhism in China *''Memoirs of Emine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constans
Flavius Julius Constans ( 323 – 350), sometimes called Constans I, was Roman emperor from 337 to 350. He held the imperial rank of ''caesar'' from 333, and was the youngest son of Constantine the Great. After his father's death, he was made ''augustus'' alongside his brothers in September 337. Constans was given the administration of the praetorian prefectures of Italy, Illyricum, and Africa. He defeated the Sarmatians in a campaign shortly afterwards. Quarrels over the sharing of power led to a civil war with his eldest brother and co-emperor Constantine II, who invaded Italy in 340 and was killed in battle with Constans's forces near Aquileia. Constans gained from him the praetorian prefecture of Gaul. Thereafter there were tensions with his remaining brother and co-''augustus'' Constantius II (), including over the exiled bishop Athanasius of Alexandria. In the following years he campaigned against the Franks, and in 343 he visited Roman Britain, the last legitimate emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shi Hong
Shi Hong (石弘) (313–334), courtesy name Daya (大雅), was briefly an emperor of the Jie-led Later Zhao dynasty of China after the death of his father Shi Le, Later Zhao's founder. Because after his cousin Shi Hu deposed him, he was created the Prince of Haiyang (海陽王), he is sometimes known by that title. Background Shi Hong was Shi Le's second son, by his concubine Consort Cheng. Unlike the militaristic Shi Le, Shi Hong was known for his literary studies and kindness. After his older brother Shi Xing (石興) died, Shi Le made him his heir apparent. In 330, after Shi Le declared himself first "Heavenly Prince" (''Tian Wang'') and then emperor, he created Shi Hong crown prince. Shi Le, concerned that his powerful nephew Shi Hu, a ferocious general, had too much power, began to transfer some of Shi Hu's power to Shi Hong, but this only served to aggravate Shi Hu, who already resented Shi Hong for being younger but yet crown prince, believing that, as the general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavius Dalmatius
:''This article deals with the censor. For the Caesar (335-337) Flavius Dalmatius, son of the censor, see Dalmatius. Flavius Dalmatius (died 337), also known as Dalmatius the Censor, was a censor (333), and a member of the Constantinian dynasty, which ruled over the Roman Empire at the beginning of the 4th century. Dalmatius was the son of Constantius Chlorus and Flavia Maximiana Theodora, and thus half-brother of the Emperor Constantine I. Dalmatius spent his youth in the Gallic Tolosa. It is probable that his two sons, Dalmatius and Hannibalianus, were born here. During the mid-320s, Flavius Dalmatius returned to Constantinople, to the court of his half-brother, and was appointed consul and censor in 333. In Antioch, Flavius was responsible for the security of the eastern borders of the realm. During this period, he examined the case of bishop Athanasius of Alexandria, an important opponent of Arianism, who was accused of murder. In 334, Flavius suppressed the revolt of Cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |