|
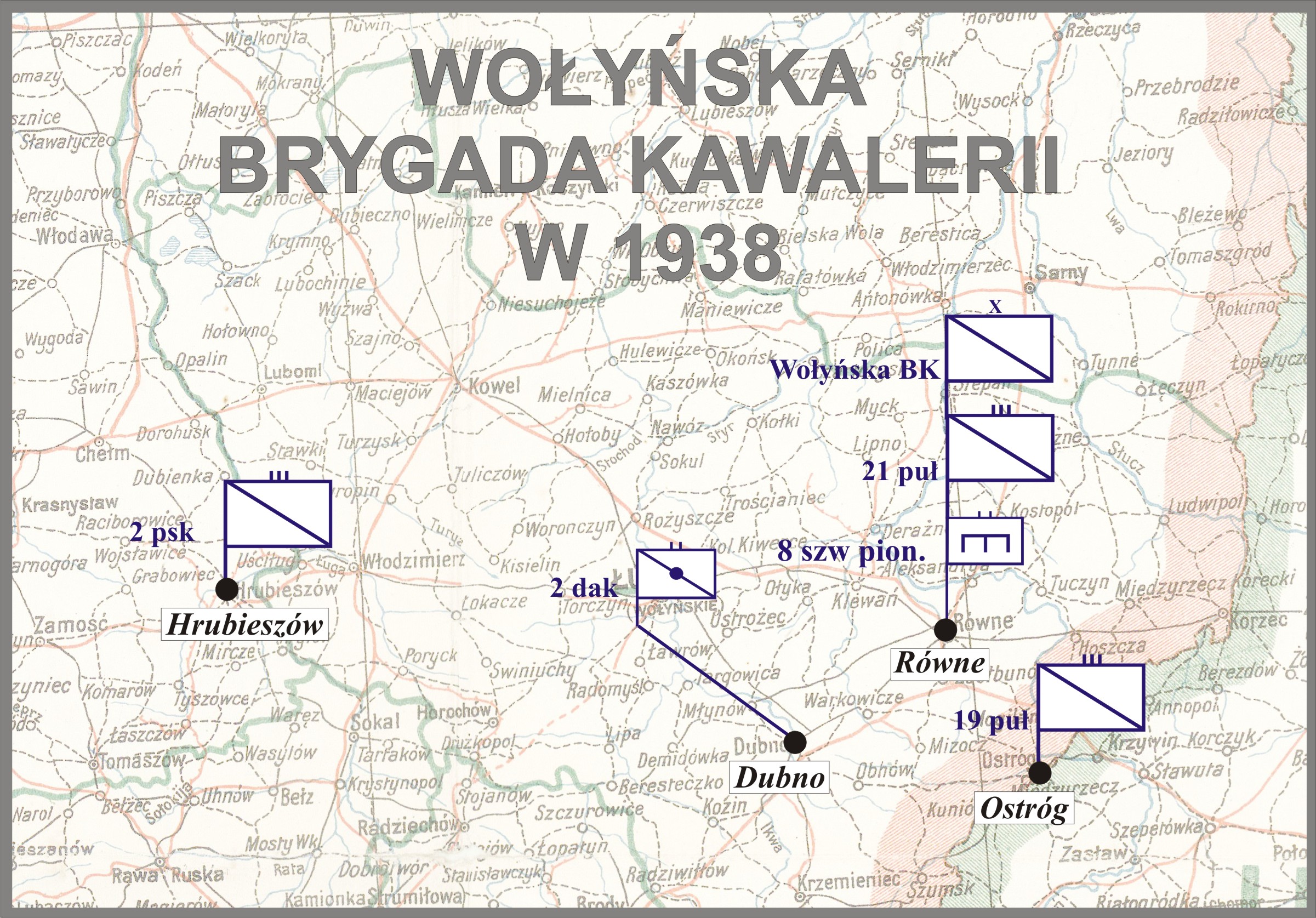
21st Vistula Uhlan Regiment
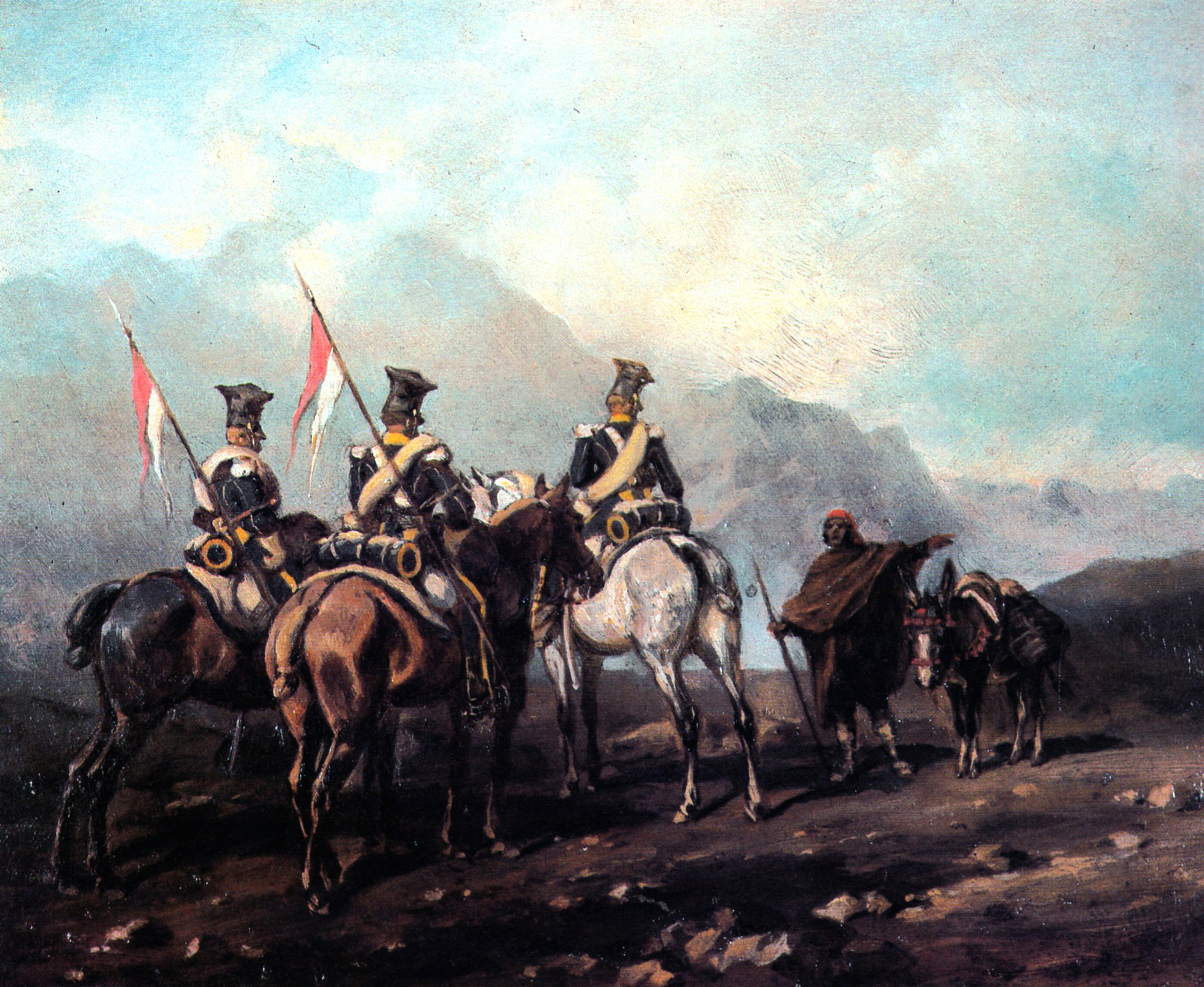
21st Vistula Uhlan Regiment (Polish language, Polish: 21 Pułk Ułanów Nadwiślańskich, 21 puł) was a cavalry unit of the Polish Army in the Second Polish Republic. Formed in 1920, it fought both in the Polish–Soviet War and the Invasion of Poland. The regiment was garrisoned in the town of Rivne, Rowne, Volhynia, and in 1939 belonged to Volhynian Cavalry Brigade. Beginnings The regiment was formed in July 1920, during the Polish–Soviet War, as the ''11th Mounted Border Rifles Regiment'' (''11 Pulk Konnych Strzelcow Granicznych''). Its cadre consisted of NCOs, trained at two military schools, in Ciechanów and Stara Wies near Warsaw. Due to efforts of Colonel Bronislaw Zaniewski, who commanded the Border Rifles, a cavalry regiment was created, based on the NCOs from both schools. On July 24, 1920, NCO's from Ciechanów, commanded by Bohdan Dabrowski, arrived at Stara Wies, and Dabrowski himself was appointed commandant of the whole regiment. In early August 1920, Colonel Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Language
Polish (Polish: ''język polski'', , ''polszczyzna'' or simply ''polski'', ) is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group written in the Latin script. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In addition to being the official language of Poland, it is also used by the Polish diaspora. There are over 50 million Polish speakers around the world. It ranks as the sixth most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional dialects and maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals. The traditional 32-letter Polish alphabet has nine additions (''ą'', ''ć'', ''ę'', ''ł'', ''ń'', ''ó'', ''ś'', ''ź'', ''ż'') to the letters of the basic 26-letter Latin alphabet, while removing three (x, q, v). Those three letters are at times included in an extended 35-letter alphabet, although they are not used in native words. The traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wyszogród
Wyszogród is a town in central Poland, in Masovian Voivodeship, in Płock County, by the Vistula River. The population of Wyszogród was 2,793 in 2004. History The settlement dates back to the 7th century, when there was a Slavic pagan temple at the site. In the 11th century Wyszogród became fortified and started to act as a local centre of commerce. In the 12th century it became the seat of local castellany and soon it became one of the seats of the Dukes of Masovia within fragmented Piast-ruled Poland. Relocated on Magdeburg Law in 1398, Wyszogród became one of the most important inland ports and centres of textile production in the area. Brewing and crafts also developed. In the 16th century, King Sigismund II Augustus approved the statutes of the guilds of tailors and furriers, and Sigismund III Vasa issued new privileges for several guilds. During the Deluge the town was pillaged and burnt by the Swedes. Several subsequent fires destroyed Wyszogród almost completely. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legion Of The Vistula
The Legion of the Vistula ( pl, Legia Nadwiślańska) was a unit of Poles in the service of Napoleonic France, one of the larger Polish legions of the Napoleonic period. Creation of the Legion The Legion was formed in Breslau, Neustadt, Brieg, Neisse and Friedland, in the region of Silesia in February 1807 from an infantry regiment and cavalry regiment in the service of the Kingdom of Naples that were descended from Jan Henryk Dąbrowski's Dąbrowski's Legions and Karol Kniaziewicz's Danube Legion originally raised in the 1790s. The new formation was expanded from the Neapolitan cadre into a formation of three infantry regiments and one cavalry regiment, initially named the Polish-Italian Legion as it had been organized around the Poles formerly in Italian service. Most of the recruits came from ex-Prussian and ex-Austrian territories, particularly Poznań and Pomerania. The Polish-Italian Legion fought its first engagement at the siege of Klodzko and then was transferred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haradzeya
Haradzeya ( be, Гарадзея, russian: Городея, pl, Horodziej, lt, Gorodėja) is an urban-type settlement in Belarus, located in the Nyasvizh District of Minsk Region. History The first known documental record of the village dates back to 1530. Horodziej was a privately owned village located in the Nowogródek County of the Nowogródek Voivodeship of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth until the Second Partition of Poland (1793) when it was annexed by Tsarist Russia. Initially, the village often changed owners, before it became the property of the powerful Radziwiłł family in 1575. A Roman Catholic church was built in the 17th century. The village was briefly occupied by the Germans in 1918 and after Poland regained independence (1918) it came under Polish administration in 1919 and was finally reintegrated with Polish territory after the Polish-Soviet War (1919–1921). Administratively Horodziej was part of the Nowogródek Voivodeship. After the destructi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baranowicze
Baranavichy ( ; be, Бара́навічы, Łacinka: , ; russian: Бара́новичи; yi, באַראַנאָוויטש; pl, Baranowicze) is a city in the Brest Region of western Belarus, with a population (as of 2019) of 179,000. It is notable for an important railway junction and is home to Baranavichy State University. General information The city of Baranavichy is located on the Baranavichy Plain in the interfluve of Shchara and its tributary Myshanka. Baranavichy is located virtually on the straight line, connecting regional centre Brest (206 km) and Minsk (149 km). Nearby cities: Lyakhavichy (17 km), Slonim (42 km), Nyasvizh (51 km), Navahrudak (52 km), and Hantsavichy (72 km). Baranavichy is located on flat terrain where the height difference does not exceed 20 m (from 180 to 200 m above sea level). The altitude of the city is 193 m above sea level. Total length of the city is 10 km from west to east and 7 km from south t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voranava
Voranava or Voronovo ( be, Воранава, russian: Вороново, pl, Woronów, Werenowo, lt, Varanavas) is a town in Belarus, in Grodno Region. It is the administrative center of the Voranava district. It is located about from Lida and from the Belarusian-Lithuanian border. History Within the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Voranava was part of Vilnius Voivodeship. In 1795, the town was acquired by the Russian Empire in the course of the Third Partition of Poland. From 1921 until 1939, Voranava was part of the Second Polish Republic. In September 1939, the town was occupied by the Red Army and, on 14 November 1939, incorporated into the Byelorussian SSR. From 23 June 1941 until 11 July 1944, Voranava was occupied by Nazi Germany and administered as a part of the ''Generalbezirk Weißruthenien Generalbezirk Weissruthenien (General District White Ruthenia) was one of the four administrative subdivisions of ''Reichskommissariat Ostland'', the 1941-1945 civilian occupation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilno
Vilnius ( , ; see also #Etymology and other names, other names) is the capital and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urban area, which stretches beyond the city limits, is estimated at 718,507 (as of 2020), while according to the Vilnius territorial health insurance fund, there were 753,875 permanent inhabitants as of November 2022 in Vilnius city and Vilnius district municipalities combined. Vilnius is situated in southeastern Lithuania and is the second-largest city in the Baltic states, but according to the Bank of Latvia is expected to become the largest before 2025. It is the seat of Lithuania's national government and the Vilnius District Municipality. Vilnius is known for the architecture in its Old Town of Vilnius, Old Town, declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1994. The city was #Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grodno
Grodno (russian: Гродно, pl, Grodno; lt, Gardinas) or Hrodna ( be, Гродна ), is a city in western Belarus. The city is located on the Neman River, 300 km (186 mi) from Minsk, about 15 km (9 mi) from the Polish border and 30 km (19 mi) away from Lithuania. In 2019 the city had 373,547 inhabitants. Grodno is the capital of Grodno Region and Grodno District. Alternative names In Belarusian Classical Orthography (Taraškievica) the city is named as (Horadnia). In Latin it was also known as (), in Polish as , in Lithuanian as , in Latvian as , in German as , and in Yiddish as (Grodne). History The modern city of Gordno originated as a small fortress and a fortified trading outpost maintained by the Rurikid princes on the border with the lands of the Baltic tribal union of the Yotvingians. The first reference to Grodno dates to 1005.word The official foundation year is 1127. In this year Grodno was mentioned in the Primary Chronicle as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eišiškės
Eišiškės (, pl, Ejszyszki, russian: Эйши́шки/Eishishki, be, Эйшы́шкі/Eishyshki, yi, אײשישאָק/Eyshishok/Eishishok) is a small city in southeastern Lithuania on the border with Belarus. It is situated on a small group of hills, surrounded by marshy valley of Verseka and Dumblė Rivers. The rivers divide the town into two parts; the northern part is called Jurzdika. As of the census in 2011, Eišiškės had a population of 3,416. It has a hospital and two high schools (one for Polish and another for Lithuanian students). Names According to the Lithuanian Chronicles, the town was named after Eikšys, possibly one of the sons of Karijotas. According to Yaffa Eliach, "Local Jewish folklore had its own account of how the name of the town came into being: Once upon a time in the early days of the shtetl, a man came home and was greeted by his wife with a special treat of freshly cooked varenie (preserves), made from the berries that grow in such abundance in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Niemen River
The Battle of the Niemen River (sometimes referred to as the Second Battle of Grodno) was the second-greatest battle of the Polish–Soviet War. It took place near the middle Neman River between the cities of Suwałki, Grodno and Białystok. After suffering almost complete defeat in the Battle of Warsaw (1920), Battle of Warsaw (August 1920), Mikhail Tukhachevsky's Red Army forces tried to establish a defensive line, against Józef Piłsudski's counter-attacking Polish Army, running northward from the Polish-Lithuanian border to Polesie, and centering on Grodno. Between September 15 and September 25, 1920, the Poles outflanked the Soviets, once again defeating them. After the mid-October Battle of the Szczara River, the Polish Army had reached the Tarnopol-Dubno-Minsk-Drissa line. Although this part of the conflict is usually referred to as a battle both in Polish and Russian historiography, some historians argue that it was more of a military operation with a series of battles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sokółka
Sokółka (; lt, Sokulka, Sakalinė, be, Саку́лка, yi, סאקאלקע, Sokolke) is a town in northeastern Poland, seat of the Sokółka County in Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is a busy rail junction located on the international Warsaw–Białystok–Grodno line, with additional connections which go to Suwałki and the Lithuanian border. History The settlement was founded as a royal village located on the route connecting Knyszyn and Grodno. Sokółka was granted town rights by King Sigismund III Vasa in 1609. The town's layout with its central square is attributed to starost Antoni Tyzenhauz. In the Third Partition of Poland, in 1795, the town was annexed by Prussia, and in 1807 it passed to the Russian Partition of Poland. In 1861, Walery Wróblewski came to Sokółka and founded a secret organization in preparation for a Polish uprising, which broke out in 1863. He was one of the main organizers of the January Uprising in the territory between Białystok and Grodno. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pruszków
Pruszków ( yi, פּרושקאָוו) is a city in east-central Poland, situated in the Masovian Voivodeship since 1999. It was previously in Warszawa Voivodeship (1975–1998). Pruszków is the capital of Pruszków County, located along the western edge of the Warsaw urban area. In the 1990s and 2000s the city was synonymous with the "Pruszków gang", one of two major organised crime groups in the country. Currently it is best known for being the country's cycling centre with a purpose built indoor velodrome. History Pruszków was incorporated as a town in 1916 during World War I, although the village was first mentioned in chronicles in the 15th century. Within the Polish Crown, it was a private village of Polish nobility, administratively located in the Masovian Voivodeship in the Greater Poland Province. The development of the town was aided by the construction of the Warsaw-Vienna Railway in the 19th century and the construction of the Elektryczna Kolej Dojazd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |