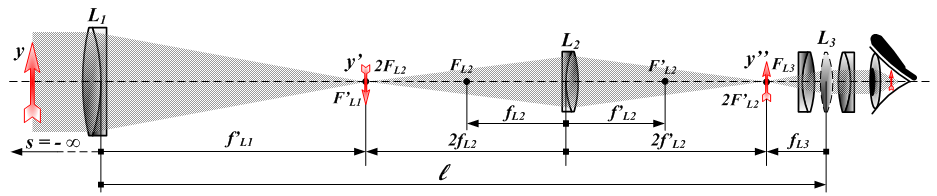
|
35mm Adapter
A depth-of-field adapter (often shortened to DOF adapter) is used to achieve shallow depth of field on a video camera whose fixed lens or interchangeable lens selection is limited or economically prohibitive at providing such effect. A DOF adapter could theoretically be used on a multitude of platforms, although it is most useful on prosumer digital camcorders where high resolution is a capability but the sensor size is still small enough to elicit use of the adapter. The term 35mm adapter is common, since most designs use a focusing screen the size of a 35mm film frame (24×36 mm) and interface with lenses designed for 35mm cameras. The use of adapters has decreased largely due to the video function available on newer DSLR cameras. How it works A DOF adapter focuses an image onto a translucent screen (similar to how one would look at a focused image through a system camera's viewfinder) located between an external lens and the camera's main lens. The camcorder is able to frame t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depth Of Field
The depth of field (DOF) is the distance between the nearest and the furthest objects that are in acceptably sharp focus in an image captured with a camera. Factors affecting depth of field For cameras that can only focus on one object distance at a time, depth of field is the distance between the nearest and the farthest objects that are in acceptably sharp focus. "Acceptably sharp focus" is defined using a property called the " circle of confusion". The depth of field can be determined by focal length, distance to subject, the acceptable circle of confusion size, and aperture. Limitations of depth of field can sometimes be overcome with various techniques and equipment. The approximate depth of field can be given by: : \text \approx \frac for a given circle of confusion (c), focal length (f), f-number (N), and distance to subject (u). As distance or the size of the acceptable circle of confusion increases, the depth of field increases; however, increasing the size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatic Aberration
In optics, chromatic aberration (CA), also called chromatic distortion and spherochromatism, is a failure of a lens to focus all colors to the same point. It is caused by dispersion: the refractive index of the lens elements varies with the wavelength of light. The refractive index of most transparent materials decreases with increasing wavelength. Since the focal length of a lens depends on the refractive index, this variation in refractive index affects focusing. Chromatic aberration manifests itself as "fringes" of color along boundaries that separate dark and bright parts of the image. Types There are two types of chromatic aberration: ''axial'' (''longitudinal''), and ''transverse'' (''lateral''). Axial aberration occurs when different wavelengths of light are focused at different distances from the lens (focus ''shift''). Longitudinal aberration is typical at long focal lengths. Transverse aberration occurs when different wavelengths are focused at different posit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filmizing
Film look (also known as filmizing or film-look) is a process in which video is altered in overall appearance to appear to have been shot on film stock. The process is usually electronic, although filmizing can sometimes occur as an unintentional by-product of some optical techniques, such as telerecording. The effect is the exact opposite of a process called VidFIRE. Differences between video and film * Frame rate: 24 frames per second for film, 30 or 40 frames per second for old SD video. Modern video cameras shoot 24 and up as well. * Shutter angle: Shorter (90° to 210°) for film, often ~350° for old video. Modern video cameras have adjustable electronic, or – in ''Arri's'' video cameras – mechanical shutters. * Dynamic range: film and video systems have widely varying limits to the luminance dynamic ranges that they can capture. Modern video cameras are much closer to the dynamic range of film, and their use is better understood by directors. * Field of view ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relay Lens
In optics, a relay lens is a lens or a group of lenses that receives the image from the objective lens and relays it to the eyepiece. Relay lenses are found in refracting telescopes, endoscopes, and periscopes to optically manipulate the light path, extend the length of the whole optical system, and usually serve the purpose of inverting the image. They may be made of one or more conventional lenses or achromatic doublets, or a long cylindrical gradient-index of refraction lens (a GRIN lens). Relay lenses operate by producing intermediate planes of focus. For example, in a SLR camera the zoom lens produces an image plane where the image sensor or photographic film would usually go. If you place another lens with focal length ''f'' at the distance 2''f'' from that image plane and then put an image sensor at 2''f'' beyond that lens, that lens will relay the first image to the second image with 1:1 magnification (see thin lens formula showing that with object distance s=2f f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses. Lenses are used in various imaging devices like telescopes, binoculars and cameras. They are also used as visual aids in glasses to correct defects of vision such as myopia and hypermetropia. History The word '' lens'' comes from '' lēns'', the Latin name of the lentil (a seed of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achromatic Doublet
An achromatic lens or achromat is a lens that is designed to limit the effects of chromatic and spherical aberration. Achromatic lenses are corrected to bring two wavelengths (typically red and blue) into focus on the same plane. The most common type of achromat is the achromatic doublet, which is composed of two individual lenses made from glasses with different amounts of dispersion. Typically, one element is a negative (concave) element made out of flint glass such as F2, which has relatively high dispersion, and the other is a positive (convex) element made of crown glass such as BK7, which has lower dispersion. The lens elements are mounted next to each other, often cemented together, and shaped so that the chromatic aberration of one is counterbalanced by that of the other. In the most common type (shown), the positive power of the crown lens element is not quite equalled by the negative power of the flint lens element. Together they form a weak positive lens that will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LCD Screen
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly but instead use a backlight or reflector to produce images in color or monochrome. LCDs are available to display arbitrary images (as in a general-purpose computer display) or fixed images with low information content, which can be displayed or hidden. For instance: preset words, digits, and seven-segment displays, as in a digital clock, are all good examples of devices with these displays. They use the same basic technology, except that arbitrary images are made from a matrix of small pixels, while other displays have larger elements. LCDs can either be normally on (positive) or off (negative), depending on the polarizer arrangement. For example, a character positive LCD with a backlight will have black lettering on a background that is the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Orientation
Page orientation is the way in which a rectangular page is oriented for normal viewing. The two most common types of orientation are ''portrait'' and ''landscape''. The term "portrait orientation" comes from visual art terminology and describes the dimensions used to capture a person's face and upper body in a picture; in such images, the height of the display area is greater than the width. The term "landscape orientation" also reflects visual art terminology, where pictures with more width than height are needed to fully capture the horizon within an artist's view. Besides describing the way documents can be viewed and edited, the concepts of "portrait" and "landscape" orientation can also be used to describe video and photography display options (where the concept of " aspect ratio" replaces that of "page orientation"). Many types of visual media use landscape mode, especially the 4:3 aspect ratio used for classic TV formatting, which is 4 units or pixels wide and 3 units ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barrel Distortion
In geometric optics, distortion is a deviation from rectilinear projection; a projection in which straight lines in a scene remain straight in an image. It is a form of aberration in optical systems, optical aberration. Radial distortion Although distortion can be irregular or follow many patterns, the most commonly encountered distortions are radially symmetric, or approximately so, arising from the symmetry of a photographic lens. These ''radial distortions'' can usually be classified as either ''barrel'' distortions or ''pincushion'' distortions. Mathematically, barrel and pincushion distortion are quadratic function, quadratic, meaning they increase as the ''square'' of distance from the center. In mustache distortion the quartic function, quartic (degree 4) term is significant: in the center, the degree 2 barrel distortion is dominant, while at the edge the degree 4 distortion in the pincushion direction dominates. Other distortions are in principle possible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Camera
A video camera is an optical instrument that captures videos (as opposed to a movie camera, which records images on film). Video cameras were initially developed for the television industry but have since become widely used for a variety of other purposes. Video cameras are used primarily in two modes. The first, characteristic of much early broadcasting, is live television, where the camera feeds real time images directly to a screen for immediate observation. A few cameras still serve live television production, but most live connections are for security, military/tactical, and industrial operations where surreptitious or remote viewing is required. In the second mode the images are recorded to a storage device for archiving or further processing; for many years, videotape was the primary format used for this purpose, but was gradually supplanted by optical disc, hard disk, and then flash memory. Recorded video is used in television production, and more often surveillance an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vignetting
In photography and optics, vignetting is a reduction of an image's brightness or saturation toward the periphery compared to the image center. The word '' vignette'', from the same root as '' vine'', originally referred to a decorative border in a book. Later, the word came to be used for a photographic portrait that is clear at the center and fades off toward the edges. A similar effect is visible in photographs of projected images or videos off a projection screen, resulting in a so-called "hotspot" effect. Vignetting is often an unintended and undesired effect caused by camera settings or lens limitations. However, it is sometimes deliberately introduced for creative effect, such as to draw attention to the center of the frame. A photographer may deliberately choose a lens that is known to produce vignetting to obtain the effect, or it may be introduced with the use of special filters or post-processing procedures. When using superzoom lenses, vignetting may occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)