|
353d Special Operations Group
The 353rd Special Operations Wing is an operational unit of the United States Air Force Special Operations Command, stationed at Kadena Air Base, Japan. The Wing's first predecessor was activated in 1944 as the 3rd Air Commando Group. The unit was assigned to Fifth Air Force in the Philippines in 1944 for operations with North American P-51 Mustangs, Douglas C-47 Skytrains, and Stinson L-5 Sentinels. It attacked Japanese airfields and installations in the Philippines, supported ground forces on Luzon, and provided escort for missions to Formosa and the China coast. It also made raids on airfields and railways on Formosa, and furnished cover for convoys. In addition, the group transported personnel, dropped supplies to ground troops and guerrilla forces, evacuated casualties from front-line strips, adjusted artillery fire, and flew courier and mail routes. The second predecessor of the Wing is the 553rd Reconnaissance Wing, which conducted electronic surveillance, particularly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Force Special Operations Command
Air Force Special Operations Command (AFSOC), headquartered at Hurlburt Field, Florida, is the special operations component of the United States Air Force. An Air Force major command (MAJCOM), AFSOC is also the U.S. Air Force component command to United States Special Operations Command (USSOCOM), a unified combatant command located at MacDill Air Force Base, Florida. AFSOC provides all Air Force Special Operations Forces (SOF) for worldwide deployment and assignment to regional unified combatant commands. Before 1983, Air Force special operations forces were primarily assigned to the Tactical Air Command (TAC) and were generally deployed under the control of U.S. Air Forces in Europe (USAFE) or, as had been the case during the Vietnam War, Pacific Air Forces (PACAF). Just as it had relinquished control of the C-130 theater airlift fleet to Military Airlift Command (MAC) in 1975, TAC relinquished control of Air Force SOF to MAC in December 1982. AFSOC was initially e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas C-47 Skytrain
The Douglas C-47 Skytrain or Dakota ( RAF, RAAF, RCAF, RNZAF, and SAAF designation) is a military transport aircraft developed from the civilian Douglas DC-3 airliner. It was used extensively by the Allies during World War II and remained in front-line service with various military operators for many years.Parker 2013, pp. 13, 35, 37, 39, 45-47. Design and development The C-47 differed from the civilian DC-3 by way of numerous modifications, including being fitted with a cargo door, hoist attachment and strengthened floor - along with a shortened tail cone for glider-towing shackles, and an astrodome in the cabin roof.Wilson, Stewart. ''Aircraft of WWII''. Fyshwick, ACT, Australia: Aerospace Publications Pty Ltd., 1998. . During World War II, the armed forces of many countries used the C-47 and modified DC-3s for the transport of troops, cargo, and wounded. The U.S. naval designation was R4D. More than 10,000 aircraft were produced in Long Beach and Santa Monica, Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
21st Special Operations Squadron
The 21st Special Operations Squadron is a unit within the 353rd Special Operations Group, United States Air Force based at Yokota Air Base, Japan. The unit has been activated and inactivated a number of times in its history. Prior to October 2007 it was with the 352d Special Operations Group, United States Air Force, United States European Command, and based at Royal Air Force base RAF Mildenhall in Suffolk, England. It can trace its roots back to the ''21st Pursuit Squadron'', which was activated on 1 February 1940 at Moffett Field, California. It took part in the combat in the Philippine Islands, from 8 December 1941. Being inactivated on 2 April 1946, later being activated as the ''21st Helicopter Squadron'', and inactivated again. Then activated for the Vietnam war on 30 June 1967, assigned to Tactical Air Command, later being redesignated the ''21st Special Operations Squadron'' on 1 August 1968. The squadron took part in both Operation Frequent Wind, and the Mayag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed MC-130
The Lockheed MC-130 is the basic designation for a family of special mission aircraft operated by the United States Air Force Special Operations Command (AFSOC), a wing of the Air Education and Training Command, and an AFSOC-gained wing of the Air Force Reserve Command. Based on the Lockheed C-130 Hercules transport, the MC-130s' missions are the infiltration, exfiltration, and resupply of special operations forces, and the air refueling of (primarily) special operations helicopter and tilt-rotor aircraft. The first of the variants, the MC-130E, was developed to support clandestine special operations missions during the Vietnam War. Eighteen were created by modifying C-130E transports, and four lost through attrition, but the remainder served more than four decades after their initial modification. An update, the MC-130H Combat Talon II, was developed in the 1980s from the C-130H and went into service in the 1990s. Four of the original 24 H-series aircraft have been lost i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Special Operations Squadron
The 1st Special Operations Squadron is part of the 353d Special Operations Group at Kadena Air Base, Japan. It operates the MC-130J Commando II, providing special operation capabilities. Air crews are trained in night low-level flying, using night vision goggles to deliver troops and equipment into denied areas during adverse weather conditions at night by airdrop or landing. History The 1st conducted gunnery testing and training from 1939 to 1942. It flew administrative airlift from 1949 to 1952 and 1953–1954. The 1st flew combat missions in Southeast Asia from 8 July 1963 – 7 November 1972 and 15 December 1972 – 28 January 1973. It also trained South Vietnamese air force pilots in counter-insurgency operations from, July 1963 – November 1972. It acquired the Combat Talon mission from the redesignated 90th Tactical Fighter Squadron on 15 December 1972. Three MC-130 Combat Talons from the 1st SOS led the Night One mission of Operation Eagle Claw, the hostage rescue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Pacific Command
United States Indo-Pacific Command (USINDOPACOM) is a unified combatant command of the United States Armed Forces responsible for the Indo-Pacific region. Formerly known as United States Pacific Command (USPACOM) since its inception in 1947, the command was renamed to U.S. Indo-Pacific Command in 2018, in recognition of the increasing connectivity between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It is the oldest and largest of the unified combatant commands. Its commander, the senior U.S. military officer in the Pacific, is responsible for military operations in an area that encompasses more than , or roughly 52 percent of the Earth's surface, stretching from the waters of the West Coast of the United States to the east coast maritime borderline waters of Pakistan at the meridian 66° longitude east of Greenwich and from the Arctic to the Antarctic. The commander reports to the President of the United States through the Secretary of Defense and is supported by service component and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Operations Command, Pacific
The Special Operations Command Pacific, known as SOCPAC, is a sub-unified command of the United States Department of Defense for special operations forces in the United States Indo-Pacific Command (USINDOPACOM) area of responsibility. History The Special Operations Center, Pacific Command was established 1 November 1965. Headquartered in Okinawa, the unit provided unconventional warfare task force support for operations in Southeast Asia. After these functions transferred to the Commander in Chief, Pacific Command (CINCPAC), the command dissolved on 1 July 1969. A special operations staff was established in the CINCPAC Operations Directorate on 15 May 1976, for planning and coordinating in-theater special operations. In October 1983, the U.S. Joint Chiefs of Staff established special operations commands in the Pacific and European Theaters. Special Operations Command, Pacific (SOCPAC) was activated on 1 November 1983 with only eighteen personnel. Six years later, on 28 December ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal Corps, the USAF was established as a separate branch of the United States Armed Forces in 1947 with the enactment of the National Security Act of 1947. It is the second youngest branch of the United States Armed Forces and the fourth in order of precedence. The United States Air Force articulates its core missions as air supremacy, global integrated intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance, rapid global mobility, global strike, and command and control. The United States Air Force is a military service branch organized within the Department of the Air Force, one of the three military departments of the Department of Defense. The Air Force through the Department of the Air Force is headed by the civilian Secretary of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and led to heavy, fairly immobile siege engines. As technology improved, lighter, more mobile field artillery cannons developed for battlefield use. This development continues today; modern self-propelled artillery vehicles are highly mobile weapons of great versatility generally providing the largest share of an army's total firepower. Originally, the word "artillery" referred to any group of soldiers primarily armed with some form of manufactured weapon or armor. Since the introduction of gunpowder and cannon, "artillery" has largely meant cannons, and in contemporary usage, usually refers to shell-firing guns, howitzers, and mortars (collectively called ''barrel artillery'', ''cannon artillery'', ''gun artillery'', or - a lay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
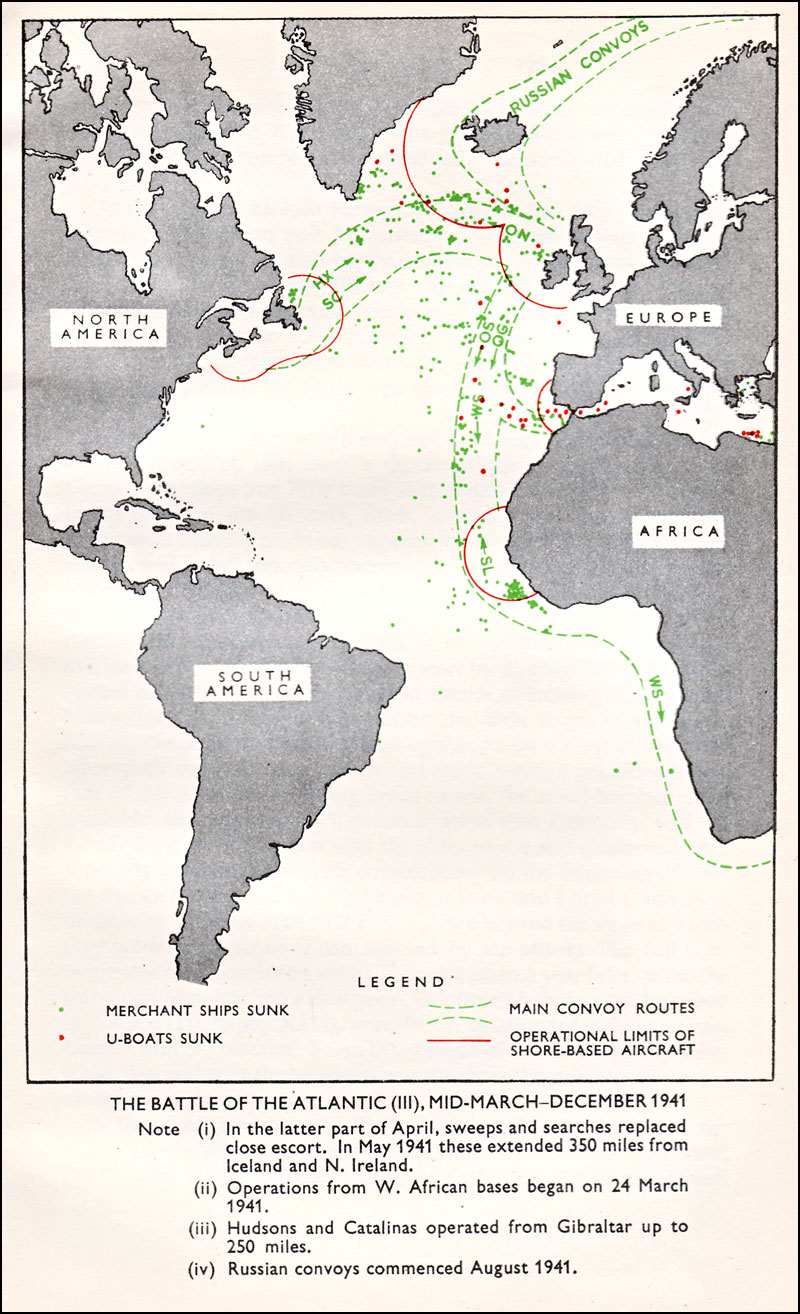
Military Convoy
A convoy is a group of vehicles, typically motor vehicles or ships, traveling together for mutual support and protection. Often, a convoy is organized with armed defensive support and can help maintain cohesion within a unit. It may also be used in a non-military sense, for example when driving through remote areas. Naval convoys Age of Sail Naval convoys have been in use for centuries, with examples of merchant ships traveling under naval protection dating to the 12th century. The use of organized naval convoys dates from when ships began to be separated into specialist classes and national navies were established. By the French Revolutionary Wars of the late 18th century, effective naval convoy tactics had been developed to ward off pirates and privateers. Some convoys contained several hundred merchant ships. The most enduring system of convoys were the Spanish treasure fleets, that sailed from the 1520s until 1790. When merchant ships sailed independently, a privateer coul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |