|
286th Rifle Division (Soviet Union)
The 286th Rifle Division () was an infantry division of the Soviet Union's Red Army during World War II. Formed in the summer of 1941, the division entered combat during the fall of that year, fighting in operations attempting to break the siege of Leningrad. The division fought in the same area until the relief of Leningrad in February 1944, when it was transferred northwards to fight in the Vyborg–Petrozavodsk Offensive, which ended the Continuation War. The division was transferred to Poland with the end of the Continuation War, and fought in the Vistula–Oder Offensive and the Prague Offensive in early 1945. The division was disbanded soon after the end of the war in the summer of 1945. History The 286th began forming on 10 July 1941 at Cherepovets, part of the Arkhangelsk Military District. Its basic order of battle included the 994th, 996th, and 998th Rifle Regiments, as well as the 854th Artillery Regiment. In mid-August the division was transferred to the Reserve of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8th Army (Soviet Union)
The 8th Army was a field army of the Soviet Red Army during the Second World War. Winter War The 8th Army was formed in October 1939 (or 14 September 1939) from the Novgorod Army Operational Group of the Leningrad Military District with the task of providing security of the Northwestern borders of the USSR. (The Novgorod Group had been created a month before, on 13 August 1939 by the order No. 0129 of the Chairman of the People's Commissariat for Defence, Marshal of the Soviet Union K.E. Voroshilov. The Group was created for operations in Estonia and Latvia.) On 30 November 1939 the Soviet Union attacked Finland in the Winter War. The strength of the 8th Army, or overall the Red Army, in the north of Lake Ladoga (Ladoga Karelia), surprised the Finnish general staff. The Finns deployed only two divisions, and they had a support group of three brigades, bringing their total strength to over 30,000 uniforms. The Soviets had a division for almost all roads leading west to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Units And Formations Established In 1941
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry Divisions Of The Soviet Union In World War II
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine infantry. Although disused in modern times, heavy infantry also commonly made up the bulk of many historic armies. Infantry, cavalry, and artillery have traditionally made up the core of the combat arms professions of various armies, with the infantry almost always comprising the largest portion of these forces. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets '' infant''. The individual-soldier term ''infantry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Group Of Forces
The Central Group of Forces (Russian: Центральная группа войск) was a formation of the Soviet Armed Forces used to incorporate Soviet troops in Central Europe on two occasions: in Austria and Hungary from 1945 to 1955 and troops stationed in Czechoslovakia after the Prague Spring of 1968. History First formation After the end of the Second World War, the Soviet High Command (Stavka) reorganized its troops on the territories it liberated from the Nazi occupation and now occupied. Stavka Directive Nr 11097 on 10 June 1945 created several new formations, known as ''Groups of Forces'', equivalent to military districts but located outside the Soviet Union. The Central Group of Forces was created around that time from the 1st Ukrainian Front to control troops in Austria and Hungary, and did so from 1945 until 1955, when Soviet troops were withdrawn from Austria after the Austrian State Treaty was agreed. Its first commander was Marshal of the Soviet Union Iva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Silesian Offensive
The Upper Silesian offensive was a strategically significant Soviet offensive on the Eastern Front of World War II in 1945. It was aimed at capturing the considerable industrial and natural resources located in Upper Silesia and involved forces of the 1st Ukrainian Front under Marshal Ivan Konev. Due to the importance of the region to the Germans, considerable forces were provided to Army Group Centre for its defence and the Germans were only slowly pushed back to the Czech border. Fighting for the region lasted from mid January right until the last day of the war in Europe on May 8, 1945. Prelude After the end of the Soviet summer offensive of 1944 (Operation Bagration), the frontline of the Eastern Front had stabilised roughly in the middle of Poland, running from Riga on the Baltic coast over Warsaw via the Vistula to the Carpathian Mountains. Most of the pre-war German territory was still under control of the Third Reich at the end of 1944. On 12 january 1945, Soviet t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auschwitz Concentration Camp
Auschwitz concentration camp ( (); also or ) was a complex of over 40 concentration and extermination camps operated by Nazi Germany in occupied Poland (in a portion annexed into Germany in 1939) during World War II and the Holocaust. It consisted of Auschwitz I, the main camp (''Stammlager'') in Oświęcim; Auschwitz II-Birkenau, a concentration and extermination camp with gas chambers; Auschwitz III-Monowitz, a labor camp for the chemical conglomerate IG Farben; and dozens of subcamps. The camps became a major site of the Nazis' final solution to the Jewish question. After Germany sparked World War II by invading Poland in September 1939, the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) converted Auschwitz I, an army barracks, into a prisoner-of-war camp. The initial transport of political detainees to Auschwitz consisted almost solely of Poles for whom the camp was initially established. The bulk of inmates were Polish for the first two years. In May 1940, German criminals brought to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Ukrainian Front
The 1st Ukrainian Front (Russian: Пéрвый Украи́нский фронт), previously the Voronezh Front (Russian: Воронежский Фронт) was a major formation of the Soviet Army during World War II, being equivalent to a Western army group. Background During the first months of the war, officers from 16 regions of Ukraine conscripted about 2.5 million people from military enlistment offices. 1.3 million militiamen from the left-bank and southern regions of Ukraine fought against the enemy. In 1941, about 3.185 million citizens of the Ukrainian SSR were sent to the Soviet Red Army and Navy. Replenishing mostly the units of the Southern and Southwestern fronts, the Ukrainian people formed the basis of the 37th, 38th, and 40th armies; and the 13th and 17th rifle divisions. Due to the conscription of civilians, the proportion of Ukrainian citizens fighting in south-west Ukraine reached 50%. This significantly exceeded the percentage of Ukrainians from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
109th Rifle Corps
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
21st Army (Soviet Union)
The Soviet 21st Army was a field army of the Red Army during World War II. Operational history June–September 1941 21st Army was a part of the Second Operational Echelon of the Red Army. It was formed from the forces of the Volga Military District in May 1941 and was initially based on 63rd Rifle Corps ( 53rd, 148th, and 167th Rifle Divisions) and 66th Rifle Corps. The army was under the command of Lieutenant-General Vasily Gerasimenko, and its chief of staff was Major-General Vasily Gordov. The commander of 63rd Rifle Corps was Lieutenant-General Leonid Petrovsky and the commander of 66th Rifle Corps was Major-General Fyodor Sudakov. In early June the army was moved to the eastern fringes of the Pripyat Marshes south of Homel. At the outbreak of hostilities on 22 June the army was redeployed north to defend the right bank of the Dnepr between Rybchev and Stary-Bykhov. At the same time 25th Mechanized Corps, under the command of Major-General Semyon Krivoshein, was assign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
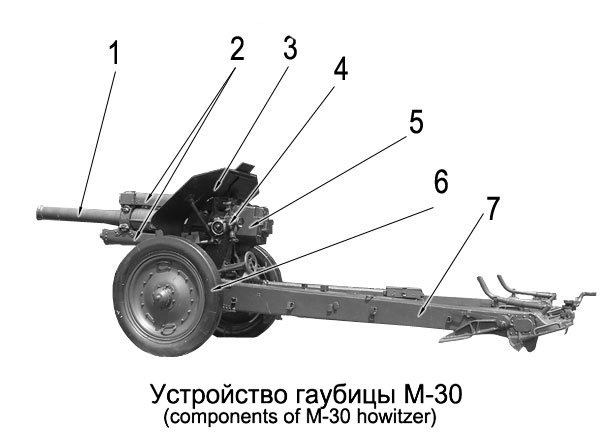
122 Mm Howitzer M1938 (M-30)
The 122 mm howitzer M1938 (M-30) (GRAU index: 52-G-463) was a Soviet 121.92 mm (4.8 inch) howitzer. The weapon was developed by the design bureau of Motovilikha Plants, headed by F. F. Petrov, in the late 1930s, and was in production from 1939 to 1955. The M-30 saw action in World War II, mainly as a divisional artillery piece of the Red Army (RKKA). Captured guns were also employed later in the conflict by the German Wehrmacht and the Finnish Army. Post World War II the M-30 saw combat in numerous conflicts of the mid- to late twentieth century in service of other countries' armies, notably in the Middle East. Development In 1930 Red Army (RKKA) authorities started to look for a new divisional-level howitzer to replace the pre-World War I 122 mm howitzer M1909 and 122 mm howitzer M1910. Although both pieces were eventually modernized, resulting in the 122-mm howitzer M1909/37 and the 122-mm howitzer M1910/30 respectively, these upgrades did not address some short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |