|
2015 Tuscan Regional Election
The Tuscan regional election of 2015 took place on 31 May 2015. Electoral system Tuscany uses its own legislation of 2014 to elect its Regional Council. The councillors are elected in provincial constituencies by proportional representation using the D'Hondt method. Florence constituency is further divided into 4 sub-constituencies. Preferential voting is allowed: a maximum of two preferences can be expressed for candidates of the same party list and provided the two chosen candidates are of different gender. In this system parties are grouped in alliances, supporting a candidate for the post of President of Tuscany. The candidate receiving at least 40% of the votes is elected to the post and his/her list (or the coalition) is awarded a majority in the Regional Council. If no candidate gets more than 40% of the votes, a run-off is held fourteen days after, with only the two top candidates from the first round allowed. The winning candidate is assured a majority in the Regional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Council Of Tuscany
The Regional Council of Tuscany (''Consiglio Regionale della Toscana'') is the legislative assembly of Tuscany. It was first elected in 1970, when the ordinary regions were instituted, on the basis of the Constitution of Italy of 1948. Composition The Regional Council of Tuscany was originally composed of 50 regional councillors. In the 2005 regional election the number of councillors increased to 65, while in the 2010 regional election it was reduced to 53. Following the 2014 regional electoral reform the number of regional councillors was reduced to 40, with an additional seat reserved for the President of the Region. Political groups After the 2020 regional election, the Regional Council of Tuscany is currently composed of the following political groups: Historical composition ;Notes Presidents This is a list of the Presidents of the Regional Council (Italian: ''Presidenti del Consiglio regionale''): ;Notes See also * Regional council *Politics of Tuscany *Pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Grosseto
The province of Grosseto ( it, links=no, provincia di Grosseto) is a province in the Tuscany region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Grosseto. As of 2013 the province had a total population of 225,098 people. Geography The Province of Grosseto completely occupies the southern end of Tuscany, and with a territorial area of , it is the most extensive in the region and one of the least dense in population in Italy. The province is bordered to the northwest by the Province of Livorno, to the north by the Province of Pisa, to the northeast by the Province of Siena, and to the southeast by the Province of Viterbo in Lazio. To the south is the Tyrrhenian Sea, which includes the southern islands of the Tuscan archipelago, including Isola del Giglio and the smaller Giannutri islands and Formiche di Grosseto and Formica di Burano. The Arcipelago Toscano National Park spans both the provinces of Grosseto and Livorno, and includes the seven main islands of the Tuscan Archipelago: Elba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
More Tuscany
More Tuscany (''Più Toscana'', PT) is a regionalist political party in Italy active in Tuscany, Italy. The party was formed in October 2012 by a group of splinters from Lega Nord Toscana (LNT) led by Antonio Gambetta Vianna, a former president of the party, and Gian Luca Lazzeri, who were supporters of Claudio Morganti, former leader of LNT and MEP. PT, which is defined by its members as a research institute, promotes the knowledge, appreciation and advancement of the "Tuscan people", its culture, heritage and traditions. Morganti's leadership was openly contested by some party members and, between April and December 2011, two of the four LNT regional councillors left in protest, even though Morganti had resigned from party secretary in September. In October 2012 the two remaining regional councillors of the party, Vianna and Lazzeri, responded to the emphasis posed by Lega Nord's federal secretary Roberto Maroni on the North and the establishment of a Padanian euroregion b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lega Toscana (2011)
Lega Toscana ("Tuscany League", LT) is a regionalist political party in Italy active in Tuscany. The party was formed in January 2011 as Lega per la Toscana ("League for Tuscany") by a group of splinters from Lega Nord Toscana (LNT) led by Emilio Paradiso, a former president of the party, and Federico Tosoni, both based in Prato. They opposed Lega Nord's return to separatism, while they were strong proponents of federalism. As well as other splinters who had earlier formed Tuscan Identity, Paradiso and Tosoni had been rivals of Claudio Morganti, former leader of LNT and MEP. In January 2012 the party was joined by a group of LNT splinters from the province of Lucca led by Franco Paiuzza. In the 2015 regional election a joint list of the League for Tuscany and More Tuscany won 0.6% of the vote. In the local elections of 2019, Emilio Paradiso ran for mayor of Prato. Eventually, Paradiso and his party scored just 1.3% of the votes and failed the election to the municipal counc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forza Italia (2013)
Forza ItaliaThe name is not usually translated into English: ''forza'' is the second-person singular imperative of ''forzare'', in this case translating to "to compel" or "to press", and so means something like "Forward, Italy", "Come on, Italy" or "Go, Italy!". ''Forza Italia!'' was used as a sport slogan, and was also the slogan of Christian Democracy in the 1987 general election (see Giovanni Baccarin, ''Che fine ha fatto la DC?'', Gregoriana, Padova 2000). See Forza Italia for details. (transl. "Forward Italy", "Come on Italy" or "Let's go Italy"; FI) is a centre-right political party in Italy, whose ideology includes elements of liberal conservatism, Christian democracy and liberalism. FI is a member of the European People's Party. Silvio Berlusconi (former Prime Minister of Italy, 1994–1995, 2001–2006, and 2008–2011) is the party's leader and president, while Antonio Tajani (former President of the European Parliament, 2017–2019) functions as vice president and na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centre-right Coalition (Italy)
The centre-right coalition ( it, coalizione di centro-destra) is an alliance of political parties in Italy, active—under several forms and names—since 1994, when Silvio Berlusconi entered politics and formed his Forza Italia party. Despite its name, the alliance mostly falls on the right-wing of the political spectrum. In the 1994 general election, under the leadership of Berlusconi, the centre-right ran with two coalitions, the Pole of Freedoms in northern Italy and Tuscany (mainly Forza Italia and the Northern League) and the Pole of Good Government (mainly Forza Italia and National Alliance) in central and southern Italy. In the 1996 general election, after the Northern League had left in late 1994, the centre-right coalition took the name of Pole for Freedoms. The Northern League returned in 2000, and the coalition was re-formed as the House of Freedoms; this lasted until 2008. Since 2008, when Forza Italia and National Alliance merged into The People of Freedom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Socialist Party (2007)
The Italian Socialist Party ( it, Partito Socialista Italiano, PSI) is a social-democratic political party in Italy. The party was founded in 2007–2008 by the merger of the following social-democratic parties and groups: Enrico Boselli's Italian Democratic Socialists (legal successor of the Italian Socialist Party), the faction of the New Italian Socialist Party led by Gianni De Michelis, The Italian Socialists of Bobo Craxi, Democracy and Socialism of Gavino Angius, the Association for the Rose in the Fist of Lanfranco Turci, ''Socialism is Freedom'' of Rino Formica and some other minor organizations. Until October 2009, the party was known as Socialist Party ( it, Partito Socialista, PS). From 2008 to 2019, Riccardo Nencini from Tuscany has been party leader. Elected senator with the Democratic Party in 2013 and re-elected in 2018, he was Deputy Minister of Infrastructures and Transports from 2014 to 2019 ( Renzi Cabinet and Gentiloni Cabinet). In March 2019, Nencini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centre-left Coalition (Italy)
The centre-left coalition ( it, coalizione di centro-sinistra) is an alliance of political parties in Italy active, under several forms and names, since 1995 when The Olive Tree was formed under the leadership of Romano Prodi. The centre-left coalition has ruled the country for more than 15 years between 1996 and 2022. In the 1996 general election The Olive Tree consisted of the majority of both the left-wing Alliance of Progressives and the centrist Pact for Italy, the two losing coalitions in the 1994 general election, the first under a system based primarily on first-past-the-post voting. In 2005 The Union was founded as a wider coalition to contest the 2006 general election, which later collapsed during the 2008 political crisis, with the fall of the Prodi II Cabinet. In recent history, the centre-left coalition has been built around the Democratic Party (PD), which was established in 2007 from a merger of Democrats of the Left and Democracy is Freedom, the main p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Siena
The province of Siena ( it, provincia di Siena, link=no, ) is a province in Tuscany, Italy. Its capital is the city of Siena. Geography The province is divided into seven historical areas: * Alta Val d'Elsa * Chianti senese * The urban area of (Monteriggioni and Siena) * Val di Merse * Crete senesi Val d'Arbia * Val di Chiana senese * Val d'Orcia and Amiata The area is a hilly one: in the north is Colline del Chianti; Monte Amiata is the highest point at ; and in the south is Monte Cetona. To the west are the Colline Metallifere (“Metalliferous Hills”), whilst the Val di Chiana lies to east. Historically, the province corresponds to the northeastern portion of the former Republic of Siena. The chief occupations are agricultural (wheat, grapes and fruit) and silk culture. The wine known as Chianti is produced here as well as in other parts of Tuscany: the Chianti Colli Senesi, however, is limited to this province. Apart from the city of Siena the principal towns are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Prato
The province of Prato ( it, provincia di Prato) is a province in the Tuscany region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Prato. It was formed from part of the province of Florence in 1992. The province has an area of and a total population of about 250,000. There are seven comune The (; plural: ) is a local administrative division of Italy, roughly equivalent to a township or municipality. It is the third-level administrative division of Italy, after regions ('' regioni'') and provinces ('' province''). The can ...s (municipalities) in the province. Notable residents * Birthplace of footballer Paolo Rossi. * Birthplace and current residence of olympic gymnast Jury Chechi. * Birthplace of actor and comedian Roberto Benigni. * Birthplace of cyclist Fiorenzo Magni. Municipalities and population Government List of presidents of the province of Prato External links Official website Events in PratoStatistical data [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Pistoia
The province of Pistoia ( it, provincia di Pistoia) is a province in the Tuscany region of central Italy. Its capital is the city of Pistoia and the province is landlocked. It has an area of and a total population of 291,788 inhabitants (as of 2015). There are 22 ''communes'' in the province. The province was formed in 1927 under the rule of Mussolini, and had the lowest income per capita in Tuscany in 1966 due to high poverty levels. This is because the province was mainly agricultural before World War II ended, and has since had to rapidly progress towards industrial capitalism and abandon its agricultural roots. The population of the province has recently been increasing, moving from 268,437 in 2011 to around 292,000 in 2015. The Mountains of Pistoia and the resorts Abetone and Val di Luce are tourist destinations for skiers, and the province contains a combination of flat land such as the area of the valley of the Ombrone and the river flowing through it, and mountainous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
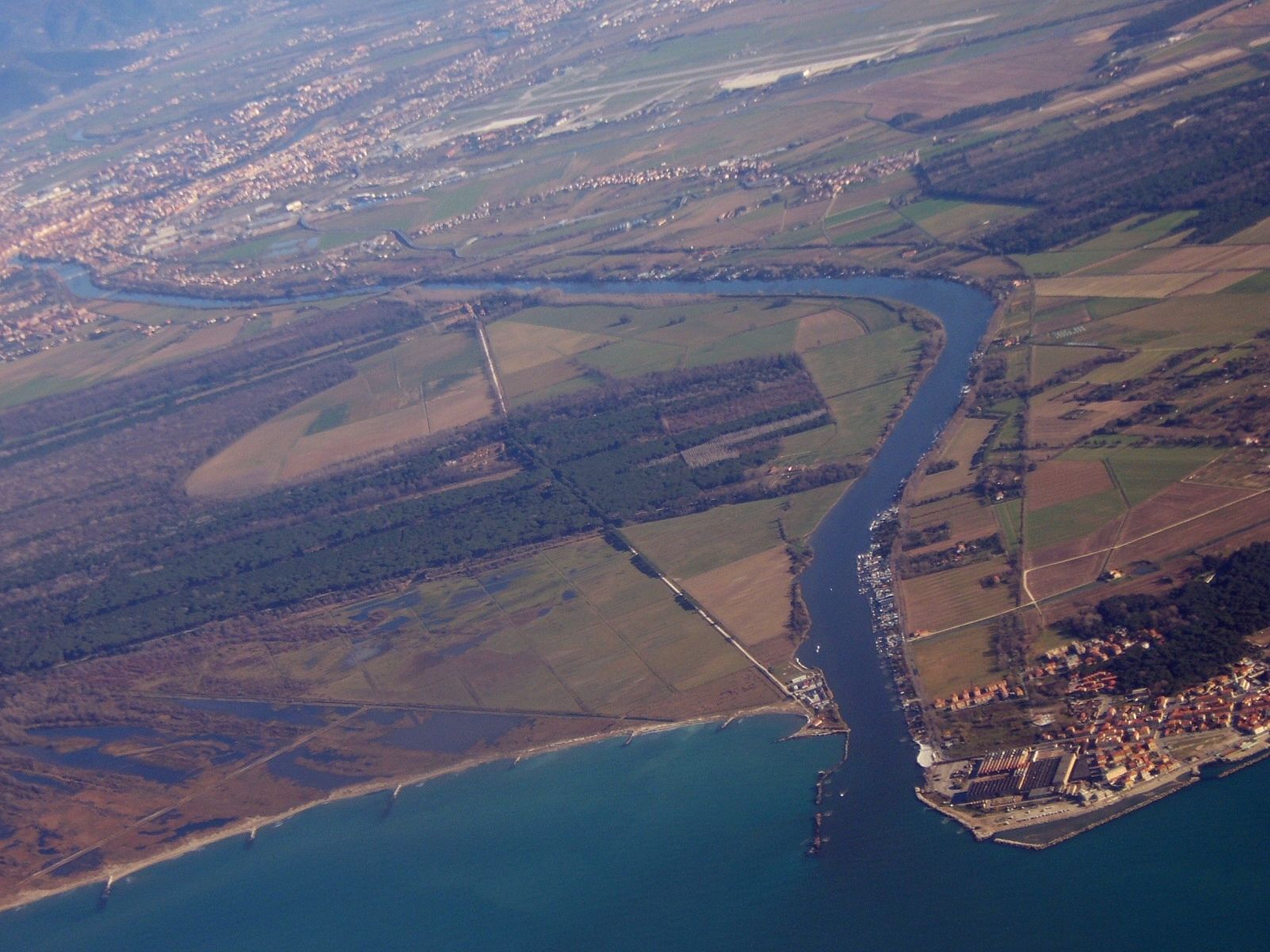
Province Of Pisa
The province of Pisa ( it, provincia di Pisa) is a province in the Tuscany region of central Italy. Its capital is the city of Pisa. With an area of and a total population of 421,642 (), it is the second most populous and fifth largest province of Tuscany. It is subdivided into 37 ''comuni''. With a history that dates to the Etruscans and Phoenicians, the province achieved considerable power and influence in the Mediterranean in the 12th and 13th centuries. Pisa, the provincial capital, is known for its Leaning Tower, and other historic landmarks that attract tourists. History The area has a long maritime history dating back to the Etruscans, the Phoenicians and the Gauls. Under the Roman Empire, it was responsible for naval battles against the Ligurians, Gauls and Carthaginians, becoming a Roman colony in 180 B.C. and gaining further colonial independence under Julius Caesar. Thanks to its complex river system, with the fall of the Roman Empire, Pisa did not suffer unduly and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)
