|
2010 In Archosaur Paleontology
The year 2010 in Archosaur paleontology was eventful. Archosaurs include the only living dinosaur group — birds — and the reptile crocodilians, plus all extinct dinosaurs, extinct crocodilian relatives, and pterosaurs. Archosaur palaeontology is the scientific study of those animals, especially as they existed before the Holocene Epoch began about 11,700 years ago. The year 2010 in paleontology included various significant developments regarding archosaurs. This article records new taxa of fossil archosaurs of every kind that have been described during the year 2010, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleontology of archosaurs that occurred in the year 2010. Newly named crurotarsans Newly named basal dinosauriforms Newly named non-avian dinosaurs * A new family of allosauroid theropods, Neovenatoridae, is published by Benson, Carrano, and Brusatte. * A new family of tyrannosauroid theropods, Proceratosauridae Proceratosauridae is a Fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosaurs
Archosauria () is a clade of diapsids, with birds and crocodilians as the only living representatives. Archosaurs are broadly classified as reptiles, in the cladistic sense of the term which includes birds. Extinct archosaurs include non-avian dinosaurs, pterosaurs, and extinct relatives of crocodilians. Modern paleontologists define Archosauria as a crown group that includes the most recent common ancestor of living birds and crocodilians, and all of its descendants. The base of Archosauria splits into two clades: Pseudosuchia, which includes crocodilians and their extinct relatives, and Avemetatarsalia, which includes birds and their extinct relatives (such as non-avian dinosaurs and pterosaurs). Older definitions of the group Archosauria rely on shared morphological characteristics, such as an antorbital fenestra in the skull, serrated teeth, and an upright stance. Some extinct reptiles, such as proterosuchids and euparkeriids, possessed these features yet originate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metriorhynchus
''Metriorhynchus'' is an extinct genus of marine crocodyliform that lived in the oceans during the Late Jurassic. The type species, ''M. brevirostris'' was named in 1829 as a species of ''Steneosaurus'' before being named as a separate genus by the German palaeontologist Christian von Meyer in 1832. The name ''Metriorhynchus'' means "Moderate snout", and is derived from the Greek ''Metrio''- ("moderate") and -''rhynchos'' ("snout"). Discovery and species Fossil specimens referrable to ''Metriorhynchus'' are known from Kimmeridgian (Late Jurassic) deposits of France. Valid species Only one valid species is recognized today, the type species ''M. geoffroyii'' (now called ''M. brevirostris''). ''"Metriorhynchus" hastifer'' and ''"M." palpebrosus'' are generically distinct from the ''Metriorhynchus'' type species, with ''hastifer'' being recovered as a geosaurine. Species in this genus were traditionally classed into two skull groups: longirostrine (long, narrow jaws) and brevirost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teleidosaurus
''Teleidosaurus'' is an extinct genus of carnivorous metriorhynchoid crocodyliform from Middle Jurassic (late Bajocian to early Bathonian stage) deposits of Normandy, France.Wilkinson LE, Young MT, Benton MJ. 2008. A new metriorhynchid crocodilian (Mesoeucrocodylia: Thalattosuchia) from the Kimmeridgian (Upper Jurassic) of Wiltshire, UK. ''Palaeontology'' 51 (6): 1307-1333. The name ''Teleidosaurus'' means "Complete lizard", and is derived from the Greek '- ("complete") and -''sauros'' ("lizard"). Discovery The type species was named ''Teleosaurus Calvadosii'' icby Jacques Amand Eudes-Deslongchamps in 1866;Eudes-Deslongchamps, J.A. 1866. Description d'une espèce inédite de Téléosaure des environs de Caen, le ''Teleosaurus calvadosii''. ''Bulletin Soc. Linn. Normandie'' 2 (1): 112-118. however, it was his son, Eugène Eudes-Deslongchamps who erected the generic name ''Teleidosaurus'' later in 1869 Eudes-Deslongchamps, E. 1869. Notice sur les animaux fossiles de la famill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eoneustes
''Eoneustes'' (meaning "dawn swimmer") is an extinct genus of metriorhynchoid crocodyliform from Middle Jurassic (late Bajocian to early Bathonian stage) deposits of France. ''Eoneustes'' was a carnivore that lived in the oceans and spent much, if not all, its life out at sea. Discovery and species *''E. bathonicus'':Mercier J. 1933. Contribution l’étude des Métriorhynchidés (crocodiliens). ''Annales de Paléontologie'' 22: 99-119. Western Europe (France) of the Middle Jurassic (early Bathonian). It is known from holotype from Calvados of Normandy, that lost during the Second World War. *''E. gaudryi'':Collot L. 1905. Reptile jurassique (''Teleidosaurus gaudryi'') trouvé à St-Seine-l'Abbaye (Côte-d'Or). ''Memoire Acad. Sci. Arts et Belles-Lettres'' 10: 41-45. Western Europe (France) of the Middle Jurassic (late Bajocian to early Bathonian). It is known from the holotype NHM R.3353, a partial skull from Côte d’Or, Burgundy Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplocynodon Darwini
''Diplocynodon'' is an extinct genus of alligatoroid that lived during the Paleocene to Middle Miocene in Europe. It looked very similar to the modern caiman in that it was small and had bony armour scutes covering its neck, back, belly, and tail. The longest ''Diplocynodon'' recovered was 4 feet in length and probably fed on small fish, frogs, and took insects when young. In the nineteenth century, ''D. steineri'' was named from Styria, Austria and ''D. styriacus'' was named from Austria and France. A third Austrian species, ''Enneodon ungeri'', was placed in its own genus. The Austrian and French species of ''Diplocynodon'' were synonymized with ''E. ungeri'' in 2011, and because the name ''Diplocynodon'' has priority over ''Enneodon'', the species is now called ''D. ungeri''. Other genera have recently been found to be synonymous with ''Diplocynodon''. ''Hispanochampsa muelleri'' of Spain was determined to be synonymous with ''Diplocynodon'' in 2006, and ''Baryphracta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplocynodon Hantoniensis Nicholson And Lydekker
''Diplocynodon'' is an extinct genus of alligatoroid that lived during the Paleocene to Middle Miocene in Europe. It looked very similar to the modern caiman in that it was small and had bony armour scutes covering its neck, back, belly, and tail. The longest ''Diplocynodon'' recovered was 4 feet in length and probably fed on small fish, frogs, and took insects when young. In the nineteenth century, ''D. steineri'' was named from Styria, Austria and ''D. styriacus'' was named from Austria and France. A third Austrian species, ''Enneodon ungeri'', was placed in its own genus. The Austrian and French species of ''Diplocynodon'' were synonymized with ''E. ungeri'' in 2011, and because the name ''Diplocynodon'' has priority over ''Enneodon'', the species is now called ''D. ungeri''. Other genera have recently been found to be synonymous with ''Diplocynodon''. ''Hispanochampsa muelleri'' of Spain was determined to be synonymous with ''Diplocynodon'' in 2006, and ''Baryphracta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplocynodon
''Diplocynodon'' is an extinct genus of alligatoroid that lived during the Paleocene to Middle Miocene in Europe. It looked very similar to the modern caiman in that it was small and had bony armour scutes covering its neck, back, belly, and tail. The longest ''Diplocynodon'' recovered was 4 feet in length and probably fed on small fish, frogs, and took insects when young. In the nineteenth century, ''D. steineri'' was named from Styria, Austria and ''D. styriacus'' was named from Austria and France. A third Austrian species, ''Enneodon ungeri'', was placed in its own genus. The Austrian and French species of ''Diplocynodon'' were synonymized with ''E. ungeri'' in 2011, and because the name ''Diplocynodon'' has priority over ''Enneodon'', the species is now called ''D. ungeri''. Other genera have recently been found to be synonymous with ''Diplocynodon''. ''Hispanochampsa muelleri'' of Spain was determined to be synonymous with ''Diplocynodon'' in 2006, and ''Baryphracta deponaie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
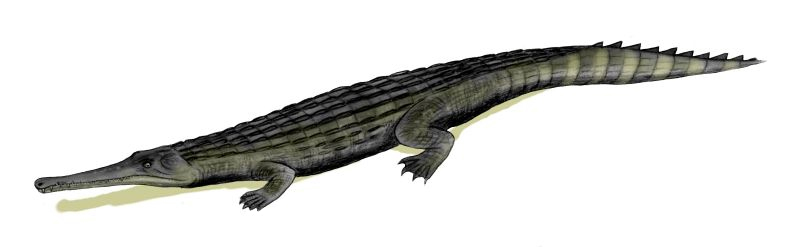
Dyrosauridae
Dyrosauridae is a family of extinct neosuchian crocodyliforms that lived from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) to the Eocene. Dyrosaurid fossils are globally distributed, having been found in Africa, Asia, Europe, North America and South America. Over a dozen species are currently known, varying greatly in overall size and cranial shape. A majority were aquatic, some terrestrial and others fully marine (see locomotion below), with species inhabiting both freshwater and marine environments. Ocean-dwelling dyrosaurids were among the few marine reptiles to survive the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. The dyrosaurids were a group of mostly marine, long jawed, crocodile-like quadrupeds up to long. The largest dyrosaurid was probably ''Phosphatosaurus'' estimated at in length. Based on bone tissue evidence, it has been hypothesized that they were slow-growing near-shore marine animals with interlocking closed jaws, able to swim as well as walk on land. External nostrils at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerrejón Formation
The Cerrejón Formation is a geologic formation in Colombia dating back to the Middle-Late Paleocene. It is found in the El Cerrejón sub-basin of the Cesar-Ranchería Basin of La Guajira and Cesar. The formation consists of bituminous coal fields that are an important economic resource. Coal from the Cerrejón Formation is mined extensively from the Cerrejón open-pit coal mine, one of the largest in the world. The formation also bears fossils that are the earliest record of Neotropical rainforests.Wing et al., 2009 Definition The formation was first named Septarias Formation and in 1958 renamed to Cerrejón Formation by Thomas van der Hammen, probably based on an earlier report by Notestein.Rodríguez & Londoño, 2002, p.163 Geology The Cerrejón Formation, with an assigned total thickness of , is subdivided into lower, middle, and upper groups based on the thickness and distribution of coal beds. On average the coal beds are thick, and range from to in thickness. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
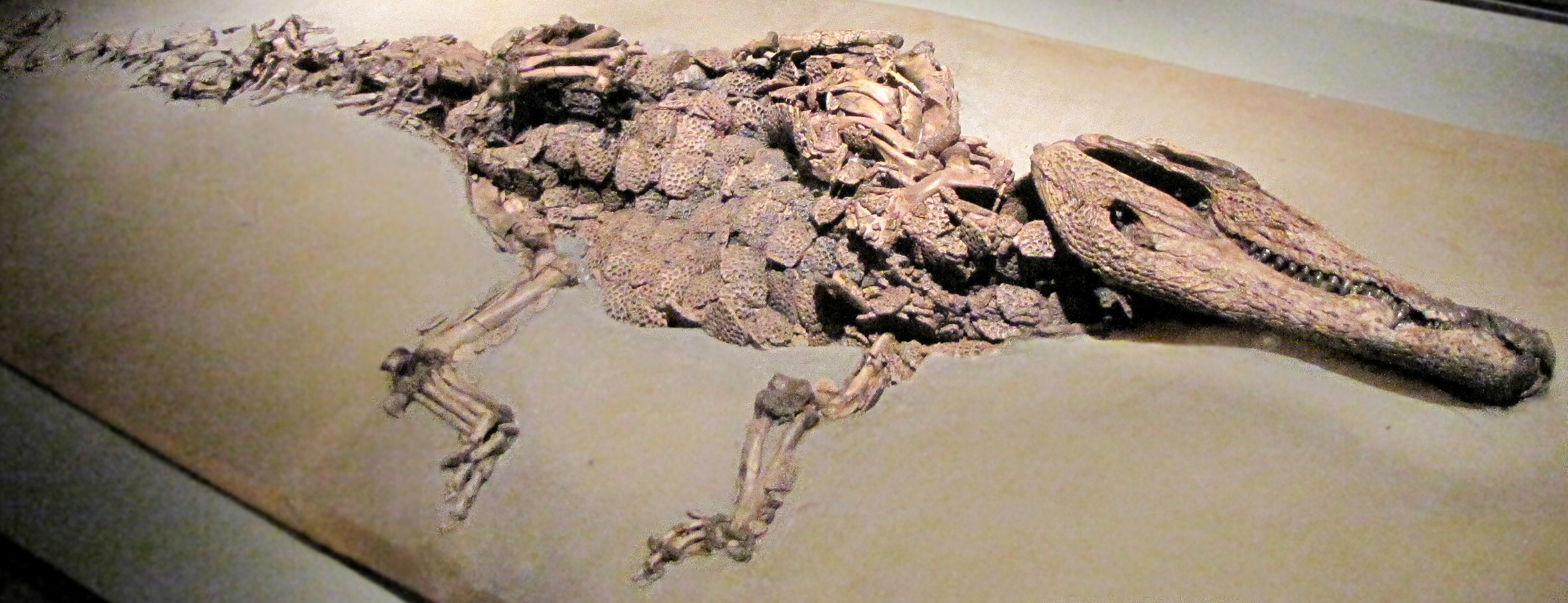
Cerrejonisuchus
''Cerrejonisuchus'' is an extinct genus of dyrosaurid crocodylomorph. It is known from a complete skull and mandible from the Cerrejón Formation in northeastern Colombia, which is Paleocene in age. Specimens belonging to ''Cerrejonisuchus'' and to several other dyrosaurids have been found from the Cerrejón open-pit coal mine in La Guajira. The length of the rostrum is only 54-59% of the total length of the skull, making the snout of ''Cerrejonisuchus'' the shortest of all dyrosaurids. Description At an estimated length of to , ''Cerrejonisuchus'' was small for a dyrosaur. This size estimate is based on the dorsal skull lengths of specimens UF/IGM 29 and UF/IGM 31. ''Cerrejonisuchus'' has the shortest body length of any known dyrosaur, much smaller than that of the longest dyrosaur, ''Phosphatosaurus gavialoides'', which was to in length. Currently the only known specimens of ''Cerrejonisuchus'' are UF/IGM 29 (the type specimen), UF/IGM 30, UF/IGM 31, and UF/IGM 32. Of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodylus Anthropophagus Postcranial Remains
''Crocodylus'' is a genus of true crocodiles in the family Crocodylidae. Taxonomy The generic name, ''Crocodylus'', was proposed by Josephus Nicolaus Laurenti in 1768. ''Crocodylus'' contains 13–14 extant (living) species and 5 extinct species. There are additional extinct species attributed to the genus ''Crocodylus'' that studies have shown no longer belong, although they have not yet been reassigned to new genera. Extant species The 13–14 living species are: Fossils ''Crocodylus'' also includes five extinct species: * † ''Crocodylus anthropophagus'' is an extinct crocodile from Plio-Pleistocene of Tanzania. * † ''Crocodylus checchiai'' is an extinct crocodile from Late Miocene of Kenya. * † ''Crocodylus falconensis'' is an extinct crocodile from Early Pliocene of Venezuela. * † ''Crocodylus palaeindicus'' is an extinct crocodile the Miocene to the Pleistocene of southern Asia. * † '' Crocodylus thorbjarnarsoni'' is an extinct crocodile from Plio-Pleistoce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








%2C_NPSPhoto_(9255693421).jpg)