|
2010 Viennese State Election
The 2010 Viennese state election was held on 10 October 2010 to elect the members of the Gemeinderat and Landtag of Vienna. The Social Democratic Party of Austria (SPÖ) lost its absolute majority for the first time since 1996. The Freedom Party of Austria (FPÖ) became the second largest party on a swing of eleven percentage points, while the Austrian People's Party (ÖVP) and The Greens both suffered losses. Mayor and Governor Michael Häupl was ultimately re-elected after the SPÖ formed a coalition with The Greens, the first state-level " red-green" coalition in Austrian history. Background The Viennese constitution mandates that cabinet positions in the city government (city councillors, german: Stadtsräten) be allocated between parties proportionally in accordance with the share of votes won by each; this is known as Proporz. The number of city councillors is voted upon by the Landtag after each election, and may legally vary between nine and fifteen. City councillors are d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemeinderat And Landtag Of Vienna
As Vienna, the capital of Austria is both a city and a state, the 100 members of the Municipal Council (''Gemeinderat'') of the city of Vienna also act as members of the Landtag (legislative assembly) of the state of Vienna. Members serve for five years. While the municipal council and the state parliament consist of the same members, they meet separately, complete with separate presiding officers: the chairman of the Municipal Council and the . This is because the Vienna City Constitution requires city and state business to be kept separate. When the deputies meet as the Municipal Council, they can only deal with matters of the city, but not the affairs of the state. When the deputies meet as the Landtag, they may only deal with the matters of the state, but not the affairs of the city. Thus, the legal situation in Vienna is different to that in other city-states such as Berlin or Hamburg. Gemeinderat of Vienna The Gemeinderat, formed for the first time after the revolution in 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proporz
''Proporz'' (, from german: Proportionalität, "proportionality") is a long-standing practice in the Second Austrian Republic in which positions in government are distributed between political parties in a manner proportional to their electoral or public support. More broadly, it describes a culture of power sharing and consensus between Austria's two major parties, the Austrian People's Party (ÖVP) and the Social Democratic Party of Austria (SPÖ), which developed throughout the period of grand coalition government from 1945 to 1966. During this time, partisan divisions were established in most government institutions and the public service, designed to balance the influence of both parties. Much of the system has been dismantled over time, particularly since the 1990s. While in 1999 all but one of the nine federal states operated ''Proporz'' systems, five have since formally abolished them. Some aspects, such as its application on a municipal level, endure to this day. Origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberal Forum
The Liberal Forum (german: Liberales Forum, LiF) was a centrist, Liberalism in Austria, liberal political party in Austria. The party was active from February 1993 to January 2014, when the party merged into NEOS – The New Austria. A member of the Liberal International and the Alliance of Liberals and Democrats for Europe Party, it was founded as a classical liberal split from the FPÖ due to its right-wing populist stances and was placed on the libertarian/post-materialist on a two-axis political spectrum, alongside The Greens – The Green Alternative, in a 2000 comparative analysis among Austrian political parties. Founding The Liberal Forum (LiF) was founded on 4 February 1993, when liberals in the Freedom Party of Austria (FPÖ), including five members of the National Council of Austria, left the party. The five ''Nationalrat'' members were Heide Schmidt, Klara Motter, Friedhelm Frischenschlager, Hans Helmut Moser, and Thomas Barmüller. Heide Schmidt (who was third pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist Party Of Austria
The Communist Party of Austria (german: Kommunistische Partei Österreichs, KPÖ) is a communist party in Austria. Established in 1918 as the Communist Party of Republic of German-Austria, German-Austria (KPDÖ), it is one of the world's oldest Communist party, communist parties. The KPÖ was banned between 1933 and 1945 under both the Austrofascism, Austrofascist regime and the Nazi Germany, Nazi German administration of Austria after the 1938 ''Anschluss''. It played an important role in the Austrian resistance against the Nazi Party, Nazis. The party currently holds two seats in the Styrian ''Landtag'' (States of Austria, state parliament), but has not had representation in the National Council (Austria), National Council (''Nationalrat'', Austria's federal parliament) since 1959. In the 2019 Austrian legislative election, legislative election held on 29 September 2019, it won only 0.7% of the votes (32,736 out of a total of 4,835,469), well below the 4% minimum to obtain seat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euroscepticism
Euroscepticism, also spelled as Euroskepticism or EU-scepticism, is a political position involving criticism of the European Union (EU) and European integration. It ranges from those who oppose some EU institutions and policies, and seek reform (''Eurorealism'', ''Eurocritical'', or ''soft Euroscepticism''), to those who oppose EU membership and see the EU as unreformable (''anti-European Unionism'', ''anti-EUism'', or ''hard Euroscepticism''). The opposite of Euroscepticism is known as ''pro-Europeanism'', or ''European Unionism''. The main drivers of Euroscepticism have been beliefs that integration undermines national sovereignty and the nation state,''Euroscepticism or Europhobia: Voice vs Exit?'' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right-wing Populism
Right-wing populism, also called national populism and right-wing nationalism, is a political ideology that combines right-wing politics and populist rhetoric and themes. Its rhetoric employs anti-elitist sentiments, opposition to the Establishment, and speaking to or for the "common people". Recurring themes of right-wing populists include neo-nationalism, social conservatism, and economic nationalism. Frequently, they aim to defend a national culture, identity, and economy against perceived attacks by outsiders. Right-wing populism in the Western world is generally associated with ideologies such as anti-environmentalism, anti-globalization, nativism, and protectionism. In Europe, the term is often used to describe groups, politicians, and political parties generally known for their opposition to immigration, especially from the Muslim world, and for Euroscepticism. Right-wing populists may support expanding the welfare state, but only for those they deem fit to receive i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
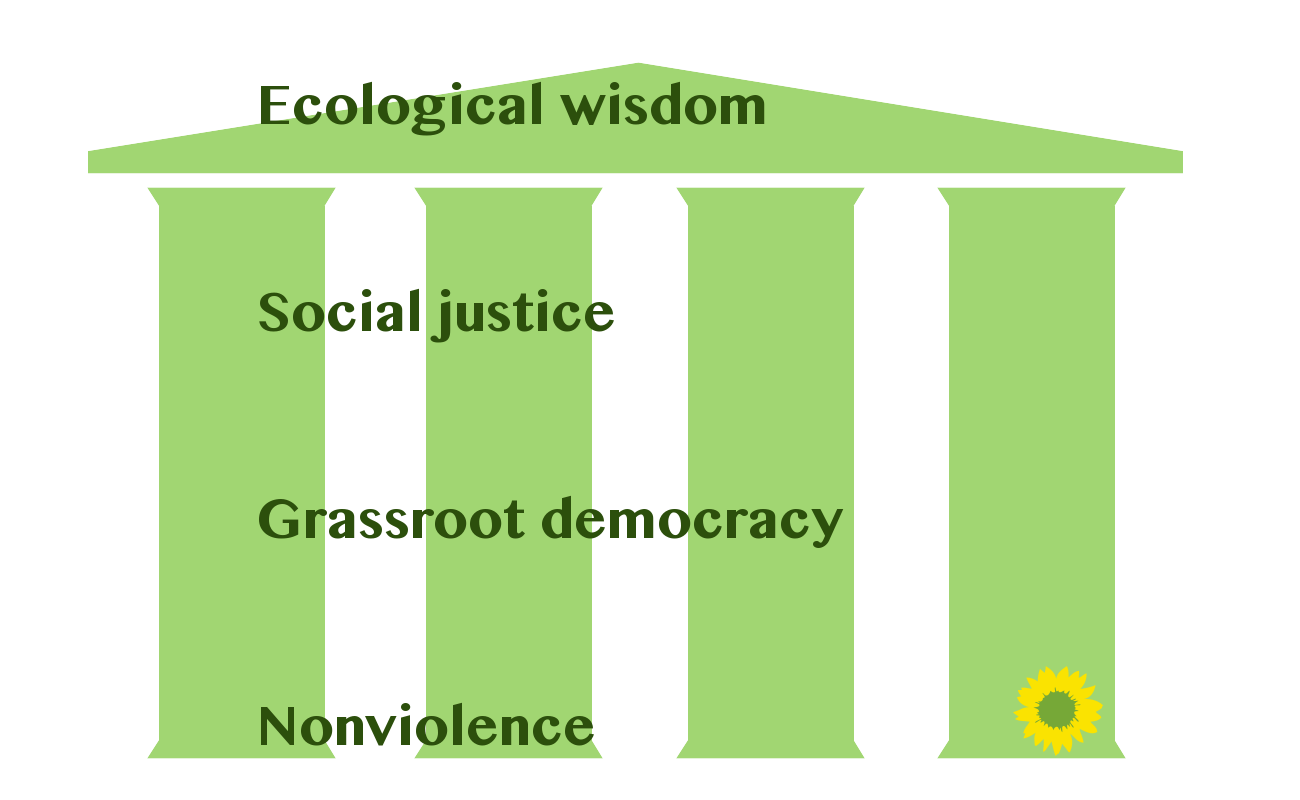
Green Politics
Green politics, or ecopolitics, is a political ideology that aims to foster an ecologically sustainable society often, but not always, rooted in environmentalism, nonviolence, social justice and grassroots democracy. Wall 2010. p. 12-13. It began taking shape in the western world in the 1970s; since then Green parties have developed and established themselves in many countries around the globe and have achieved some electoral success. The political term green was used initially in relation to ''die Grünen'' (German for "the Greens"), a green party formed in the late 1970s. The term political ecology is sometimes used in academic circles, but it has come to represent an interdisciplinary field of study as the academic discipline offers wide-ranging studies integrating ecological social sciences with political economy in topics such as degradation and marginalization, environmental conflict, conservation and control and environmental identities and social movements. Supporte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Democracy
Christian democracy (sometimes named Centrist democracy) is a political ideology that emerged in 19th-century Europe under the influence of Catholic social teaching and neo-Calvinism. It was conceived as a combination of modern democratic ideas and traditional Christian values, incorporating social justice and the social teachings espoused by the Catholic, Lutheran, Reformed, Pentecostal, and other denominational traditions of Christianity in various parts of the world. After World War II, Catholic and Protestant movements of neo-scholasticism and the Social Gospel shaped Christian democracy. On the traditional left-right political spectrum Christian Democracy has been difficult to pinpoint as Christian democrats rejected liberal economics and individualism and advocated state intervention, but simultaneously defended private property rights against excessive state intervention. This has meant that Christian Democracy has historically been considered centre left on eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Democracy
Social democracy is a Political philosophy, political, Social philosophy, social, and economic philosophy within socialism that supports Democracy, political and economic democracy. As a policy regime, it is described by academics as advocating Economic interventionism, economic and social interventions to promote social justice within the framework of a liberal-democratic polity and a capitalist-oriented mixed economy. The protocols and norms used to accomplish this involve a commitment to Representative democracy, representative and participatory democracy, measures for income redistribution, regulation of the economy in the Common good, general interest, and social welfare provisions. Due to longstanding governance by social democratic parties during the post-war consensus and their influence on socioeconomic policy in Northern and Western Europe, social democracy became associated with Keynesianism, the Nordic model, the social-liberal paradigm, and welfare states within po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D'Hondt Method
The D'Hondt method, also called the Jefferson method or the greatest divisors method, is a method for allocating seats in parliaments among federal states, or in party-list proportional representation systems. It belongs to the class of highest-averages methods. The method was first described in 1792 by future U.S. president Thomas Jefferson. It was re-invented independently in 1878 by Belgian mathematician Victor D'Hondt, which is the reason for its two different names. Motivation Proportional representation systems aim to allocate seats to parties approximately in proportion to the number of votes received. For example, if a party wins one-third of the votes then it should gain about one-third of the seats. In general, exact proportionality is not possible because these divisions produce fractional numbers of seats. As a result, several methods, of which the D'Hondt method is one, have been devised which ensure that the parties' seat allocations, which are of whole numbers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hare Quota
The Hare quota (also known as the simple quota) is a formula used under some forms of proportional representation. In these voting systems the quota is the number of votes that guarantees a candidate, or a party in some cases, captures a seat. The Hare quota is the total number of votes divided by the number of seats to be filled. This is the simplest quota, but the Droop quota is mostly used currently. The Hare quota can be used in the single transferable vote (STV-Hare) system and the largest remainder method (LR-Hare) and other quota rule compatible methods of party-list proportional representation. Both versions are named after the political scientist Thomas Hare, but the largest remainder method in which it is used is also sometimes called the Hare–Niemeyer method (after Horst Niemeyer) or the Hamilton method (after Alexander Hamilton). Formula The Hare quota may be given as: :\frac where *Total votes = the total valid poll; that is, the number of valid (unspoilt) vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |