|
2867 Šteins
2867 Šteins (provisional designation ) is an irregular, diamond-shaped background asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately in diameter. It was discovered on 4 November 1969 by Soviet astronomer Nikolai Chernykh at the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory in Nauchnij on the Crimean peninsula. In September 2008, ESA's spacecraft ''Rosetta'' flew by ''Šteins'', making it one of few minor planets ever visited by a spacecraft. The bright E-type asteroid features 23 named craters and has a rotation period of 6.05 hours. It was named for Soviet Latvian astronomer Kārlis Šteins. Orbit and classification ''Šteins'' is a non-family asteroid from the main belt's background population. It orbits the Sun in the inner asteroid belt at a distance of 2.0–2.7 AU once every 3 years and 8 months (1,327 days; semi-major axis of 2.36 AU). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.15 and an inclination of 10 ° with respect to the ecliptic. The body's observa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
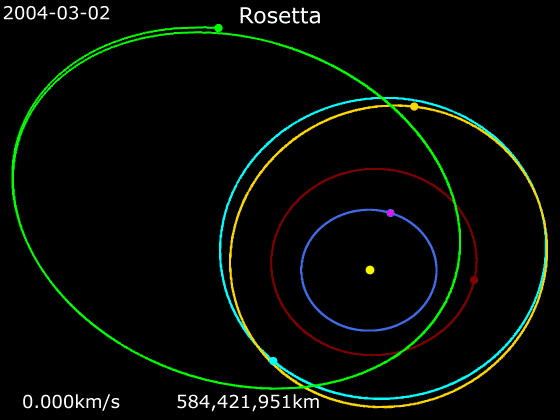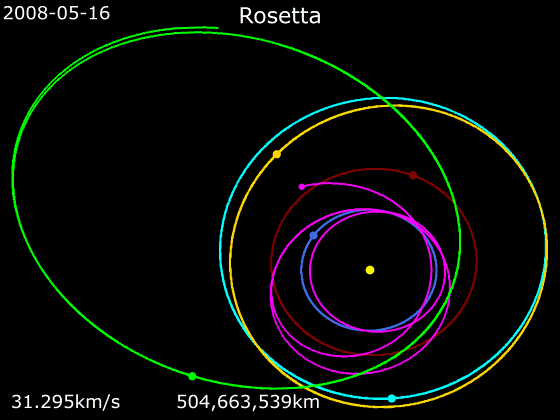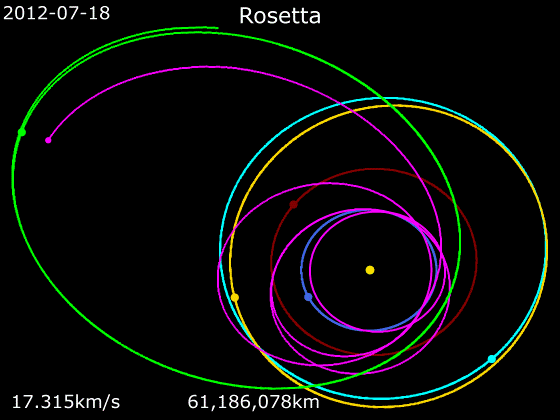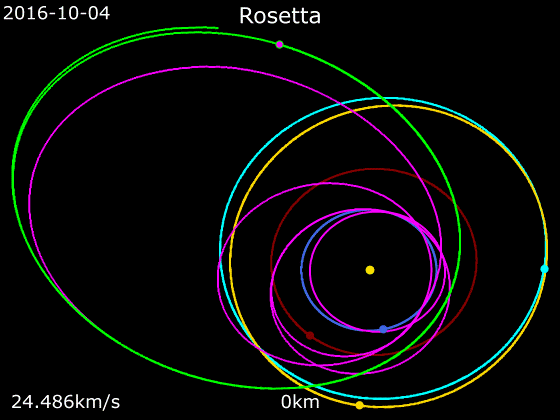
Rosetta (spacecraft)
''Rosetta'' was a space probe built by the European Space Agency launched on 2 March 2004. Along with ''Philae (spacecraft), Philae'', its lander module, ''Rosetta'' performed a detailed study of comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko (67P). During its journey to the comet, the spacecraft performed planetary flyby, flybys of Earth, Mars, and the asteroids 21 Lutetia and 2867 Šteins. It was launched as the third cornerstone mission of the ESA's Horizon 2000 programme, after ''Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, SOHO'Cluster II (spacecraft), Cluster'' and ''XMM-Newton''. On 6 August 2014, the spacecraft reached the comet and performed a series of manoeuvers to eventually orbit the comet at distances of . On 12 November, its lander module ''Philae'' performed the first successful landing on a comet, though its battery power ran out two days later. Communications with ''Philae'' were briefly restored in June and July 2015, but due to diminishing solar power, ''Rosetta'' communications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Craters On Šteins
This is a list of all named craters on minor planets in the Solar System as named by IAU's Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature. In addition tentatively named craters—such as those of Pluto—may also be referred to. The number of craters is given in parenthesis. For a full list of all craters, ''see list of craters in the Solar System This is a list of named craters in the Solar System as named by IAU's Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature. As of 2017, there is a total of 5,223 craters on 40 astronomical bodies, which includes minor planets (asteroids and dwarf plan ...''. Images File:Ceres - RC3 - Haulani Crater (22381131691) (cropped).jpg, Ceres File:Eros - PIA02923 (color).jpg, Eros File:951 Gaspra.jpg, Gaspra File:243 ida crop.jpg, Ida File:Rosetta triumphs at asteroid Lutetia.jpg, Lutetia File:(253) mathilde crop.jpg, Mathilde File:Nh-pluto-in-true-color 2x JPEG-edit-frame.jpg, Pluto File:2867 Šteins by Rosetta (reprocessed).png, Šteins Fil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Planet
According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a minor planet is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the Sun that is exclusively classified as neither a planet nor a comet. Before 2006, the IAU officially used the term ''minor planet'', but that year's meeting reclassified minor planets and comets into dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies (SSSBs).Press release, IAU 2006 General Assembly: Result of the IAU Resolution votes International Astronomical Union, August 24, 2006. Accessed May 5, 2008. Minor planets include asteroids ( |
European Space Operations Centre
The European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) serves as the main mission control centre for the European Space Agency (ESA) and is located in Darmstadt, Germany. ESOC's primary function is the operation of unmanned spacecraft on behalf of ESA and the launch and early orbit phases (LEOP) of ESA and third-party missions. The Centre is also responsible for a range of operations-related activities within ESA and in cooperation with ESA's industry and international partners, including ground systems engineering, software development, flight dynamics and navigation, development of mission control tools and techniques and space debris studies. ESOC's current major activities comprise operating planetary and solar missions, such as Mars Express and the Trace Gas Orbiter, astronomy & fundamental physics missions, such as Gaia (spacecraft) and XMM Newton, and Earth observation missions such as CryoSat2 and Swarm (spacecraft). ESOC is responsible for developing, operating and maintaining E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
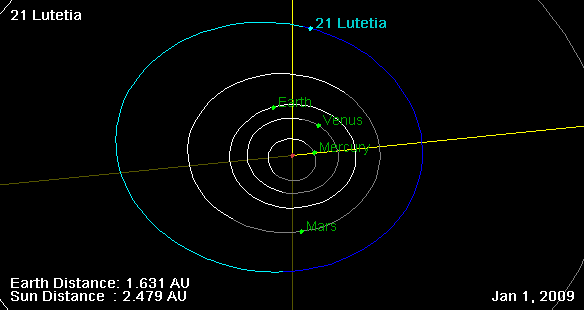
21 Lutetia
) , mp_category=Main belt , mpc_name=(21) Lutetia , orbit_ref = , epoch=May 31, 2020 ( JD 2459000.5) , semimajor=2.435 AU , perihelion=2.037 AU , aphelion=2.833 AU , eccentricity=0.16339 , period=3.80 yr (1388.1 d) , inclination=3.064° , asc_node=80.867° , arg_peri=249.997° , mean_anomaly=87.976° , dimensions=c/a = P. Vernazza et al. (2021) VLT/SPHERE imaging survey of the largest main-belt asteroids: Final results and synthesis. ''Astronomy & Astrophysics'' 54, A56 , mean_radius = , volume= , mass= , density= , rotation=0.3402 d (8.1655 h) , axial_tilt = 96° , right_asc_north_pole = 51.8 ± 0.4° , declination = +10.8 ± 0.4° , spectral_type= M (Tholen) , magnitude = 9.25 to 13.17 , abs_magnitude=7.29 , albedo=0.19 ± 0.01 (geometrical)0.073 ± 0.002 (bond) , single_temperature=170–245 K Lutetia (minor planet designation: 21 Lutetia) is a large M-type asteroid in the main asteroid belt. It measures about 100 kilometers in diameter ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animation Of Rosetta Trajectory
Animation is a method by which still figures are manipulated to appear as moving images. In traditional animation, images are drawn or painted by hand on transparent celluloid sheets to be photographed and exhibited on film. Today, most animations are made with computer-generated imagery (CGI). Computer animation can be very detailed 3D animation, while 2D computer animation (which may have the look of traditional animation) can be used for stylistic reasons, low bandwidth, or faster real-time renderings. Other common animation methods apply a stop motion technique to two- and three-dimensional objects like paper cutouts, puppets, or clay figures. A cartoon is an animated film, usually a short film, featuring an exaggerated visual style. The style takes inspiration from comic strips, often featuring anthropomorphic animals, superheroes, or the adventures of human protagonists. Especially with animals that form a natural predator/prey relationship (e.g. cats and mice, coyo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palomar Observatory
Palomar Observatory is an astronomical research observatory in San Diego County, California, United States, in the Palomar Mountain Range. It is owned and operated by the California Institute of Technology (Caltech). Research time at the observatory is granted to Caltech and its research partners, which include the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), Yale University, and the National Optical Observatories of China. The observatory operates several telescopes, including the Hale Telescope, the Samuel Oschin Telescope (dedicated to the Zwicky Transient Facility, ZTF), the Palomar Telescope, and the Gattini-IR telescope. Decommissioned instruments include the Palomar Testbed Interferometer and the first telescopes at the observatory, an Schmidt camera from 1936. History Hale's vision for large telescopes and Palomar Observatory Astronomer George Ellery Hale, whose vision created the Palomar Observatory, built the world's largest telescope four times in succession. He publishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precovery
In astronomy, precovery (short for pre-discovery recovery) is the process of finding the image of an object in images or photographic plates predating its discovery, typically for the purpose of calculating a more accurate orbit. This happens most often with minor planets, but sometimes a comet, a dwarf planet, a natural satellite, or a star is found in old archived images; even exoplanet precovery observations have been obtained. "Precovery" refers to a pre-discovery image; "recovery" refers to imaging of a body which was lost to our view (as behind the Sun), but is now visible again ''(also see lost minor planet and lost comet)''. Orbit determination requires measuring an object's position on multiple occasions. The longer the interval between observations, the more accurately the orbit can be calculated; however, for a newly discovered object, only a few days' or weeks' worth of measured positions may be available, sufficient only for a preliminary (imprecise) orbit calculatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observation Arc
In observational astronomy, the observation arc (or arc length) of a Solar System body is the time period between its earliest and latest observations, used for tracing the body's path. It is usually given in days or years. The term is mostly used in the discovery and tracking of asteroids and comets. Arc length has the greatest influence on the accuracy of an orbit. The number and spacing of intermediate observations has a lesser effect. Short arcs A very short arc leaves a high uncertainty parameter. The object might be in one of many different orbits, at many distances from Earth. In some cases, the initial arc was too short to determine if the object was in orbit around the Earth, or orbiting out in the asteroid belt. With a 1-day observation arc, was thought to be a trans-Neptunian dwarf planet, but is now known to be a 1 km main-belt asteroid. With an observation arc of 3 days, was thought to be a Mars-crossing asteroid that could be a threat to Earth, but was later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic against the background of stars. The ecliptic is an important reference plane and is the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system. Sun's apparent motion The ecliptic is the apparent path of the Sun throughout the course of a year. Because Earth takes one year to orbit the Sun, the apparent position of the Sun takes one year to make a complete circuit of the ecliptic. With slightly more than 365 days in one year, the Sun moves a little less than 1° eastward every day. This small difference in the Sun's position against the stars causes any particular spot on Earth's surface to catch up with (and stand directly north or south of) the Sun about four minutes later each day than it would if Earth did not orbit; a day on Earth is therefore 24 hours ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object. For a satellite orbiting the Earth directly above the Equator, the plane of the satellite's orbit is the same as the Earth's equatorial plane, and the satellite's orbital inclination is 0°. The general case for a circular orbit is that it is tilted, spending half an orbit over the northern hemisphere and half over the southern. If the orbit swung between 20° north latitude and 20° south latitude, then its orbital inclination would be 20°. Orbits The inclination is one of the six orbital elements describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit. It is the angle between the orbital plane and the plane of reference, normally stated in degrees. For a satellite orbiting a planet, the plane of reference is usually the plane containing the planet's equator. For pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Eccentricity
In astrodynamics, the orbital eccentricity of an astronomical object is a dimensionless parameter that determines the amount by which its orbit around another body deviates from a perfect circle. A value of 0 is a circular orbit, values between 0 and 1 form an elliptic orbit, 1 is a parabolic escape orbit (or capture orbit), and greater than 1 is a hyperbola. The term derives its name from the parameters of conic sections, as every Kepler orbit is a conic section. It is normally used for the isolated two-body problem, but extensions exist for objects following a rosette orbit through the Galaxy. Definition In a two-body problem with inverse-square-law force, every orbit is a Kepler orbit. The eccentricity of this Kepler orbit is a non-negative number that defines its shape. The eccentricity may take the following values: * circular orbit: ''e'' = 0 * elliptic orbit: 0 < ''e'' < 1 * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)


.jpg)