|
2M (DOS)
2M is a DOS program by the Spanish programmer Ciriaco García de Celis. It enables higher than normal capacity formatting of floppy disks. It saw active development from 1993 to 1995. The last version, v3.0, was released on 6 March 1995. It was written in C and assembler and compiled using Borland C++ 3.1. The program consisted of two major components: 2M and 2MGUI (from "2M Guinness"). Of these, 2M was the main program enabling the formatting, reading and writing of high density 3.5" disks formatted to a capacity of either 1804 KiB or 1886 KB, and 2MGUI was a proof-of-concept program that demonstrated the ability to format any normal high density 3.5" disk to a capacity of over two million bytes (1972 KiB) on any disk drive. Both programs implemented disk I/O speedups in the form of "Sector Sliding" and "DiskBoost", which work on the principle of ordering the physical sectors on the disk to facilitate pauseless reading over track changes. 2MGUI utilized bit banging and tricked th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk Formatting
Disk formatting is the process of preparing a data storage device such as a hard disk drive, solid-state drive, floppy disk, memory card or USB flash drive for initial use. In some cases, the formatting operation may also create one or more new file systems. The first part of the formatting process that performs basic medium preparation is often referred to as "low-level formatting". Partitioning is the common term for the second part of the process, dividing the device into several sub-devices and, in some cases, writing information to the device allowing an operating system to be booted from it. The third part of the process, usually termed "high-level formatting" most often refers to the process of generating a new file system. In some operating systems all or parts of these three processes can be combined or repeated at different levels and the term "format" is understood to mean an operation in which a new disk medium is fully prepared to store files. Some formatting utilitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
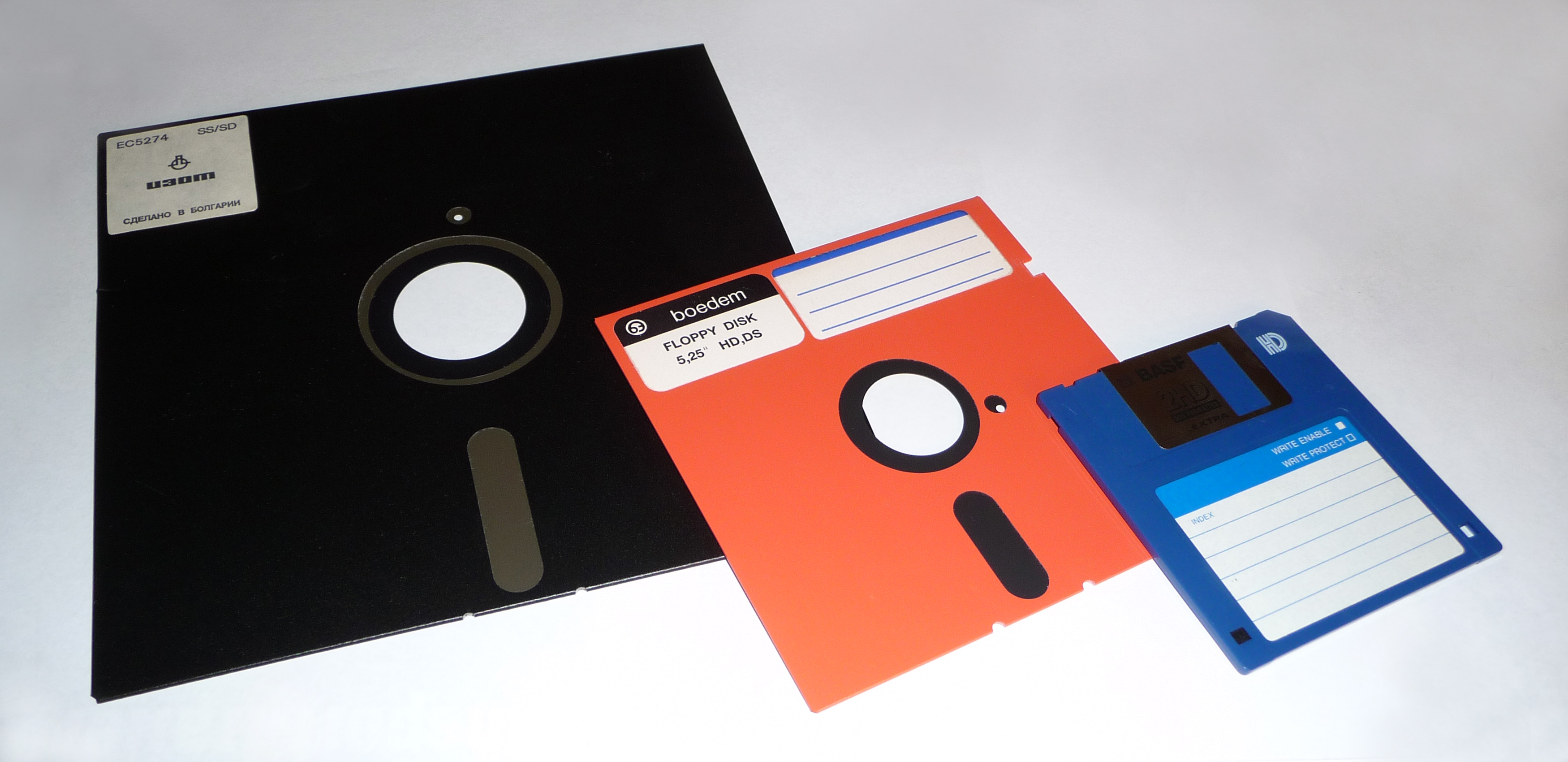
Floppy Disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, or a diskette) is an obsolescent type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a fabric that removes dust particles from the spinning disk. Floppy disks store digital data which can be read and written when the disk is inserted into a floppy disk drive (FDD) connected to or inside a computer or other device. The first floppy disks, invented and made by IBM, had a disk diameter of . Subsequently, the 5¼-inch and then the 3½-inch became a ubiquitous form of data storage and transfer into the first years of the 21st century. 3½-inch floppy disks can still be used with an external USB floppy disk drive. USB drives for 5¼-inch, 8-inch, and other-size floppy disks are rare to non-existent. Some individuals and organizations continue to use older equipment to read or transfer data from floppy disks. Floppy di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borland C++
Borland C++ is a C and C++ IDE ( integrated development environment) for MS-DOS and Microsoft Windows. It was the successor to Turbo C++ and included a better debugger, the Turbo Debugger, which was written in protected mode DOS. Libraries Object Windows Library (OWL): A set of C++ classes to make it easier to develop professional graphical Windows applications. Turbo Vision: A set of C++ classes to create professional applications in DOS. Those classes mimics some of the aspects of a Windows application like: dialog boxes, messages pumps, menus, accelerators, etc. Borland Graphics Interface: A library of functions for doing simple, presentation-style 2D graphics. Drivers were included for generic CGA, EGA and VGA capability, with support for a limited number of video-modes, but more advanced, third-party drivers were also available. Add-ons Borland Power Pack for DOS: Used to create 16- and 32-bit protected mode DOS applications, which can access a limited scope of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bit Banging
In computer engineering and electrical engineering, bit banging is a "term of art" for any method of data transmission that employs software as a substitute for dedicated hardware to generate transmitted signals or process received signals. Software directly sets and samples the states of GPIOs (e.g., pins on a microcontroller), and is responsible for meeting all timing requirements and protocol sequencing of the signals. In contrast to bit banging, dedicated hardware (e.g., UART, SPI, I²C) satisfies these requirements and, if necessary, provides a data buffer to relax software timing requirements. Bit banging can be implemented at very low cost, and is commonly used in some embedded systems. Bit banging allows a device to implement different protocols with minimal or no hardware changes. In some cases, bit banging is made feasible by newer, faster processors because more recent hardware operates much more quickly than hardware did when standard communications protocols wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floppy Controller
A floppy-disk controller (FDC) has evolved from a discrete set of components on one or more circuit boards to a special-purpose integrated circuit (IC or "chip") or a component thereof. An FDC directs and controls reading from and writing to a computer's floppy disk drive (FDD). The FDC is responsible for reading data presented from the host computer and converting it to the drive's on-disk format using one of a number of encoding schemes, like FM encoding (single density) or MFM encoding (double density), and reading those formats and returning it to its original binary values. Depending on the platform, data transfers between the controller and host computer would be controlled by the computer's own microprocessor, or an inexpensive dedicated microprocessor like the MOS 6507 or Zilog Z80. Early controllers required additional circuitry to perform specific tasks like providing clock signals and setting various options. Later designs included more of this functionality on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Density
Disk density is a capacity designation on magnetic storage, usually floppy disks. Each designation describes a set of characteristics that can affect the areal density of a disk or the efficiency of the encoded data. Such characteristics include modulation method, track width, coercivity, and magnetic field direction. 8-inch media ''Single density'' (SD or 1D) describes the first generation of floppy disks that use an iron oxide coating. Floppy drives utilize 300-oersted write heads, FM encoding, and a track width of for a density of 48 tracks-per-inch (tpi) and 5876 bits-per-inch (bpi). ''Double density'' (DD or 2D) doubles capacity over SD by replacing FM encoding with an improved line code, such as modified frequency modulation (MFM), modified modified frequency modulation (M²FM), FM/MFM or group coded recording (GCR). 5¼-inch media ''SD'' (''1D'') and ''DD'' (''2D'') designations were generally identical to those of 8-inch disks. ''Quad density'' (QD or 4D) doub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Density
Disk density is a capacity designation on magnetic storage, usually floppy disks. Each designation describes a set of characteristics that can affect the areal density of a disk or the efficiency of the encoded data. Such characteristics include modulation method, track width, coercivity, and magnetic field direction. 8-inch media ''Single density'' (SD or 1D) describes the first generation of floppy disks that use an iron oxide coating. Floppy drives utilize 300-oersted write heads, FM encoding, and a track width of for a density of 48 tracks-per-inch (tpi) and 5876 bits-per-inch (bpi). ''Double density'' (DD or 2D) doubles capacity over SD by replacing FM encoding with an improved line code, such as modified frequency modulation (MFM), modified modified frequency modulation (M²FM), FM/MFM or group coded recording (GCR). 5¼-inch media ''SD'' (''1D'') and ''DD'' (''2D'') designations were generally identical to those of 8-inch disks. ''Quad density'' (QD or 4D) doubl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder-head-sector
Cylinder-head-sector (CHS) is an early method for giving addresses to each physical block of data on a hard disk drive. It is a 3D-coordinate system made out of a vertical coordinate ''head'', a horizontal (or radial) coordinate ''cylinder'', and an angular coordinate ''sector''. Head selects a circular surface: a platter in the disk (and one of its two sides). Cylinder is a cylindrical intersection through the stack of platters in a disk, centered around the disk's spindle. Combined, cylinder and head intersect to a circular line, or more precisely: a circular strip of physical data blocks called ''track''. Sector finally selects which data block in this track is to be addressed, as the track is subdivided into several equally-sized portions, each of which is an arc of (360/n) degrees, where n is the number of sectors in the track. CHS addresses were exposed, instead of simple linear addresses (going from ''0'' to the ''total block count on disk - 1''), because early hard drive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extra-high Density
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, or a diskette) is an obsolescent type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a fabric that removes dust particles from the spinning disk. Floppy disks store digital data which can be read and written when the disk is inserted into a floppy disk drive (FDD) connected to or inside a computer or other device. The first floppy disks, invented and made by IBM, had a disk diameter of . Subsequently, the 5¼-inch and then the 3½-inch became a ubiquitous form of data storage and transfer into the first years of the 21st century. 3½-inch floppy disks can still be used with an external USB floppy disk drive. USB drives for 5¼-inch, 8-inch, and other-size floppy disks are rare to non-existent. Some individuals and organizations continue to use older equipment to read or transfer data from floppy disks. Floppy disks w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distribution Media Format
Distribution Media Format (DMF) is a format for floppy disks that Microsoft used to distribute software. It allowed the disk to contain 1680 KB of data on a 3-inch disk, instead of the standard 1440 KB. As a side effect, utilities had to specially support the format in order to read and write the disks, which made copying of products distributed on this medium more difficult. An Apple Macintosh computer running Disk Copy 6.3.3 on the Mac OS 7.6 or later operating system can copy and make DMF disks. The first Microsoft software product that uses DMF for distribution were the "c" revisions of Office 4.x. It also was the first software product to use CAB files, then called "Diamond". Comparison of DMF and standard 1440 KB 3-inch diskettes: DMF in the form of a 1680 KB Virtual Floppy Disk (VFD) image and IBM Extended Density Format (XDF) images are supported by Windows Virtual PC. See also * 2M, a program that allows the formatting of high-capacity f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fdformat
Fdformat is the name of two unrelated programs: * A command-line tool for Linux that " low-level formats" a floppy disk. * A DOS tool written in Pascal by Christoph H. Hochstätter that allows users to format floppy disk A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, or a diskette) is an obsolescent type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined w ...s to a higher than usual density, enabling the user to store up to 300 kilobytes more data on a normal high density 3.5" floppy disk. It also increases the speed of diskette I/O on these specially formatted disks using a technique called "Sector Sliding". In this technique, the physical sectors on the disk are ordered in such a way that when the drive advances to the next track, the next logical sector waiting to be read is immediately available to the read head. See also * 2M, a similar program that offers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Extended Density Format
The IBM eXtended Density Format (XDF) is a way of superformatting standard high-density 3½-inch and 5¼-inch floppy disks to larger-than-standard capacities. It is supported natively by IBM's PC DOS versions 7 and 2000 and by OS/2 Warp 3 onward, using the XDF and XDFCOPY commands (directly in OS/2). When formatted as XDF disks, 3½-inch floppies can hold 1860 kB, and 5¼-inch floppies can hold 1540 kB, using different number of sectors as well as different sector size per track (not all sectors in the same track are of the same size). However, the first cylinder uses standard formatting, providing a small FAT12 section that can be accessed without XDF support and on which can be put a ReadMe file or the XDF drivers. Floppy distributions of OS/2 3.0, PC DOS 7 and onward used XDF formatting for most of the media set. Floppy disks formatted using XDF can only be read in floppy disk drives that are attached directly to the system by way of a FDC. Thus, USB attached ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |