|
2021 Luxian Earthquake
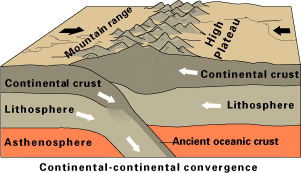
The 2021 Luxian earthquake was a damaging seismic event occurring in the early hours of September 16 at 04:33 China Standard Time. The surface wave magnitude () 6.0 or moment magnitude () 5.4 earthquake struck at a shallow depth of 7.5 km and severe shaking in an area of 4,000 square kilometers was assigned a maximum intensity of VIII on the China seismic intensity scale. Three people were killed and 146 injured when the earthquake struck Lu County, Luzhou, Sichuan Province. At least 36,800 buildings were affected, 7,800 of them seriously damaged or completely destroyed, causing about a quarter of a billion dollars worth of damage. Tectonic setting The active plate tectonics of the Sichuan Basin is dominated by the north–south continental collision of the Indian Plate and Eurasian Plate. As the Indian Plate collides along a convergent plate boundary known as the Main Himalayan Thrust, it being of continental crust does not subduct, rather it plows into the Eurasian P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Standard Time
The time in China follows a single standard time offset of UTC+08:00 (eight hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time), even though the country spans almost five geographical time zones. The official national standard time is called ''Beijing Time'' (BJT, ) domestically and ''China Standard Time'' (CST) internationally. Daylight saving time has not been observed since 1991. China Standard Time (UTC+8) is consistent across Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, Philippines, Singapore, Brunei, Mongolia, etc. History In the 1870s, the Shanghai Xujiahui Observatory was constructed by a French Catholic missionary. In 1880s officials in Shanghai French Concession started to provide a time announcement service using the Shanghai Mean Solar Time provided by the aforementioned observatory for ships into and out of Shanghai. By the end of 19th century, the time standard provided by the observatory had been switched to GMT+08:00. The practice has spread to other coastal ports, and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Collision
In geology, continental collision is a phenomenon of plate tectonics that occurs at convergent boundaries. Continental collision is a variation on the fundamental process of subduction, whereby the subduction zone is destroyed, mountains produced, and two continents sutured together. Continental collision is only known to occur on Earth. Continental collision is not an instantaneous event, but may take several tens of millions of years before the faulting and folding caused by collisions stops. The collision between India and Asia has been going on for about 50 million years already and shows no signs of abating. Collision between East and West Gondwana to form the East African Orogen took about 100 million years from beginning (610 Ma) to end (510 Ma). The collision between Gondwana and Laurasia to form Pangea occurred in a relatively brief interval, about 50 million years long. Subduction zone: the collision site The process begins as two conti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault (geology)
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longmenshan Fault
The Longmenshan Fault () is a thrust fault which runs along the base of the Longmen Mountains in Sichuan province in southwestern China. The strike of the fault plane is approximately NE. Motion on this fault is responsible for the uplift of the mountains relative to the lowlands of the Sichuan Basin to the east. Representing the eastern boundary of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, it is a border formation between the Bayan Kola block in the Plateau and the South China block in the Eurasian Plate. The 2008 Wenchuan, 2013 Lushan and 2022 Ya'an earthquakes occurred along this fault. A study by the China Earthquake Administration (CEA) states: "The late-Cenozoic deformations in this fault (''that caused the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake'') are concentrated in the Guanxian-Jiangyou fracture (hill-front fracture), Yingxiu- Beichuan fracture (mid-fracture), Wenchuan-Mao County fracture (hill-back fracture), and their related folds. The recent Ms 8.0 earthquake occurred on the Yingxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altyn Tagh Fault
The Altyn Tagh Fault (ATF) is a 2,000 km long, active, sinistral (left lateral) strike-slip fault that forms the northwestern boundary of the Tibetan Plateau with the Tarim Basin. It is one of the major sinistral strike-slip structures that together help to accommodate the eastward motion of this zone of thickened crust, relative to the Eurasian Plate. A total displacement of about ~475 km has been estimated for this fault zone since the middle Oligocene, although the amount of displacement, age of initiation and slip rate are disputed. Tectonic setting The Tibetan Plateau is an area of thickened continental crust, a result of the ongoing collision of the Indo-Australian Plate with the Eurasian Plate. The way in which this zone accommodates the collision remains unclear with two end-member models being proposed. The first regards the crust as being made up of a mosaic of strong blocks separated by weak fault zones, the 'microplate' model. The second regards the deformatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xianshuihe Fault System
The Xianshuihe fault system is a major active sinistral (left-lateral) strike-slip fault zone in southwestern China, at the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. It has been responsible for many major earthquakes, and is one of the most seismically active fault zones in this part of China. Tectonic setting The Xianshuihe fault system lies within the complex zone of continental collision between the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate. It forms one of a set of sinistral fault zones that help accommodate the eastward spreading of the Tibetan Plateau. The fault zone defines the northern and eastern edges of the Sichuan-Yunnan block, and the southeastern boundary of the Bayan Har block. Geometry The Xianshuihe fault system comprises several distinct segments, with an overall length of about 350 km. The main segments are the Ganzi (or Ganzi-Yushu), the Xianshuihe, the Anninghe-Zemuhe, and the Xiaojiang faults. Seismicity Movements on this fault system have been responsible for man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the Tibet Autonomous Region, most of Qinghai, western half of Sichuan, Southern Gansu provinces in Western China, southern Xinjiang, Bhutan, the Indian regions of Ladakh and Lahaul and Spiti (Himachal Pradesh) as well as Gilgit-Baltistan in Pakistan, northwestern Nepal, eastern Tajikistan and southern Kyrgyzstan. It stretches approximately north to south and east to west. It is the world's highest and largest plateau above sea level, with an area of (about five times the size of Metropolitan France). With an average elevation exceeding and being surrounded by imposing mountain ranges that harbor the world's two highest summits, Mount Everest and K2, the Tibetan Plateau is often referred to as "the Roof of the World". The Tibetan Plateau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduct
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with the average rate of convergence being approximately two to eight centimeters per year along most plate boundaries. Subduction is possible because the cold oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle underlying the cold, rigid lithosphere. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
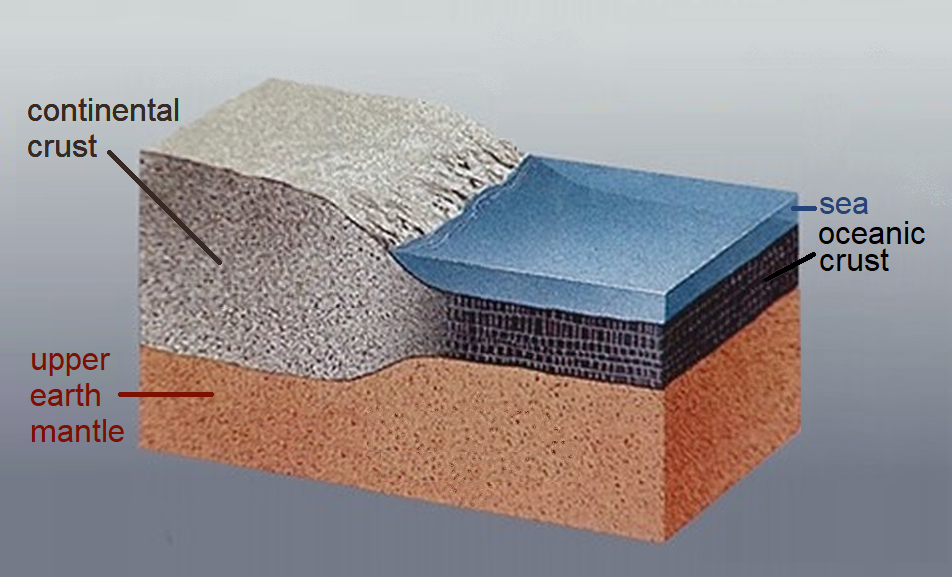
Continental Crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called ''sial'' because its bulk composition is richer in aluminium silicates (Al-Si) and has a lower density compared to the oceanic crust, called ''sima'' which is richer in magnesium silicate (Mg-Si) minerals. Changes in seismic wave velocities have shown that at a certain depth (the Conrad discontinuity), there is a reasonably sharp contrast between the more felsic upper continental crust and the lower continental crust, which is more mafic in character. The continental crust consists of various layers, with a bulk composition that is intermediate (SiO2 wt% = 60.6). The average density of continental crust is about , less dense than the ultramafic material that makes up the mantle, which has a density of around . Continental crust is also less dense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Himalayan Thrust
The Main Himalayan Thrust (MHT) is a décollement under the Himalaya Range. This thrust fault follows a NW-SE strike, reminiscent of an arc, and gently dip towards the north, beneath the region. It is the largest active continental megathrust fault in the world. Overview The MHT accommodates crustal shortening of India and Eurasia as a result of the ongoing collision between the Indian and Eurasian plates. Deformation of the crust is also accommodated along splay structures including the Main Frontal Thrust (MFT), Main Boundary Thrust (MBT), Main Central Thrust (MCT) and possibly the South Tibetan Detachment. The MHT is the root detachment of these splays. At this present moment, the MFT and MHT accounts for almost the entire rate of convergence (15-21 mm/yr). This fault defines where the India subcontinent is underthrust beneath the Himalayan orogenic wedge. In April 2015, a section of the MHT produced a blind rupture earthquake, killing nearly 9,000 Nepalese. Associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |