|
27th (N Rhodesia) Infantry Brigade
The 27th (N Rhodesia) Infantry Brigade was a brigade sized formation of the British Army, which was founded on 18 September 1940 in Northern Rhodesia. The brigade was initially called the 7th (N Rhodesia) Infantry Brigade, but was redesignated on 3 October 1940 as the 27th (N Rhodesia) Infantry Brigade. In April 1945, the brigade was redesignated to the 27th (East Africa) Infantry Brigade. The brigade was composed of units, initially, from the Northern Rhodesia Regiment. The brigade later included units from the King's African Rifles and the Mauritius Regiment. During the Second World War, the brigade formed part of various corps-sized commands, and was deployed to East Africa and the Union of South Africa in a non-combat role. The brigade also took part in the Battle of Madagascar. General officers commanding The brigade had the following commanders, during the Second World War. Order of battle The brigade was composed of the following units: * 2nd Battalion, Northern Rhod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of The British Army
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular or quadrilateral) with a distinctive design and colours. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design employed, and flags have evolved into a general tool for rudimentary signalling and identification, especially in environments where communication is challenging (such as the maritime environment, where semaphore is used). Many flags fall into groups of similar designs called flag families. The study of flags is known as "vexillology" from the Latin , meaning "flag" or "banner". National flags are patriotic symbols with widely varied interpretations that often include strong military associations because of their original and ongoing use for that purpose. Flags are also used in messaging, advertising, or for decorative purposes. Some military units are called "flags" after their use of flags. A ''flag'' (Arabic: ) is equivalent to a brigade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
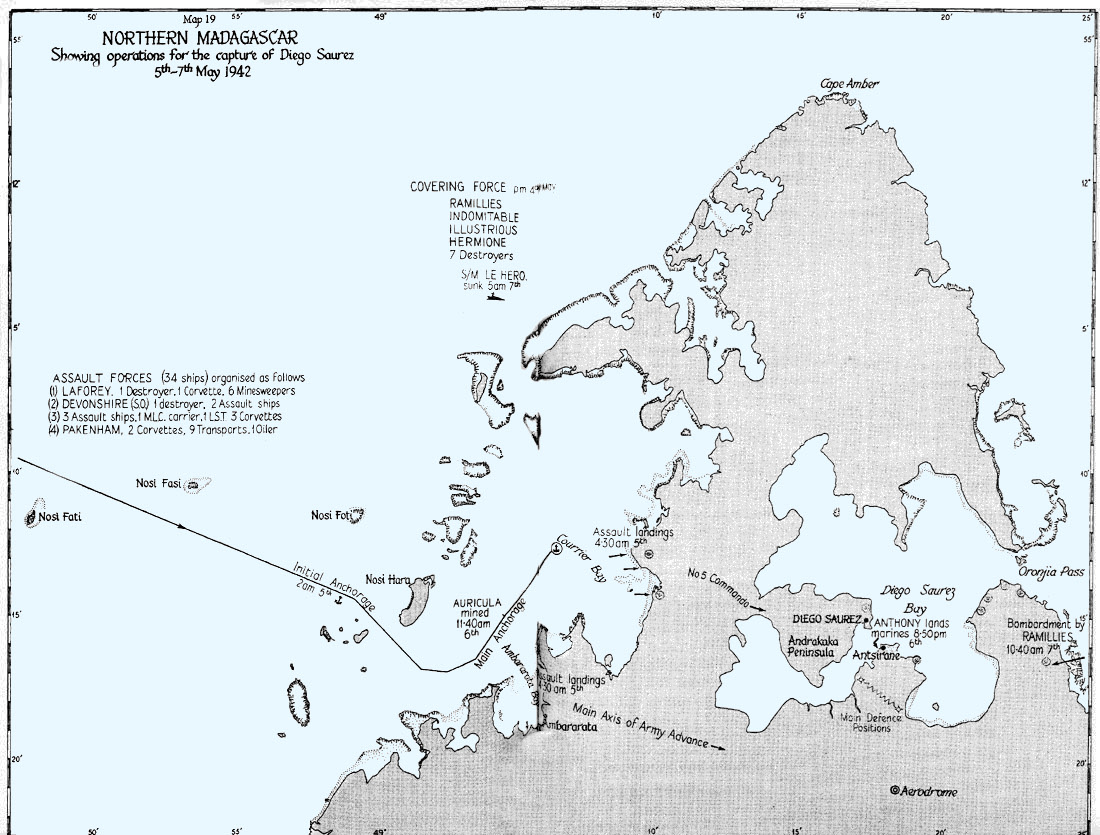
Battle Of Madagascar
The Battle of Madagascar (5 May – 6 November 1942) was a British campaign to capture the Vichy French-controlled island Madagascar during World War II. The seizure of the island by the British was to deny Madagascar's ports to the Imperial Japanese Navy and to prevent the loss or impairment of the Allied shipping routes to India, Australia and Southeast Asia. It began with Operation Ironclad, the seizure of the port of Diego-Suarez (now Antsiranana) near the northern tip of the island, on 5 May 1942. A subsequent campaign to secure the entire island, Operation Stream Line Jane, was opened on 10 September. The Allies broke into the interior, linking up with forces on the coast and secured the island by the end of October. Fighting ceased and an armistice was granted on 6 November. This was the first large-scale operation by the Allies combining sea, land and air forces. The island was placed under Free French control.Rigge p. 100 Background Geopolitical Diego-Suarez is a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Units And Formations Of Northern Rhodesia In World War II
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry Brigades Of The British Army In World War II
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine infantry. Although disused in modern times, heavy infantry also commonly made up the bulk of many historic armies. Infantry, cavalry, and artillery have traditionally made up the core of the combat arms professions of various armies, with the infantry almost always comprising the largest portion of these forces. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets ''infant''. The individual-soldier term ''infantryma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Fox-Pitt (British Army)
Major General William Augustus Fitzgerald Lane Fox-Pitt, (28 January 1896 – 26 April 1988) was a British Army officer who served in both the First World War and Second World War. Early life Fox-Pitt was born in London on 28 January 1896, to Lieutenant Colonel W. A. Fox-Pitt, a soldier with the Grenadier Guards. For his education he attended Charterhouse School before following his father into the army, joining the Cheshire Regiment in August 1914. First World War and interwar career Fox-Pitt sailed for France with the Cheshire Regiment in October 1914 before transferring to the newly formed Welsh Guards the following year. While with the regiment, he was wounded in the fighting at the Hohenzollern Redoubt. Commanding a company at Ginchy on the Somme in 1916, he won a Military Cross. The citation for the award stated: Fox-Pitt was injured once more during 1918. Remaining with the Welsh Guards after the war, Fox-Pitt commanded the regiment's 1st Battalion from 1934 to 1939 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Henry Scott Galletly
Brigadier Thomas Henry Scott Galletly (23 August 1905 – 5 April 1972) was a senior officer in the British Army during the Second World War.''Kelly’s Handbook to the Titled, Landed and Official Classes 1958'', Published by Kelly’s Directories Limited 1958 He was Commanding Officer of the 28th (East Africa) Infantry Brigade in Burma between 21 February 1945 and 1 June 1945, the 27th (East Africa) Infantry Brigade between 30 May 1945 and 14 June 1945 and, from 18 July 1945, was Commanding Officer of the 27th (East Africa) Infantry Brigade. Career Thomas Henry Scott Galletly was born on 23 August 1905 in Hendon, Middlesex, the son of Thomas Galletly of Normanton, Rutland and Edith Galletly of Sharnbrook, Bedfordshire. He was educated at Bedford Modern School and Sandhurst. During the Second World War, he served in Abyssinia (1941) and Madagascar (1942). He served as Acting Commanding Officer of the 27th (N Rhodesia) Infantry Brigade in Madagascar (1943), the 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colin Frederick Blackden
Brigadier Colin Frederick Blackden (1897 – November 1986) was an officer in the British Army during the Second World War. Blackden was acting commander of several brigades of the King's African Rifles during the East African Campaign.Africa Orientale Italiana 1940-1941 by Pierluigi Romeo di Colloredo Mels Command history * Acting Commanding Officer, 2nd (East Africa) Infantry Brigade, East Africa – 1940 * Acting Commanding Officer, 22nd (East Africa) Infantry Brigade, detached to 11th African Division – 1941 * Commanding Officer, Lines of Communication Area, East Africa – 1941 to 1942 * Commanding Officer 27th (N Rhodesia) Infantry Brigade The 27th (N Rhodesia) Infantry Brigade was a brigade sized formation of the British Army, which was founded on 18 September 1940 in Northern Rhodesia. The brigade was initially called the 7th (N Rhodesia) Infantry Brigade, but was redesignated ..., East Africa – 1942 * Commanding Officer, Sub-Area, East Africa – 1943 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonel (United Kingdom)
Colonel (Col) is a rank of the British Army and Royal Marines, ranking below brigadier, and above lieutenant colonel. British colonels are not usually field commanders; typically they serve as staff officers between field commands at battalion and brigade level. The insignia is two diamond-shaped pips (properly called "Bath Stars") below a crown. The crown has varied in the past with different monarchs; Elizabeth II's reign used St Edward's Crown. The rank is equivalent to captain in the Royal Navy and group captain in the Royal Air Force. Etymology The rank of colonel was popularized by the tercios that were employed in the Spanish Army during the 16th and 17th centuries. General Gonzalo Fernández de Córdoba divided his troops in to ''coronelías'' (meaning "column of soldiers" from the Latin, ''columnella'' or "small column"). These units were led by a ''coronel''. This command structure and its titles were soon adopted as ''colonello'' in early modern Italian and in Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant Colonel (United Kingdom)
Lieutenant colonel (Lt Col), is a rank in the British Army and Royal Marines which is also used in many Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth countries. The rank is superior to Major (United Kingdom), major, and subordinate to Colonel (United Kingdom), colonel. The comparable Royal Navy rank is Commander (Royal Navy), commander, and the comparable rank in the Royal Air Force and many Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth air forces is Wing commander (rank), wing commander. The rank insignia in the British Army and Royal Marines, as well as many Commonwealth countries, is a crown above a Order of the Bath, four-pointed "Bath" star, also colloquially referred to as a British Army officer rank insignia, "pip". The crown has varied in the past with different monarchs; the current one being the St Edward's Crown, Crown of St Edward. Most other Commonwealth countries use the same insignia, or with the state emblem replacing the crown. In the modern British Armed forces, the establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigadier (United Kingdom)
Brigadier (Brig) is a senior rank in the British Army and the Royal Marines. Brigadier is the superior rank to colonel, and subordinate to major-general. It corresponds to the rank of brigadier general in many other nations. The rank has a NATO rank code of OF-6, placing it equivalent to the Royal Navy commodore and the Royal Air Force air commodore ranks and the brigadier general (1-star general) rank of the United States military and numerous other NATO nations. Insignia The rank insignia for a brigadier is a St Edward's Crown over three "pips" ( "Bath" stars). The rank insignia for a brigadier-general was crossed sword and baton. Usage Brigadier was originally an appointment conferred on colonels (as commodore was an appointment conferred on naval captains) rather than a substantive rank. However, from 1 November 1947 it became a substantive rank in the British Army. The Royal Marines, however, retained it as an acting rank until 1997, when both commodore and brigadier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Of South Africa
The Union of South Africa ( nl, Unie van Zuid-Afrika; af, Unie van Suid-Afrika; ) was the historical predecessor to the present-day Republic of South Africa. It came into existence on 31 May 1910 with the unification of the Cape, Natal, Transvaal, and Orange River colonies. It included the territories that were formerly a part of the South African Republic and the Orange Free State. Following World War I, the Union of South Africa was a signatory of the Treaty of Versailles and became one of the founding members of the League of Nations. It was conferred the administration of South West Africa (now known as Namibia) as a League of Nations mandate. It became treated in most respects as another province of the Union, but it never was formally annexed. Like Canada, Australia and New Zealand, the Union of South Africa was a self-governing dominion of the British Empire. Its full sovereignty was confirmed with the Balfour Declaration of 1926 and the Statute of Westminster 1931. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigade
A brigade is a major tactical military formation that typically comprises three to six battalions plus supporting elements. It is roughly equivalent to an enlarged or reinforced regiment. Two or more brigades may constitute a division. Brigades formed into divisions are usually infantry or armored (sometimes referred to as combined arms brigades). In addition to combat units, they may include combat support units or sub-units, such as artillery and engineers, and logistic units. Historically, such brigades have sometimes been called brigade-groups. On operations, a brigade may comprise both organic elements and attached elements, including some temporarily attached for a specific task. Brigades may also be specialized and comprise battalions of a single branch, for example cavalry, mechanized, armored, artillery, air defence, aviation, engineers, signals or logistic. Some brigades are classified as independent or separate and operate independently from the traditional divi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |