|
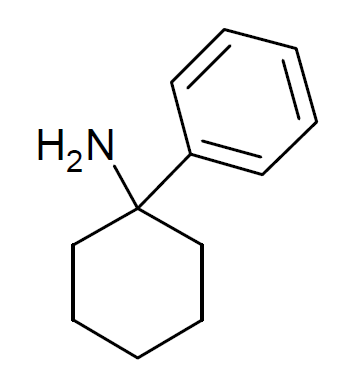
3-Fluoro-PCP
3-Fluoro-PCP (3'-F-PCP, 3F-PCP) is a recreational designer drug from the arylcyclohexylamine family, with dissociative effects. It was first identified in Slovenia in October 2020, and was made illegal in Hungary in April 2021. See also * 3-Fluorodeschloroketamine * 3-Chloro-PCP * 3-Methyl-PCP * 3-MeO-PCP * 4-Keto-PCP * Fluorexetamine Fluorexetamine (3'-Fluoro-2-oxo-PCE, FXE) is a recreational designer drug from the arylcyclohexylamine family, with dissociative effects. Effects are slightly more stimulating than regular ketamine. Still produces analgesic effects with stimulat ... References Arylcyclohexylamines Designer drugs Dissociative drugs 4-Piperidinyl compounds Fluoroarenes {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arylcyclohexylamine
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs. History Phencyclidine (PCP) is believed to be the first arylcyclohexylamine with recognized anesthetic properties, but several arylcyclohexylamines were described before PCP in the scientific literature, beginning with PCA (1-phenylcyclohexan-1-amine) the synthesis of which was first published in 1907. PCE was reported in 1953 and PCMo (4-(1-phenyl-cyclohexyl)-morpholine see chart below for figure) in 1954, with PCMo described as a potent sedative. Arylcyclohexylamine anesthetics were intensively investigated at Parke-Davis, beginning with the 1956 synthesis of phencyclidine and later the related compound ketamine. The 1970s saw the debut of these compounds, especially PCP and its analogues, as illicitly used recreational drugs due to their dissociative hallucinogenic and euphoriant effects. Since that time, the class has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-Fluorodeschloroketamine
3-Fluorodeschloroketamine (3F-DCK, 3-FDCK, FXM) is a recreational designer drug related to ketamine. It is from the arylcyclohexylamine family and has dissociative effects. It was made illegal in Finland in August 2019. See also * 2-Fluorodeschloroketamine * 3-Fluoro-PCP * Deschloroketamine * Fluorexetamine * Methoxmetamine Methoxmetamine (also known as 3-MeO-2'-Oxo-PCM, MXM and MMXE) is a dissociative anesthetic of the arylcyclohexylamine class that is closely related to methoxetamine and methoxyketamine, and has been sold online as a designer drug. Reference ... References Arylcyclohexylamines Designer drugs Dissociative drugs Fluoroarenes Secondary amines {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-Keto-PCP
4-Keto-PCP is a recreational designer drug from the arylcyclohexylamine family, with dissociative effects. It has potency in between that of ketamine and phencyclidine but with somewhat more sedating effects in animal studies. See also * 3-HO-PCP * 3-Fluoro-PCP * Bromadol * Dimetamine * Methoxetamine Methoxetamine, abbreviated as MXE, is a dissociative hallucinogen that has been sold as a designer drug. It differs from many dissociatives such as ketamine and phencyclidine (PCP) that were developed as pharmaceutical drugs for use as general ... References Arylcyclohexylamines Designer drugs Dissociative drugs 1-Piperidinyl compounds {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorexetamine
Fluorexetamine (3'-Fluoro-2-oxo-PCE, FXE) is a recreational designer drug from the arylcyclohexylamine family, with dissociative effects. Effects are slightly more stimulating than regular ketamine. Still produces analgesic effects with stimulating dissociative effects. Has reportedly been sold over the internet since around 2017, though has remained relatively uncommon. See also * 3-Fluoro-PCP * 2-Fluorodeschloroketamine * 3-Fluorodeschloroketamine * Deoxymethoxetamine * Hydroxetamine * Methoxetamine * MXiPr MXiPr (Methoxisopropamine, Isopropyloxetamine, Isopropyxetamine') is a recreational designer drug with dissociative effects. It is an arylcyclohexylamine derivative, related to drugs such as ketamine and methoxetamine. It was first identified ... References Arylcyclohexylamines Designer drugs Dissociative drugs Fluoroarenes {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arylcyclohexylamines
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs. History Phencyclidine (PCP) is believed to be the first arylcyclohexylamine with recognized anesthetic properties, but several arylcyclohexylamines were described before PCP in the scientific literature, beginning with PCA (1-phenylcyclohexan-1-amine) the synthesis of which was first published in 1907. PCE was reported in 1953 and PCMo (4-(1-phenyl-cyclohexyl)-morpholine see chart below for figure) in 1954, with PCMo described as a potent sedative. Arylcyclohexylamine anesthetics were intensively investigated at Parke-Davis, beginning with the 1956 synthesis of phencyclidine and later the related compound ketamine. The 1970s saw the debut of these compounds, especially PCP and its analogues, as illicitly used recreational drugs due to their dissociative hallucinogenic and euphoriant effects. Since that time, the class has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Designer Drug
A designer drug is a structural or functional analog of a controlled substance that has been designed to mimic the pharmacological effects of the original drug, while avoiding classification as illegal and/or detection in standard drug tests. Designer drugs include psychoactive substances that have been designated by the European Union as new psychoactive substances (NPS) as well as analogs of performance-enhancing drugs such as designer steroids. Some of these were originally synthesized by academic or industrial researchers in an effort to discover more potent derivatives with fewer side effects, and shorter duration (and possibly also because it is easier to apply for patents for new molecules) and were later co-opted for recreational use. Other designer drugs were prepared for the first time in clandestine laboratories. Because the efficacy and safety of these substances have not been thoroughly evaluated in animal and human trials, the use of some of these drugs may result i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissociative
Dissociatives, colloquially dissos, are a subclass of hallucinogens which distort perception of sight and sound and produce feelings of detachment – dissociation – from the environment and/or self. Although many kinds of drugs are capable of such action, dissociatives are unique in that they do so in such a way that they produce hallucinogenic effects, which may include dissociation, a general decrease in sensory experience, hallucinations, dream-like states or anesthesia. Some of these substances, which are nonselective in action and affect the dopamine and/or opioid systems, may be capable of inducing euphoria or symptoms which are more akin to the effects of certain “hard drugs” or common drugs of abuse. This is likely why dissociatives are considered to be addictive with a fair to moderate potential for abuse, unlike psychedelics. Despite some dissociatives, such as phencyclidine (PCP) possessing stimulating properties, most dissociatives seem to have a general depre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-Chloro-PCP
3-Chloro-PCP (3'-Cl-PCP) is a recreational designer drug from the arylcyclohexylamine family, with dissociative effects. It has comparable potency to phencyclidine but with a slightly different effects profile, being somewhat more potent as an NMDA antagonist but around the same potency as a dopamine reuptake inhibitor. It was first identified in Slovenia in December 2020, and was made illegal in Hungary in April 2021. See also * 3-F-PCP * 3-Me-PCP * 3-MeO-PCP * 4-Keto-PCP 4-Keto-PCP is a recreational designer drug from the arylcyclohexylamine family, with dissociative effects. It has potency in between that of ketamine and phencyclidine but with somewhat more sedating effects in animal studies. See also * 3-HO ... References Arylcyclohexylamines Designer drugs Dissociative drugs Chloroarenes 1-Piperidinyl compounds {{pharm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-Methyl-PCP
3-Methyl-PCP (3'-Methyl-PCP, ''meta''-Methyl-PCP, 3-Me-PCP) is a recreational designer drug with dissociative effects. It is an arylcyclohexylamine derivative, related to drugs such as 3'-MeO-PCP and 3'-Me-PCPy. It was first synthesised in the 1960s, but was only identified on the illicit market in Hungary in September 2020, and was made illegal in Hungary in April 2021. See also * 3-Cl-PCP * 3-HO-PCP * 3-F-PCP * Deoxymethoxetamine * MXiPr MXiPr (Methoxisopropamine, Isopropyloxetamine, Isopropyxetamine') is a recreational designer drug with dissociative effects. It is an arylcyclohexylamine derivative, related to drugs such as ketamine and methoxetamine. It was first identified ... References Arylcyclohexylamines Designer drugs Dissociative drugs O-methylated phenols Substances discovered in the 1960s {{hallucinogen-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-MeO-PCP
3-Methoxyphencyclidine (3-MeO-PCP) is a dissociative hallucinogen of the arylcyclohexylamine class related to phencyclidine (PCP) which has been sold online as a designer drug. It acts mainly as an NMDA receptor antagonist, though it has also been found to interact with the sigma σ receptor and the serotonin transporter. The drug does not possess any opioid activity nor does it act as a dopamine reuptake inhibitor. Pharmacology 3-MeO-PCP has a K of 20 nM for the dizocilpine (MK-801) site of the NMDA receptor, 216 nM for the serotonin transporter (SERT), and 42 nM for the sigma σ receptor. It does not bind to the norepinephrine or dopamine transporter nor to the sigma σ receptor (Ki >10,000 nM). Based on its structural similarity to 3-hydroxy-PCP (3-HO-PCP), which uniquely among arylcyclohexylamines has high affinity for the μ-opioid receptor in addition to the NMDA receptor, it was initially expected that 3-MeO-PCP would have opioid activity. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Designer Drugs
A designer drug is a structural or functional analog of a controlled substance that has been designed to mimic the pharmacological effects of the original drug, while avoiding classification as illegal and/or detection in standard drug tests. Designer drugs include psychoactive substances that have been designated by the European Union as new psychoactive substances (NPS) as well as analogs of performance-enhancing drugs such as designer steroids. Some of these were originally synthesized by academic or industrial researchers in an effort to discover more potent derivatives with fewer side effects, and shorter duration (and possibly also because it is easier to apply for patents for new molecules) and were later co-opted for recreational use. Other designer drugs were prepared for the first time in clandestine laboratories. Because the efficacy and safety of these substances have not been thoroughly evaluated in animal and human trials, the use of some of these drugs may result i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissociative Drugs
Dissociatives, colloquially dissos, are a subclass of hallucinogens which distort perception of sight and sound and produce feelings of detachment – dissociation – from the environment and/or self. Although many kinds of drugs are capable of such action, dissociatives are unique in that they do so in such a way that they produce hallucinogenic effects, which may include dissociation, a general decrease in sensory experience, hallucinations, dream-like states or anesthesia. Some of these substances, which are nonselective in action and affect the dopamine and/or opioid systems, may be capable of inducing euphoria or symptoms which are more akin to the effects of certain “hard drugs” or common drugs of abuse. This is likely why dissociatives are considered to be addictive with a fair to moderate potential for abuse, unlike psychedelics. Despite some dissociatives, such as phencyclidine (PCP) possessing stimulating properties, most dissociatives seem to have a general depre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |