|
20 Virginis
This is the list of notable stars in the constellation A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The origins of the e ... Virgo, sorted by decreasing brightness. See also * List of stars by constellation References * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:List of stars in Virgo *List Virgo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sky, night, but their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed stars, fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterism (astronomy), asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye, all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life star formation, begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Its stellar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spica
Spica is the brightest object in the constellation of Virgo and one of the 20 brightest stars in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation α Virginis, which is Latinised to Alpha Virginis and abbreviated Alpha Vir or α Vir. Analysis of its parallax shows that it is located 250 light-years from the Sun. It is a spectroscopic binary star and rotating ellipsoidal variable; a system whose two stars are so close together they are egg-shaped rather than spherical, and can only be separated by their spectra. The primary is a blue giant and a variable star of the Beta Cephei type. Spica, along with Arcturus and Denebola—or Regulus, depending on the source—forms the Spring Triangle asterism, and, by extension, is also part of the Great Diamond together with the star Cor Caroli. Nomenclature In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omicron Virginis
Omicron Virginis (ο Vir, ο Virginis) is a star in the zodiac constellation of Virgo. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.12. Based upon parallax measurements, it is about 163 light years from the Sun. ο Virginis is a G-type giant star with a stellar classification of G8 IIIa CN-1Ba1CH1. This indicates that it is a Barium star. Typically Barium stars are close binaries with a white dwarf companion, but no companion has been detected for ο Virginis. It has been suggested that an excess SiIV emission flux is due to an unseen white dwarf companion. ο Virginis is a giant star around ten times larger than the Sun. Although it is slightly cooler, it is radiating about 60-132 times the luminosity of the Sun. It is over twice as massive as the Sun and is around a billion years old. A simplified statistical analysis suggests that ο Virginis is likely to be a red giant branch star fusing hydrogen in a shell around an inert hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iota Virginis
Iota Virginis (ι Virginis, abbreviated Iota Vir, ι Vir) is a binary star in the constellation of Virgo. Its apparent magnitude is 4.08. Based on its parallax, it is assumed to be relatively nearby, at . Its two components are designated Iota Virginis A (officially named Syrma , the traditional name for the system) and B. Nomenclature ''ι Virginis'' ( Latinised to ''Iota Virginis'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the two components as ''Iota Virginis A'' and ''B'' derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It bore the traditional name ''Syrma'', derived from the Arabic سرما (تطريز ''sirmā'' "train (of a garment)". In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalogue and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name ''Syrma'' for Iota Virginis on 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
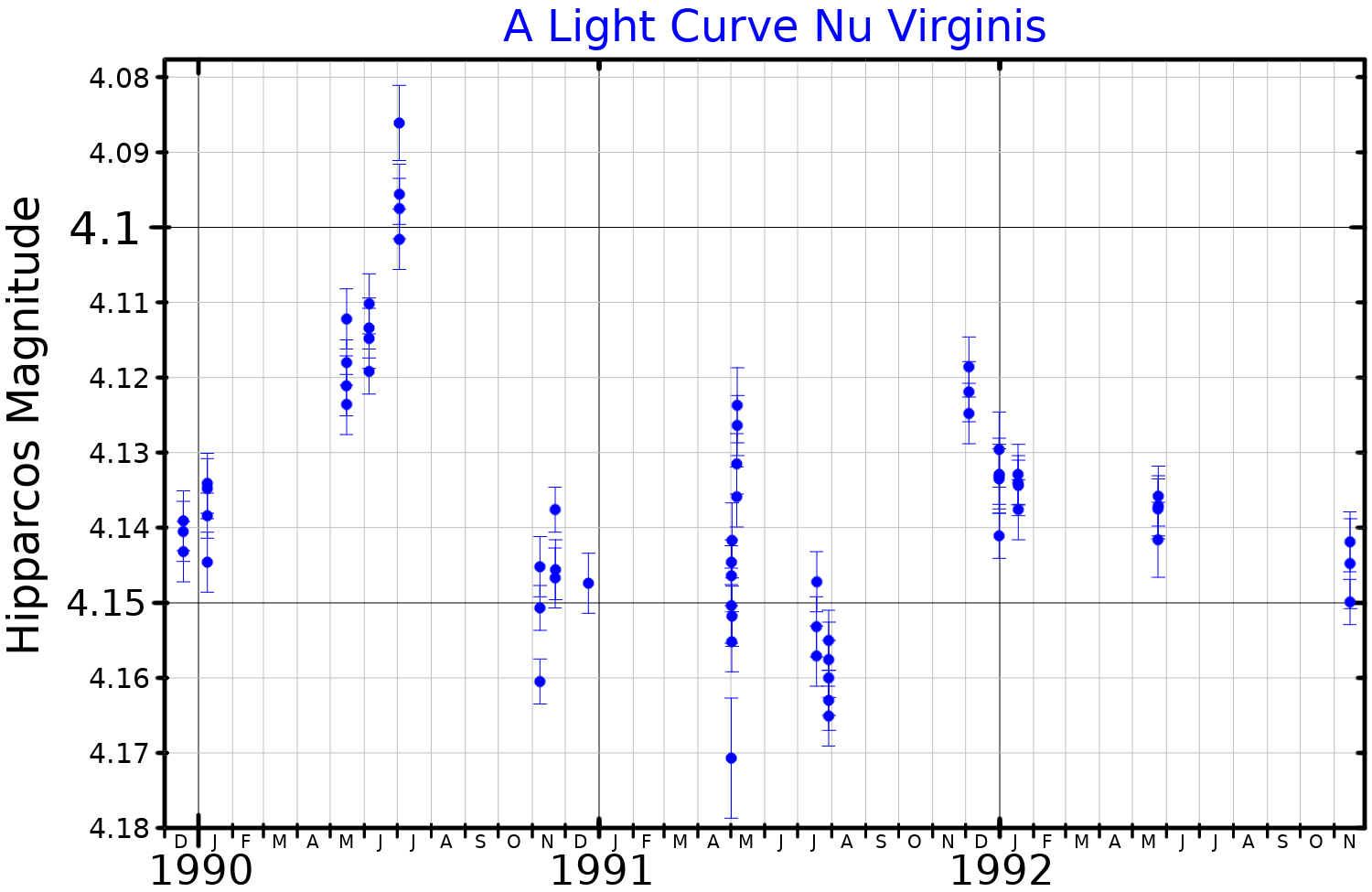
Nu Virginis
ν Virginis, Latinized as Nu Virginis, is a single star in the zodiac constellation of Virgo, located at the western tip of the classic constellation and nearly due south of the prominent star Denebola. It is a red-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.04 and can be seen with the naked eye. Because the star lies near the ecliptic it is subject to occultations by the Moon. Parallax measurements provide an estimated distance of around 294 light years from the Sun, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +50 km/s. This object is an M-type red giant, currently on the asymptotic giant branch, with a stellar classification of M1 III. It is an SRB-type semiregular variable star with its brightness varying by 0.0125 in magnitude. These variations have four periods lasting 11.1, 12.3, 16.8, and 23.7 days. This star has about 1.6 times the mass of the sun, but it has expanded to 54 times the Sun's radius and shines 631 times ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eta Virginis
Eta Virginis (η Virginis, abbreviated Eta Vir, η Vir) is a triple star system in the zodiac constellation of Virgo. From parallax measurements taken during the Hipparcos mission it is about from the Sun. It has a combined apparent visual magnitude of 3.89, bright enough to be seen with the naked eye in dark skies. The system consists of a binary pair designated Eta Virginis A together with a third companion, Eta Virginis B. A's two components are themselves designated Eta Virginis Aa (officially named Zaniah , the traditional name of the system) and Ab. Nomenclature ''η Virginis'' ( Latinised to ''Eta Virginis'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the two constituents as ''Eta Virginis A'' and those of ''A's''components - ''Eta Virginis Aa'' and ''Ab'' - derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It bore the traditional name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mu Virginis
Mu Virginis, Latinized from μ Virginis, is a star in the zodiac constellation of Virgo. It was listed in the ''Calendarium'' of Al Achsasi al Mouakket as ''rijl al-‘awwā’'', Arabic رجل العواء, meaning "The foot of the barking (dog)". With an apparent visual magnitude of 3.88, it is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. The position of the star near the celestial equator means it is visible from most of the Earth. Based upon parallax measurements, Mu Virginis is located some 59.6 light-years from the Sun. Rijl al Awwa is an F-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of F2 V, although it does show some evidence of being a more evolved star. It has an effective temperature of 6,751 K in its outer atmosphere. The estimated age of the star is 1.5 billion years, and it has a relatively high 47.0 km/s projected rotational velocity. A 1990 study of the star gave it a giant star classification, and modeled it with 1.7 times ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
109 Virginis
109 Virginis is a single, white-hued star in the zodiac constellation of Virgo, located some 134.5 light years away from the Sun. It is the seventh-brightest member of this constellation, having an apparent visual magnitude of +3.72. This is an A-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of A0 V, and is a suspected chemically peculiar star. However, Abt and Morrell (1995) gave it a class of A0 IIInn, matching a giant star with "nebulous" lines. It is spinning rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 285 km/s, which is giving the star an oblate shape with an equatorial bulge that is an estimated 31% larger than the polar radius. The star is 320 million years old with 2.58 times the mass of the Sun and about 2.7 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 63 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Virginis
Beta Virginis, a name Latinised from β Virginis, is a star in the equatorial constellation of Virgo. It has the proper name Zavijava (), and, despite its designation ' beta', is the fifth-brightest star in Virgo with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.604. The distance to this star is 35.7 light-years based on parallax, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +4.1 km/s. It is 0.69 of a degree north of the ecliptic, so it can be occulted by the Moon and (rarely) by planets. The next planetary occultation of Beta Virginis will take place on 11 August 2069, by Venus. Properties This is an F-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of F9 V, which means it is generating energy through core hydrogen fusion. Sun-like oscillations have been detected in Beta Virginis, allowing its internal structure to be modeled in more detail. It is around 2.9 billion years old with a projected rotational velocity of 4.3 km/s and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Virginis
Delta Virginis (δ Virginis, abbreviated Del Vir, δ Vir), formally named Minelauva , is a star in the zodiac constellation of Virgo. With an apparent visual magnitude of 3.4, this star is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. Based upon parallax measurements, it is located at a distance of about from the Sun. Nomenclature ''δ Virginis'' ( Latinised to ''Delta Virginis'') is the star's Bayer designation. It bore the traditional, medieval names ''Auva'' and ''Minelauva'' from the Arabic من العواء ''min al-ʽawwāʼ'', meaning "in the lunar mansion of ''ʽawwaʼ''" (a name of unknown meaning). In 2016, the IAU organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name ''Minelauva'' for this star on 30 June 2017 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names. This star, along with Beta Virginis (Zavijava), Gamma Virginis (Porrima), Eta Virginis (Zaniah) and Epsilon Virgini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeta Virginis
Zeta Virginis (ζ Virginis, abbreviated Zeta Vir, ζ Vir) is a binary star in the zodiac constellation of Virgo. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +3.376 and is located about a half degree south of the celestial equator. Based on parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is about distant from the Sun. The two components are designated Zeta Virginis A (officially named Heze , a mid-20th-century name for the system) and B. Nomenclature ''ζ Virginis'' ( Latinised to ''Zeta Virginis'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the two components as ''Zeta Virginis A'' and ''B'' derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Zeta Virginis bore the name ''Heze'' in a 1951 publication, ''Atlas Coeli'' (Skalnate Pleso Atlas of the Heavens), by Czech astronomer Antonín Bečvář. Its origin is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon Virginis
Epsilon Virginis (ε Virginis, abbreviated Epsilon Vir, ε Vir), formally named Vindemiatrix , is a star in the zodiac constellation of Virgo. The apparent visual magnitude of this star is +2.8, making it the third-brightest member of Virgo. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, Vindemiatrix lies at a distance of about from the Sun, give or take a half light-year. Stellar properties Vindemiatrix is a giant star with a stellar classification of G8 III. With 2.6 times the mass of the Sun, it has reached a stage in its evolution where the hydrogen fuel in its core is exhausted. As a result, it has expanded to over ten times the Sun's girth and is now radiating around 77 times as much luminosity as the Sun. This energy is being emitted from its outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 5,086 K, which gives it the yellow-hued glow of a G-type star. Since 1943, the spectrum of this star has served as one of the stable anchor poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |