|
33d Air Rescue Squadron
The 33d Rescue Squadron is part of the 18th Wing at Kadena Air Base, Japan. It operates Sikorsky HH-60 Pave Hawk aircraft conducting search and rescue missions. The squadron was established when the 2d Air Rescue Squadron was expanded to Group status in 1952. Since that time, it has carried out air rescue duties with fixed wing aircraft until 1952, and thereafter with both fixed wing aircraft and helicopters. It has been stationed almost continuously in Okinawa since the 1950s. History Initial activation at Kadena Air Base In 1952 Air Rescue Service expanded its existing squadrons to groups. In this reorganization, the 2d Air Rescue Squadron became a group,Bailey, Carl E. (undated), Lineage and Honors History of the 2 Air Rescue Group, Air Force Historical Research Agency and the 33d Air Rescue Squadron was activated at Kadena Air Base, Okinawa with the mission of the former Flight C of the 2d Squadron. The squadron performed search and rescue and recovery missions from Kade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HH-60 Pave Hawk
The Sikorsky MH-60G/HH-60G Pave Hawk is a four-blade, twin-engine, medium-lift utility military helicopter manufactured by Sikorsky Aircraft. It is a derivative of the UH-60 Black Hawk and incorporates the US Air Force PAVE electronic systems program. The HH-60/MH-60 is a member of the Sikorsky S-70 family. The MH-60G Pave Hawk's primary mission is insertion and recovery of special operations personnel, while the HH-60G Pave Hawk's core mission is recovery of personnel under hostile conditions, including combat search and rescue. Both versions conduct day or night operations into hostile environments. Because of its versatility, the HH-60G may also perform peacetime operations such as civil search and rescue, emergency aeromedical evacuation (MEDEVAC), disaster relief, international aid and counter-drug activities. Design and development In 1981, the U.S. Air Force chose the UH-60A Black Hawk to replace its HH-3E Jolly Green Giant helicopters. After acquiring some UH-60s, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naha Air Base
, formally known as the , is an air base of the Japan Air Self-Defense Force formerly under control of the United States Air Force. It is located at Naha Airport on the Oroku Peninsula in Naha, Okinawa, Japan. History Imperial Period Naha Airfield was constructed in 1933 as Oroku Naval Air Base, an air base of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN). In 1936 control of the air base was transferred to the Japanese Ministry of Communications and formally renamed Naha Airfield. In 1942 control of the air base again reverted to the IJN, which reverted the name of the installation to Oroku Naval Air Base. The facility was captured by the United States during World War II in the Battle of Okinawa on 1 April 1945. US period After World War II the installation became a major United States Air Force (USAF) base under the operational control of Pacific Air Forces (PACAF), and was known as Naha Air Base (Naha AB). The installation became a joint military-civilian air field in 1954 with the resum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
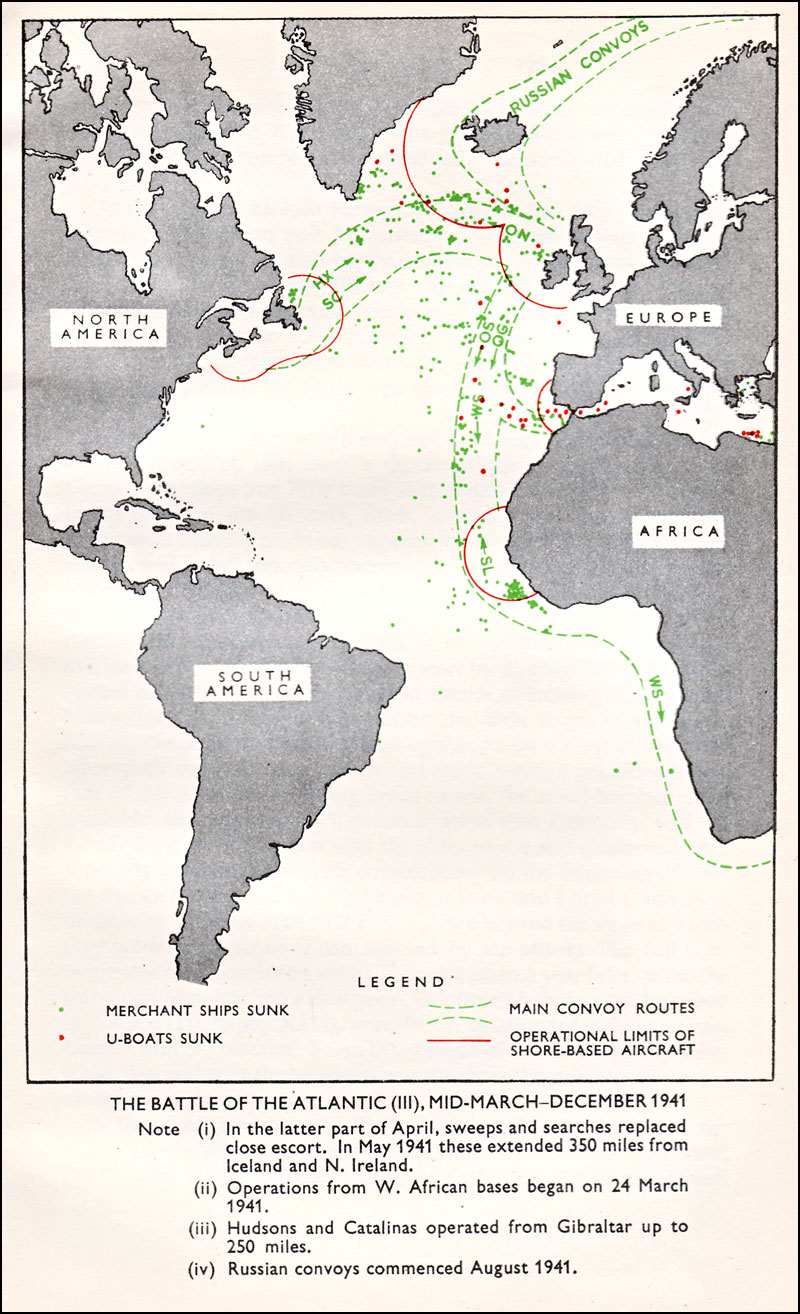
Convoy
A convoy is a group of vehicles, typically motor vehicles or ships, traveling together for mutual support and protection. Often, a convoy is organized with armed defensive support and can help maintain cohesion within a unit. It may also be used in a non-military sense, for example when driving through remote areas. Naval convoys Age of Sail Naval convoys have been in use for centuries, with examples of merchant ships traveling under naval protection dating to the 12th century. The use of organized naval convoys dates from when ships began to be separated into specialist classes and national navies were established. By the French Revolutionary Wars of the late 18th century, effective naval convoy tactics had been developed to ward off pirates and privateers. Some convoys contained several hundred merchant ships. The most enduring system of convoys were the Spanish treasure fleets, that sailed from the 1520s until 1790. When merchant ships sailed independently, a privateer cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forward Operating Base Frontenac
Forward is a relative direction, the opposite of backward. Forward may also refer to: People *Forward (surname) Sports * Forward (association football) * Forward (basketball), including: ** Point forward ** Power forward (basketball) ** Small forward * Forward (ice hockey) ** Power forward (ice hockey) * In rugby football: ** Forwards (rugby league), in rugby league football ** Forwards (rugby union), in rugby union football * Forward Sports, a Pakistan sportswear brand * BK Forward, a Swedish club for association football and bandy Politics * Avante (political party) (Portuguese for ''forward''), a political party in Brazil * Forward (Belgium), a political party in Belgium * Forward (Denmark), a political party in Denmark * Forward (Greenland), a political party in Greenland * Forward Party (United States), a centrist American political party * Kadima (Hebrew for ''forward''), a political party in Israel * La République En Marche! (sometimes translated as ''Forward!''), a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Evacuation
Medical evacuation, often shortened to medevac or medivac, is the timely and efficient movement and en route care provided by medical personnel to wounded being evacuated from a battlefield, to injured patients being evacuated from the scene of an accident to receiving medical facilities, or to patients at a rural hospital requiring urgent care at a better-equipped facility using medically equipped air ambulances, especially helicopters. Examples include civilian EMS vehicles, civilian aeromedical helicopter services, and military air ambulances. This term also covers the transfer of patients from the battlefield to a treatment facility or from one treatment facility to another by medical personnel, such as from a local hospital to a trauma center. History The first medical transport by air was recorded in Serbia in the autumn of 1915 during First World War. One of the ill soldiers in that first medical transport was Milan Rastislav Štefánik, a Slovak pilot-volunteer who was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kandahar Air Base
Ahmad Shah Baba International Airport, also referred to as Kandahar International Airport ( ps, د کندهار نړيوال هوايي ډګر) and by some military officials as Kandahar Airfield, KAF) , is located about south-east of the city Kandahar in Afghanistan. It serves as the nation's second main international airport and as one of the largest main operating bases, capable of housing up to 250 aircraft of different sizes. The current head of the airport is Maulvi Fathullah Mansour. The airport was designed and built by the United States in the early 1960s. It was occupied by the Soviet Union, Soviets during the 1980s Soviet–Afghan War. Following their withdrawal the airport remained in control of Mohammad Najibullah, Najibullah's Democratic Republic of Afghanistan, government until he stepped down in 1992. Thereafter, local warlords and the Taliban took control of the airport until the United States invasion of Afghanistan, American invasion in late 2001. It was also th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
129th Rescue Squadron
The 129th Rescue Squadron (129 RQS) is a unit of the California Air National Guard 129th Rescue Wing located at Moffett Federal Airfield, Mountain View, California. The 129th is equipped with the HH-60G Pave Hawk helicopter. If activated to federal service, the 129 RQS is gained within the United States Air Force by the Air Combat Command (ACC). Overview The primary mission is to prepare for wartime taskings as specified by applicable gaining commands. The peacetime mission is under the control of the Governor of California. Upon mobilization, primary specified mission is combat search and rescue (CSAR). When directed by the California State Office of Emergency Services (OES) and/or the Department of Defense (DoD), the mission is to provide disaster relief support as required. This includes search and rescue (SAR) assistance to civil authorities, including International Civil Aeronautics Organization (ICAO) signatories, and foreign governments. Federal Mission (United States Air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combat Search And Rescue
Combat search and rescue (CSAR) are search and rescue operations that are carried out during war that are within or near combat zones. A CSAR mission may be carried out by a task force of helicopters, ground-attack aircraft, aerial refueling tankers and an airborne command post. The USAF HC-130, which was introduced in 1965, has served in the latter two roles. History The First World War was the background for the development of early combat search and rescue doctrine, especially in the more fluid theaters of war in the Balkans and the Middle East. In the opening fluid stages of the First World War the Royal Navy Air Service Armoured Car Section was formed with armed and armoured touring cars to find and pick up aircrew who had been forced down. When trench warfare made this impossible the cars were transferred to other theatres, most notably the Middle East. In 1915, during the First World War, Squadron Commander Richard Bell-Davies of the British Royal Naval Air Ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikorsky HH-60G Pave Hawk
The Sikorsky MH-60G/HH-60G Pave Hawk is a four-blade, twin-engine, medium-lift utility military helicopter manufactured by Sikorsky Aircraft. It is a derivative of the UH-60 Black Hawk and incorporates the US Air Force PAVE electronic systems program. The HH-60/MH-60 is a member of the Sikorsky S-70 family. The MH-60G Pave Hawk's primary mission is insertion and recovery of special operations personnel, while the HH-60G Pave Hawk's core mission is recovery of personnel under hostile conditions, including combat search and rescue. Both versions conduct day or night operations into hostile environments. Because of its versatility, the HH-60G may also perform peacetime operations such as civil search and rescue, emergency aeromedical evacuation (MEDEVAC), disaster relief, international aid and counter-drug activities. Design and development In 1981, the U.S. Air Force chose the UH-60A Black Hawk to replace its HH-3E Jolly Green Giant helicopters. After acquiring some UH-60s, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Aeronautic Association
The National Aeronautic Association of the United States (NAA) is a non-profit 501(c)(3) organization and a founding member of the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI). Founded in 1905, it is the oldest national aviation club in the United States and one of the oldest in the world, it serves as the “Aeroclub of the United States” and, by its Mission Statement it is "…dedicated to the advancement of the art, sport and science of aviation in the United States.” The NAA is headquartered at the Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport, in Washington, D.C. History The NAA was founded in 1905 as the Aero Club of America (ACA), by members of the Automobile Club of America. From its inception, ACA’s goal was to promote aviation in any way possible, as both a sport and a commercial endeavor. In 1922 it was incorporated as the Aero Club’s successor, and continued the original group’s mission of promoting aviation. The NAA has been steeply involved with the growt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
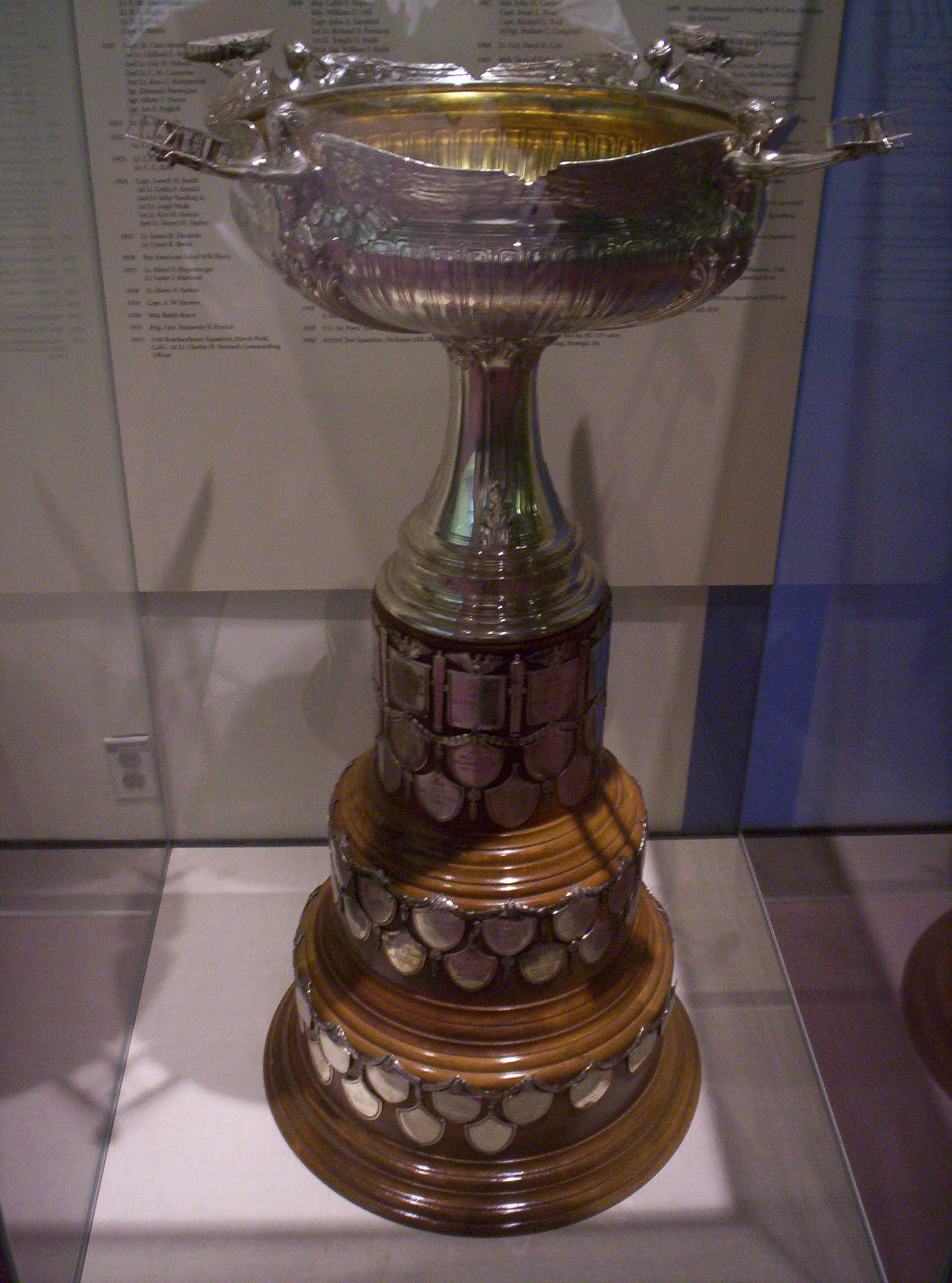
MacKay Trophy
The Mackay Trophy is awarded yearly by the United States Air Force for the "most meritorious flight of the year" by an Air Force person, persons, or organization. The trophy is housed in the Smithsonian Institution's National Air and Space Museum. The award is administered by the U.S. National Aeronautic Association. The award was established on 27 January 1911 by Clarence Mackay, who was then head of the Postal Telegraph-Cable Company and the Commercial Cable Company. Originally, aviators could compete for the trophy annually under rules made each year or the War Department could award the trophy for the most meritorious flight of the year. Awardees The following is a list of awardees: 1910s 1920s 1930s 1940s ...
|
44th Fighter Squadron
The 44th Fighter Squadron is a unit of the United States Air Force, part of the 18th Wing at Kadena Air Base in Okinawa, Japan. The 44th Pursuit Squadron was activated on 1 January 1941 and assigned to the 18th Pursuit Group. The 44th Fighter Squadron is equipped with the F-15C/D Eagle. Mission The 44 FS operates the F-15C Eagle aircraft conducting air superiority missions. History World War II The 44th Flew patrols over the Pacific from Hawaii from 7 December 1941 – October 1942. It went on to fly combat missions in the South and Southwest Pacific from 21 December 1942 – 15 August 1945. Vietnam War It again flew combat missions in Southeast Asia from 18 December 1964 – 25 February 1965, 21 April – 22 June 1965, 19 – 29 October 1965, and 25 April 1967 – 6 October 1970. The squadron was unmanned from 31 December 1966 – 24 April 1967 and November 1970–15 May 1971. Japan It has flown air defense over Okinawa and Japan since 1971. On 17 January 2006 an F-15C of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)




