|
24 Preludes, Op. 11 (Scriabin)
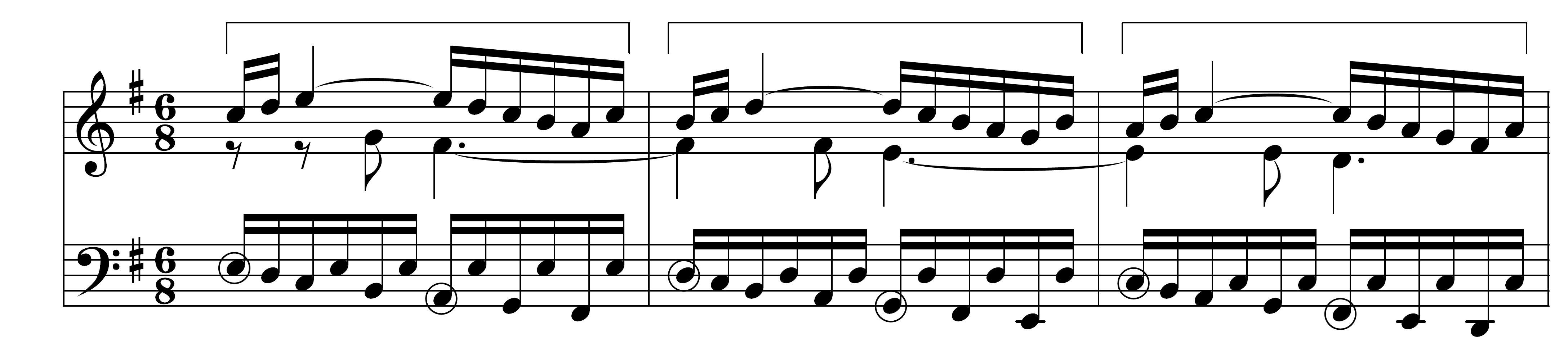
Alexander Scriabin's 24 Preludes, Op. 11 is a set of preludes composed in the course of eight years between 1888–96,Scriabin did not write the 24 preludes chronologically, but instead in different places over the course of eight years. Prelude No. 4 was written in Moscow in 1888, followed by No. 6 in 1889 in Kiev. No. 10 was written in 1893–4 in Moscow, and No. 14 in 1895 in Dresden. Nos. 3, 19, 24 in 1895 in Heidelberg, and Nos. 12, 17, 18 and 23 also in 1895 in Witznau. No. 5 was written in 1896 in Amsterdam, Nos. 8 and 22 also in 1896 in Paris, while Nos. 1, 2, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 16, 20 and 21 were written that same year in Moscow. being also one of Scriabin's first published works with M.P. Belaieff in 1897,Belyayev divided the preludes into four parts of six preludes each. in Leipzig, Germany, together with his 12 Études, Op. 8 (1894–95). Structural analysis Scriabin's 24 preludes were modeled after Frédéric Chopin's own set of 24 Preludes, Op. 28: They also covered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welte-Mignon
M. Welte & Sons, Freiburg and New York was a manufacturer of orchestrions, organs and reproducing pianos, established in Vöhrenbach by Michael Welte (1807–1880) in 1832. Overview From 1832 until 1932, the firm produced mechanical musical instruments of the highest quality. The firm's founder, Michael Welte (1807-1880), and his company were prominent in the technical development and construction of orchestrions from 1850, until the early 20th century. In 1872, the firm moved from the remote Black Forest town of Vöhrenbach into a newly developed business complex beneath the main railway station in Freiburg, Germany. They created an epoch-making development when they substituted the playing gear of their instruments from fragile wood pinned cylinders to perforated paper rolls. In 1883, Emil Welte (1841-1923), the eldest son of Michael, who had emigrated to the United States in 1865, patented the paper roll method (), the model of the later piano roll. In 1889, the tec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eighth Note
180px, Figure 1. An eighth note with stem extending up, an eighth note with stem extending down, and an eighth rest. 180px, Figure 2. Four eighth notes beamed together. An eighth note (American) or a quaver (British) is a musical note played for one eighth the duration of a whole note (semibreve). Its length relative to other rhythmic values is as expected—e.g., half the duration of a quarter note (crotchet), one quarter the duration of a half note (minim), and twice the value of a sixteenth note. It is the equivalent of the ''fusa'' in mensural notation. Eighth notes are notated with an oval, filled-in note head and a straight note stem with one note flag (see Figure 1). The stem is on the right of the notehead extending upwards or on the left extending downwards, depending primarily on where the notehead lies relative to the middle line of the staff. A related symbol is the eighth rest (or quaver rest), which denotes a silence for the same duration. Eighth notes may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E Major
E major (or the key of E) is a major scale based on E, consisting of the pitches E, F, G, A, B, C, and D. Its key signature has four sharps. Its relative minor is C-sharp minor and its parallel minor is E minor. Its enharmonic equivalent, F-flat major, has eight flats, including the double-flat B, which makes it impractical to use. The E major scale is: Music in E major Antonio Vivaldi used this key for the "Spring" concerto from ''The Four Seasons''. Johann Sebastian Bach used E major for a violin concerto, as well as for his third partita for solo violin; the key is especially appropriate for the latter piece because its tonic (E) and subdominant (A) correspond to open strings on the violin, enhancing the tone colour (and ease of playing) of the bariolage in the first movement. Only two of Joseph Haydn's 106 symphonies are in E major: No. 12 and No. 29. Ludwig van Beethoven used E major for two of his piano sonatas, Op. 14/1 and Op. 109. Starting with B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coda (music)
In music, a coda () (Italian for "tail", plural ''code'') is a passage that brings a piece (or a movement) to an end. It may be as simple as a few measures, or as complex as an entire section. In classical music The presence of a coda as a structural element in a movement is especially clear in works written in particular musical forms. Codas were commonly used in both sonata form and variation movements during the Classical era. In a sonata form movement, the recapitulation section will, in general, follow the exposition in its thematic content, while adhering to the home key. The recapitulation often ends with a passage that sounds like a termination, paralleling the music that ended the exposition; thus, any music coming after this termination will be perceived as extra material, i.e., as a coda. In works in variation form, the coda occurs following the last variation and will be very noticeable as the first music not based on the theme. One of the ways that Beethoven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridge (music)
In music, especially Western popular music, a bridge is a contrasting section that prepares for the return of the original material section. In a piece in which the original material or melody is referred to as the "A" section, the bridge may be the third eight-bar phrase in a thirty-two-bar form (the B in AABA), or may be used more loosely in verse-chorus form, or, in a compound AABA form, used as a contrast to a full AABA section. The bridge is often used to contrast with and prepare for the return of the verse and the chorus. "The b section of the popular song chorus is often called the ''bridge'' or ''release''." Etymology The term comes from a German word for bridge, ''Steg'', used by the Meistersingers of the 15th to the 18th century to describe a transitional section in medieval bar form. The German term became widely known in 1920s Germany through musicologist Alfred Lorenz and his exhaustive studies of Richard Wagner's adaptations of bar form in his popular 19th-cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Form
In music, ''form'' refers to the structure of a musical composition or musical improvisation, performance. In his book, ''Worlds of Music'', Jeff Todd Titon suggests that a number of organizational elements may determine the formal structure of a piece of music, such as "the arrangement of musical units of rhythm, melody, and/or harmony that show repetition (music), repetition or variation (music), variation, the arrangement of the instruments (as in the order of solo (music), solos in a jazz or bluegrass performance), or the way a symphonic piece is orchestration, orchestrated", among other factors. It is, "the ways in which a composition is shaped to create a meaningful musical experience for the listener."Kostka, Stefan and Payne, Dorothy (1995). ''Tonal Harmony'', p.152. McGraw-Hill. . These organizational elements may be broken into smaller units called phrases, which express a musical idea but lack sufficient weight to stand alone. Musical form unfolds over time through th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alto
The musical term alto, meaning "high" in Italian (Latin: ''altus''), historically refers to the contrapuntal part higher than the tenor and its associated vocal range. In 4-part voice leading alto is the second-highest part, sung in choruses by either low women's or high men's voices. In vocal classification these are usually called contralto and male alto or countertenor. Such confusion of "high" and "low" persists in instrumental terminology. Alto flute and alto trombone are respectively lower and higher than the standard instruments of the family (the standard instrument of the trombone family being the tenor trombone), though both play in ranges within the alto clef. Alto recorder, however, is an octave higher, and is defined by its relationship to tenor and soprano recorders; alto clarinet is a fifth lower than B-flat clarinet, already an 'alto' instrument. There is even a contra-alto clarinet, (an octave lower than the alto clarinet), with a range B♭0 – D4. Etymo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bar (music)
In musical notation, a bar (or measure) is a segment of time corresponding to a specific number of beats in which each beat is represented by a particular note value and the boundaries of the bar are indicated by vertical bar lines. Dividing music into bars provides regular reference points to pinpoint locations within a musical composition. It also makes written music easier to follow, since each bar of staff symbols can be read and played as a batch. Typically, a piece consists of several bars of the same length, and in modern musical notation the number of beats in each bar is specified at the beginning of the score by the time signature. In simple time, (such as ), the top figure indicates the number of beats per bar, while the bottom number indicates the note value of the beat (the beat has a quarter note value in the example). The word ''bar'' is more common in British English, and the word ''measure'' is more common in American English, although musicians generally u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenuto
In musical notation, ''tenuto'' (Italian, past participle of ''tenere'', "to hold"), denoted as a horizontal bar adjacent to a note, is a direction for the performer to hold or sustain a note for its full length. Its precise interpretation can be somewhat contextual in practice, especially when combined with dynamic directions affecting loudness. In that case, it can mean either ''accent the note in question by holding it to its full length (or longer, with slight rubato)'', or ''play the note slightly louder''. In other words, the ''tenuto'' mark may alter the length of a note at the same time a dynamic mark adjusts its volume. Either way, the tenuto marking indicates that a note should receive some degree of emphasis. Tenuto is one of the earliest directions to appear in music notation. Notker of St. Gall (c. 840–912) discusses the use of the letter ''t'' in plainsong notation as meaning ''trahere vel tenere debere'' in one of his letters. The mark's meaning may also be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballade (classical Music)
A ballade (from French ''ballade'', , and German ''Ballade'', , both being words for "ballad"), in classical music since the late 18th century, refers to a setting of a literary ballad, a narrative poem, in the musical tradition of the , or to a one- movement instrumental piece with lyrical and dramatic narrative qualities reminiscent of such a song setting, especially a piano ballade. In 19th century romantic music, a piano ballad (most often spelled ballade) is a genre of solo piano piecesJim Samson, "Chopin and Genre", ''Music Analysis'' 8, no. 3 (October 1989): 213–231. Reference on 216–17. written in a balletic narrative style, often with lyrical elements interspersed. This type of work made its first appearance with Chopin's Ballade No. 1 in G minor, Op. 23 of 1831–35, closely followed by the ballad included in Clara Schumann's ''Soirées musicales'' Op. 6 published in the same year. Romantic ballades In late 18th century German literature, the term ''ballade'' w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key Signature Names And Translations
When a musical key or key signature is referred to in a language other than English, that language may use the usual notation used in English (namely the letters A to G, along with translations of the words ''sharp'', ''flat'', ''major'' and ''minor'' in that language): languages which use the English system include Irish, Welsh, Hindi, Japanese (based on katakana in iroha order), Korean (based on hangul in ganada order), Chinese, Thai, Indonesian, Filipino, Swahili, Esperanto. Or it may use some different notation. Two notation systems are most commonly found beside the English system, the ''Fixed Do'' key notation and the ''German'' key notation # ''Fixed Do'' key notation – used (among others) in Italian, French, Dutch (in the Dutch-speaking part of Belgium), Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, Occitan, Breton, Basque, Russian (along with the German system), Ukrainian, Belarusian, Bulgarian, Latvian, Lithuanian (along with the German and English system), Romanian, Greek, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tempo
In musical terminology, tempo (Italian, 'time'; plural ''tempos'', or ''tempi'' from the Italian plural) is the speed or pace of a given piece. In classical music, tempo is typically indicated with an instruction at the start of a piece (often using conventional Italian terms) and is usually measured in beats per minute (or bpm). In modern classical compositions, a "metronome mark" in beats per minute may supplement or replace the normal tempo marking, while in modern genres like electronic dance music, tempo will typically simply be stated in BPM. Tempo may be separated from articulation and meter, or these aspects may be indicated along with tempo, all contributing to the overall texture. While the ability to hold a steady tempo is a vital skill for a musical performer, tempo is changeable. Depending on the genre of a piece of music and the performers' interpretation, a piece may be played with slight tempo rubato or drastic variances. In ensembles, the tempo is often ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)