|
2 Kings 9
2 Kings 9 is the ninth chapter of the second part of the Books of Kings in the Hebrew Bible or the Second Book of Kings in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. The book is a compilation of various annals recording the acts of the kings of Israel and Judah by a Deuteronomic compiler in the seventh century BCE, with a supplement added in the sixth century BCE. This chapter records Jehu's anointing as the next king of Israel and his assassinations of Jehoram the king of Israel, Ahaziah the king of Judah and Jezebel the queen mother of Israel. The narrative is a part of a major section 2 Kings 9:1–15:12 covering the period of Jehu's dynasty. Text This chapter was originally written in the Hebrew language and since the 16th century is divided into 37 verses. Textual witnesses Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter in Hebrew are of the Masoretic Text tradition, which includes the Codex Cairensis (895), Aleppo Codex (10th century), and Codex Leningradensis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Books Of Kings
The Book of Kings (, '' Sēfer Məlāḵīm'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Kings) in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. It concludes the Deuteronomistic history, a history of Israel also including the books of Joshua, Judges and Samuel. Biblical commentators believe the Books of Kings were written to provide a theological explanation for the destruction of the Kingdom of Judah by Babylon in c. 586 BCE and to provide a foundation for a return from Babylonian exile.Sweeney, p1/ref> The two books of Kings present a history of ancient Israel and Judah, from the death of King David to the release of Jehoiachin from imprisonment in Babylon—a period of some 400 years (). Scholars tend to treat the books as consisting of a first edition from the late 7th century BCE and of a second and final edition from the mid-6th century BCE.Fretheim, p. 7 Contents The Jerusalem Bible divides the two Books of Kings into eight sections: *1 Kings 1:1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codex Alexandrinus
The Codex Alexandrinus (London, British Library, Royal MS 1. D. V-VIII), designated by the siglum A or 02 (in the Gregory-Aland numbering of New Testament manuscripts), δ 4 (in the von Soden numbering of New Testament manuscripts), is a manuscript of the Greek Bible,The Greek Bible in this context refers to the Bible used by Greek-speaking Christians who lived in Egypt and elsewhere during the early history of Christianity. This Bible contained both the Old and New Testaments in Koine Greek. written on parchment. Using the study of comparative writing styles (palaeography), it has been dated to the fifth century. It contains the majority of the Greek Old Testament and the Greek New Testament. It is one of the four Great uncial codices (these being manuscripts which originally contained the whole of both the Old and New Testaments). Along with Codex Sinaiticus and Vaticanus, it is one of the earliest and most complete manuscripts of the Bible. It derives its name from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
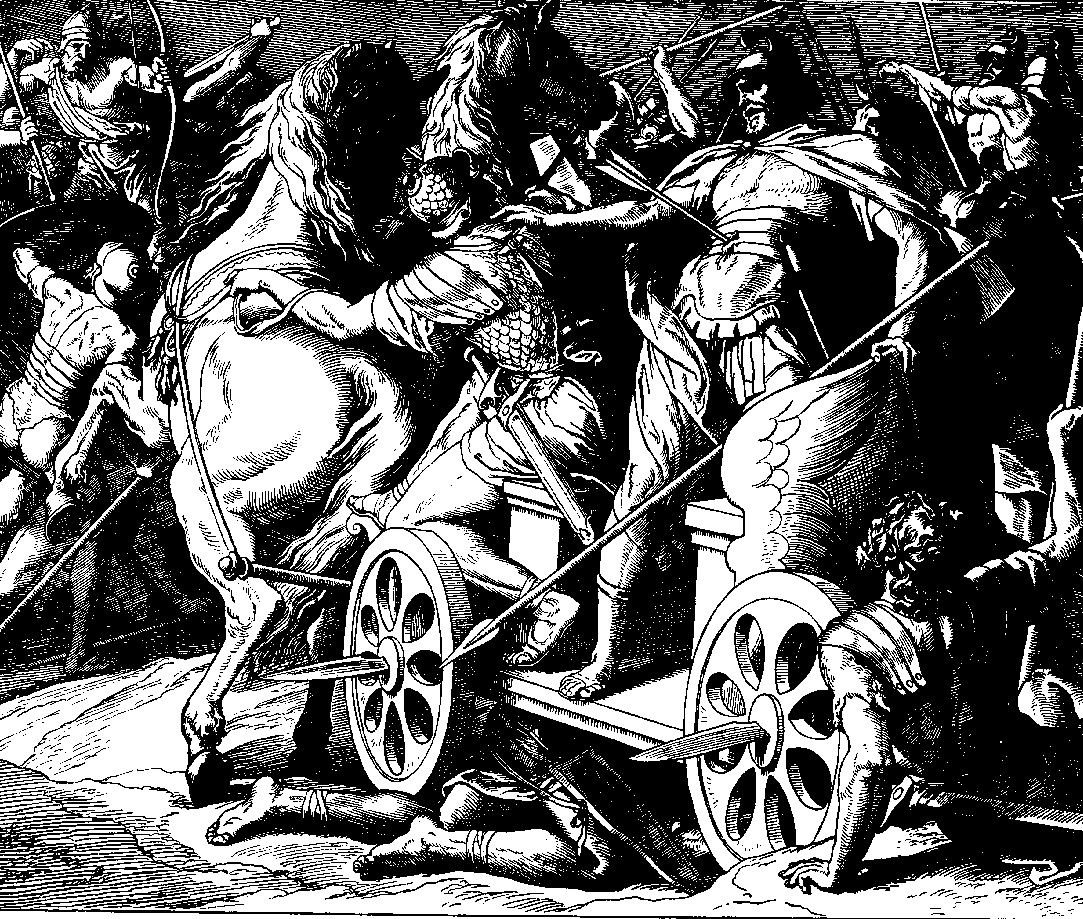
2 Kings 10
2 Kings 10 is the tenth chapter of the second part of the Books of Kings in the Hebrew Bible or the Second Book of Kings in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. The book is a compilation of various annals recording the acts of the kings of Israel and Judah by a Deuteronomic compiler in the seventh century BCE, with a supplement added in the sixth century BCE. This chapter records Jehu's massacres of the sons of Ahab, the kinsmen of Ahaziah the king of Judah and the Baal worshippers linked to Jezebel. The narrative is a part of a major section 2 Kings 9:1–15:12 covering the period of Jehu's dynasty. Text This chapter was originally written in the Hebrew language and since the 16th century is divided into 36 verses. Textual witnesses Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter in Hebrew are of the Masoretic Text tradition, which includes the Codex Cairensis (895), Aleppo Codex (10th century), and Codex Leningradensis (1008). Fragments containing parts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. is a city in Western Asia. Situated on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea, it is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world and is considered to be a holy city for the three major Abrahamic religions: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Both Israelis and Palestinians claim Jerusalem as their Capital city, capital, as Israel maintains its primary governmental institutions there and the State of Palestine ultimately foresees it as its seat of power. Because of this dispute, Status of Jerusalem, neither claim is widely recognized internationally. Throughout History of Jerusalem, its long history, Jerusalem has been destroyed at least twice, Sie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tel Megiddo
Tel Megiddo ( he, תל מגידו; ar, مجیدو, Tell el- Mutesellim, ''lit.'' "Mound of the Governor"; gr, Μεγιδδώ, Megiddo) is the site of the ancient city of Megiddo, the remains of which form a tell (archaeological mound), situated in northern Israel near Kibbutz Megiddo, about 30 km south-east of Haifa. Megiddo is known for its historical, geographical, and theological importance, especially under its Greek name Armageddon. During the Bronze Age, Megiddo was an important Canaanite city-state and during the Iron Age, a royal city in the Kingdom of Israel. Megiddo drew much of its importance from its strategic location at the northern end of the Wadi Ara defile, which acts as a pass through the Carmel Ridge, and from its position overlooking the rich Jezreel Valley from the west. Excavations have unearthed 20 strata of ruins since the Neolithic phase, indicating a long period of settlement. The site is now protected as Megiddo National Park and is a Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jezreel (city)
Tel Jezreel ( he, יִזְרְעֶאל ''Yīzrə‘e’l'', "God will sow") is an archaeological site in the eastern Jezreel Valley in northern Israel. The city of Jezreel served as a main fortress of the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Kingdom of Israel under king Ahab in the 9th century BCE. Biblical references Prior to the division of the United Kingdom of Israel, the city was the hometown of Ahinoam, second wife of King David, Michal, Saul's daughter, being the first, Ahinoam being his second, and Abigail, widow of Nabal, being his third (). According to the First Books of Kings, Book of Kings, the royal palace of Ahab, King Ahab, "one of the most famous of the royal residences of the kings of Israel", was in Jezreel, adjacent to the vineyard of Naboth (). Ahab's capital remained in Samaria (ancient city), Samaria. According to , following the prophet Elijah's victory over the prophets of Baal, Ba'al at Mount Carmel, Elijah instructs Ahab to return home to Jezreel, where he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramoth-Gilead
Ramoth-Gilead ( he, רָמֹת גִּלְעָד, meaning "Heights of Gilead"), was a Levitical city and city of refuge east of the Jordan River in the Hebrew Bible, also called "Ramoth in Gilead" (; ; ) or "Ramoth Galaad" in the Douay–Rheims Bible. It was located in the tribal territorial allotment of the tribe of Gad. Biblical events According to (), Ramothgilead was the base of Ben-Geber, one of King Solomon's regional governors. He was responsible for ("to him belonged") the towns of Jair the son of Manasseh, in Gilead and the region of Argob in Bashan: sixty large cities with walls and bronze gate-bars. It appears to have been lost to Syria (Aram-Damascus) during the battles between the northern kingdom of Israel and Syria, as Ahab, King of Israel, proposed to go to battle to win it back. After consulting prophets about the prospects of success, Ahab went to fight for Ramoth in Gilead, aided by Jehoshaphat, King of Judah. During the battle, Ahab was wounded by an arrow. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |