|
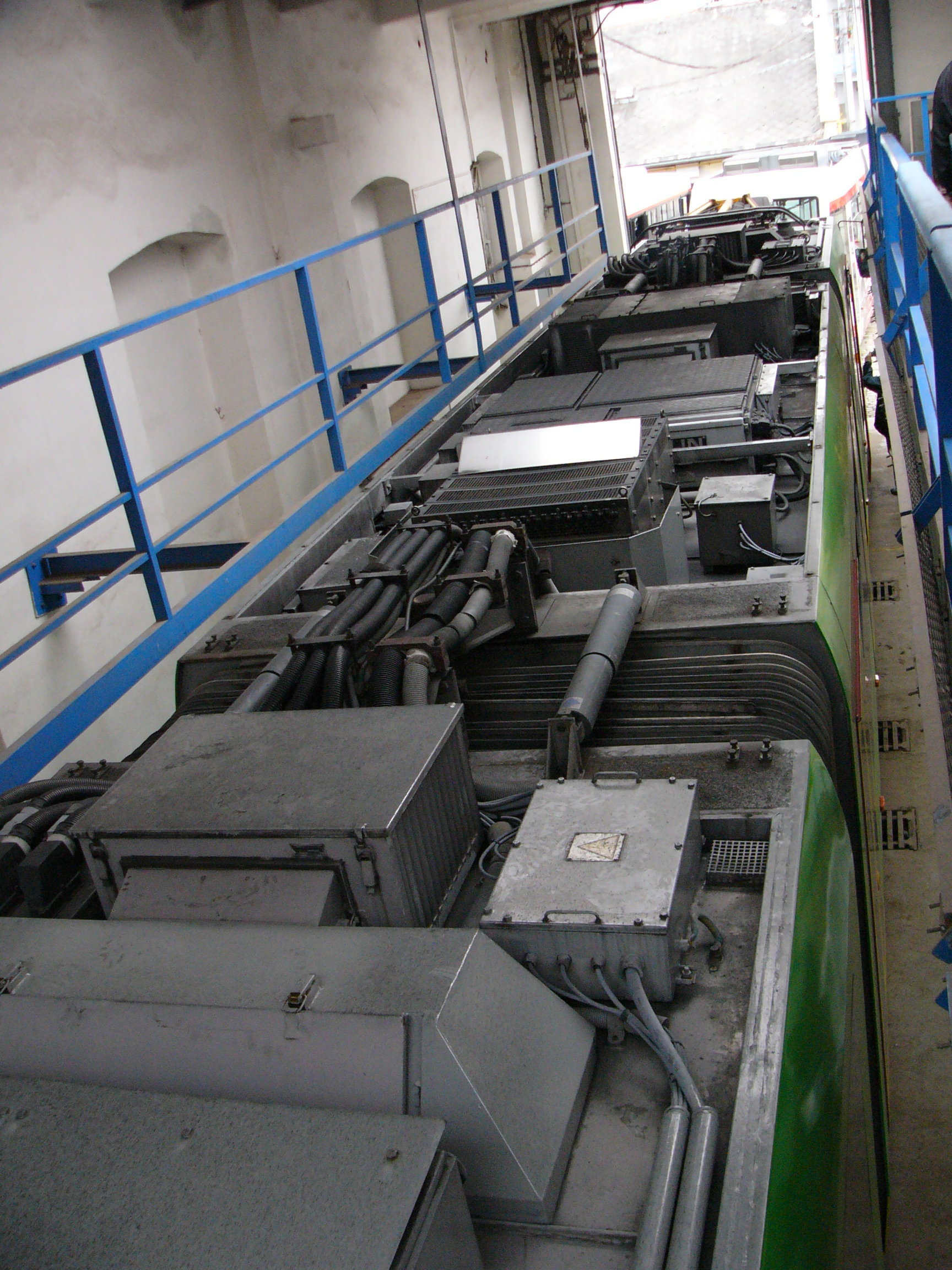
2ES10
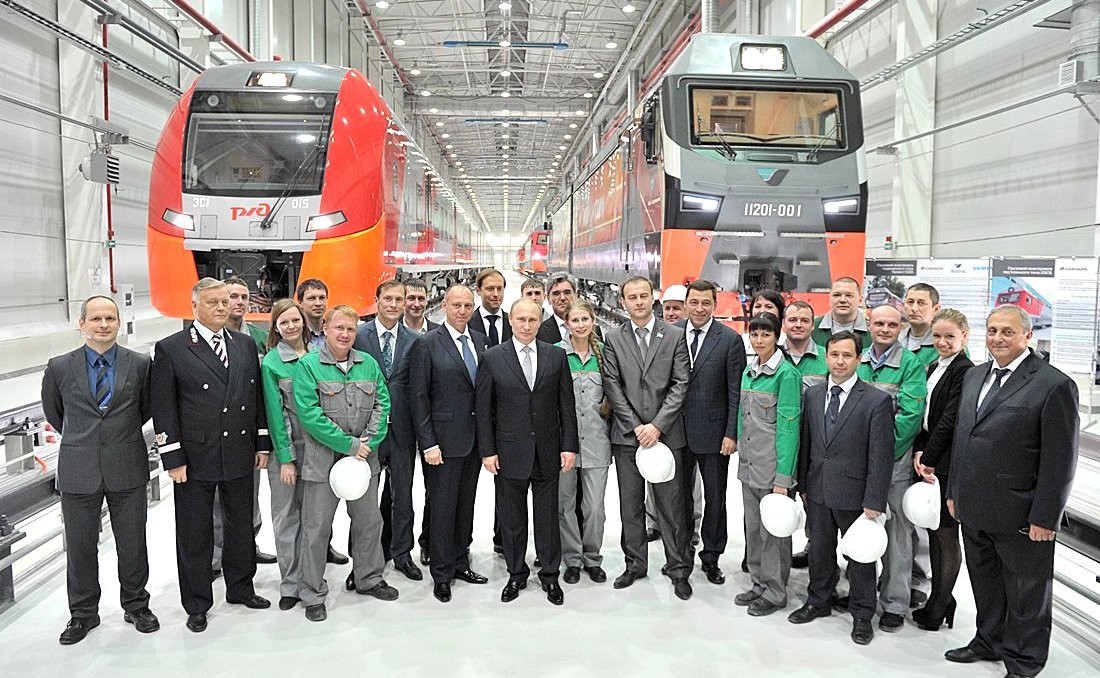
The 2ES10 is a twin section (Bo'Bo)(Bo'Bo') freight locomotive manufactured from 2010 by Ural Locomotives. RZD ordered 221 units in 2010. Ukrainian Railways ordered 50 units in 2013. History and design The 2ES10 is a two unit 8 axle electric freight locomotive manufactured for RZD by Ural Locomotives, a joint venture between Sinara Group of Russia (base platform and auxiliary equipment) and Siemens of Germany (traction electrical equipment). The 2ES10 offers double the power output of VL11 locomotives, with lower operating and maintenance costs. During trials in August 2010, a three-section 2ES10 hauled a train across the Urals. In May 2010, Russian Railways signed an order for 221 2ES10 locomotives. The first prototype locomotive was presented 18 November 2010. In 2012 the company JSC "Apatite" (ОАО "Апатит") acquired one locomotive, 2ES10-222. In 2013 Ukrainian Railways Ukrainian Railways ( uk, Укрзалізниця, Ukrzaliznytsia, abbreviated as UZ) is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ural Locomotives
Ural Locomotives (russian: Уральские локомотивы) is a railway engineering company formed as a joint venture between Sinara Transport Machines and Siemens in 2010. The manufacturing facilities are based at the Ural Railway Engineering Plant in Verkhnyaya Pyshma, which was incorporated into the Sinara Group in 2004. In October 2004 the plant began collaboration with RZD with the aim of production of electric freight locomotives. History The Ural Railway Engineering Plant was formed to locate a DC electric freight locomotive production site within Russian territory; formerly, during the Soviet era DC electric locomotive production in the USSR had been located in Tbilisi in Georgia. Initially the plant was involved in the upgrading of electric locomotives of type VL11 ''(ВЛ11)'', by 2006 the plant had produced the first unit of electric locomotive 2ES6 ''(2ЭС6)'', which was certified for use by 2008. By 2009 production capacity for up to 60 twin-unit locomoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Railways
Ukrainian Railways ( uk, Укрзалізниця, Ukrzaliznytsia, abbreviated as UZ) is a state-owned joint-stock company of rail transport in Ukraine, a monopoly that controls the vast majority of the railroad transportation in the country. It possesses a combined total track length of over 23,000 km, making it the List of countries by rail transport network size, 13th largest in the world. Ukrainian Railways is also Rail usage statistics by country, the world's 6th largest rail passenger transporter and world's 7th largest freight transporter. In 2015, Ukrainian Railways transformed through a merger of a state agency and a state-owned enterprise into a public joint stock company owned by state. Ukraine's State Administration of Railroad Transportation is subordinated to the Ministry of Infrastructure (Ukraine), Ministry of Infrastructure, administering the railways through the six territorial railway companies that immediately control and provide of all aspects of the ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinara Group
Sinara Group is a Russian investment company founded in 2001 with holdings in the property development, rail transportation and financial services sectors. History The company was founded in 2001, and in 2004 acquired industrial and agricultural companies. In 2006 the group merged with ''Металлпром''. The company division ''ОАО Синара – Транспортные Машины'' (Open joint stock company 'Sinara - transport machines') was formed in 2007, and the division ''Синара – Девелопмент'' (Sinara - development) was formed in 2009. In 2009 Sinara Group and Siemens created a joint venture for the production of twin unit electric locomotive to be based at Sinara's Ural Locomotive works near Ekaterinburg. In December 2021, the JV announced production of concept of "Lastochka" electric train with 200 mm low float in 2025. Group divisions and subsidiaries Transport engineering and production The group division ''ОАО "Синара – Тр ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Locomotives Introduced In 2010
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer faciliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urals
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through European Russia, western Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural (river), Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan.Ural Mountains Encyclopædia Britannica on-line The mountain range forms part of the Boundaries between the continents of Earth, conventional boundary between the regions of Europe and Asia. Vaygach Island and the islands of Novaya Zemlya form a further continuation of the chain to the north into the Arctic Ocean. The Ural Mountains are one of the richest mineral regions in the world, containing more than 1,000 varieties of valuable minerals. The mountains lie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Gazette International
''Railway Gazette International'' is a monthly business magazine and news website covering the railway, metro, light rail and tram industries worldwide. Available by annual subscription, the magazine is read in over 140 countries by transport professionals and decision makers, railway managers, engineers, consultants and suppliers to the rail industry. A mix of technical, commercial and geographical feature articles, plus the regular monthly news pages, cover developments in all aspects of the rail industry, including infrastructure, operations, rolling stock and signalling. History ''Railway Gazette International'' traces its history to May 1835 as ''The Railway Magazine'', when it was founded by Effingham Wilson. The ''Railway Gazette'' title dates from July 1905, created to cover railway commercial and financial affairs. In April 1914 it merged with ''The Railway Times'', which incorporated '' Herapath's Railway Journal'', and in February 1935 it absorbed the ''Railway Engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VL11
The VL11 russian: ВЛ11 is an electric mainline DC freight and passenger locomotive, built in Georgia, used in Russia and Ukraine. The initials ''VL'' are those of Vladimir Lenin (ru: Владимир Ленин), after whom the class is named. The ВЛ11 are built in two-section units, but can be built with three or four sections working with multi-tier technology. The three-section units have 12 axles, regenerative brakes and can haul loads up to 59,250 kg. They have an output of 8,040 kW. The Ukrainian State Railway Administration (Ukrzaliznytsia) has upgraded their VL11 locomotives; starting in 2012, they plan to upgrade 20 a year. The upgrade will extend the operating life of each locomotive by 15 years, and it represents only 28% of the cost of a new electric locomotive. See also * The Museum of the Moscow Railway, at Paveletsky Rail Terminal, Moscow * Rizhsky Rail Terminal, Home of the Moscow Railway Museum * Varshavsky Rail Terminal, St.Petersburg, Home of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational conglomerate corporation and the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe headquartered in Munich with branch offices abroad. The principal divisions of the corporation are ''Industry'', ''Energy'', ''Healthcare'' (Siemens Healthineers), and ''Infrastructure & Cities'', which represent the main activities of the corporation. The corporation is a prominent maker of medical diagnostics equipment and its medical health-care division, which generates about 12 percent of the corporation's total sales, is its second-most profitable unit, after the industrial automation division. In this area, it is regarded as a pioneer and the company with the highest revenue in the world. The corporation is a component of the Euro Stoxx 50 stock market index. Siemens and its subsidiaries employ approximately 303,000 people worldwide and reported global revenue of around €62 billion in 2021 according to its earnings release. History 1847 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Air Brake
A railway air brake is a railway brake power braking system with compressed air as the operating medium. Modern trains rely upon a fail-safe air brake system that is based upon a design patented by George Westinghouse on April 13, 1869. The Westinghouse Air Brake Company was subsequently organized to manufacture and sell Westinghouse's invention. In various forms, it has been nearly universally adopted. The Westinghouse system uses air pressure to charge air reservoirs (tanks) on each car. Full air pressure causes each car to release the brakes. A subsequent reduction or loss of air pressure causes each car to apply its brakes, using the compressed air stored in its reservoirs. Overview Straight air brake In the air brake's simplest form, called the ''straight air system'', compressed air pushes on a piston in a cylinder. The piston is connected through mechanical linkage to brake shoes that can rub on the train wheels, using the resulting friction to slow the train. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SA3 Coupler
SA3 couplers (also known as СА3 or СА-3 couplers per the typical foundry stamp on top of these couplers, meaning "Советская Автосцепка, 3" in Russian or "Soviet Auto-latch 3" in English) or Willison coupler and Russian coupler are railway couplings used primarily in Russia and states influenced or not influenced by the former Soviet Union, such as Finland, Iran, Poland and Mongolia. Russian railways originally used buffers and chain couplers during Imperial era, however these had several disadvantages: their draft load was limited, they were susceptible to buffer lock, and they were not semiautomatic like the North American Janney couplers. Conversion to Janney couplers (as Japan and Australia had) was considered, as was development of a new design. The Willison coupler was patented in 1916 by John Willison from Derby, England. The Knorr-Bremse company bought it and it started to be used in Germany for some heavy trains and some suburban trains in Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resistive Brake
Dynamic braking is the use of an electric traction motor as a generator when slowing a vehicle such as an electric or diesel-electric locomotive. It is termed " rheostatic" if the generated electrical power is dissipated as heat in brake grid resistors, and " regenerative" if the power is returned to the supply line. Dynamic braking reduces wear on friction-based braking components, and regeneration lowers net energy consumption. Dynamic braking may also be used on railcars with multiple units, light rail vehicles, electric trams, trolleybuses, and electric and hybrid electric automobiles. Principle of operation Converting electrical energy to the mechanical energy of a rotating shaft (electric motor) is the inverse of converting the mechanical energy of a rotating shaft to electrical energy (electric generator). Both are accomplished through the interactions of armature windings with a (relatively) moving external magnetic field, with the armature connected to an electrical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regenerative Brake
Regenerative braking is an energy recovery mechanism that slows down a moving vehicle or object by converting its kinetic energy into a form that can be either used immediately or stored until needed. In this mechanism, the electric traction motor uses the vehicle's momentum to recover energy that would otherwise be lost to the brake discs as heat. This method contrasts with conventional braking systems. In those systems, the excess kinetic energy is converted to unwanted and wasted heat due to friction in the brakes, or with rheostatic brakes, where the energy is recovered by using electric motors as generators but is immediately dissipated as heat in resistors. In addition to improving the overall efficiency of the vehicle, regeneration can significantly extend the life of the braking system as the mechanical parts will not wear out quickly. General principle The most common form of regenerative brake involves an electric motor functioning as an electric generator. In elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

