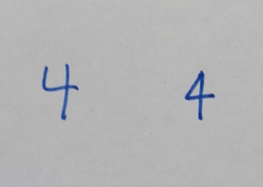|
2004 French Polynesian Legislative Election
Elections for the Assembly of French Polynesia, the Territorial Assembly of French Polynesia, were held on May 23, 2004. In a surprise result Oscar Temaru's pro-independence progressive coalition formed Government with a one-seat majority in the 57 seat parliament, defeating the conservative party led by Gaston Flosse (see also List of political parties in French Polynesia). On October 8, 2004, the Gaston Flosse led opposition party succeeded in passing a censure motion against the Government. This provoked a political crisis, and controversy about whether the national government of France should use its exceptional power to call for new elections in a local government, in case of a grave political crisis. Timeline 23 May 2004: Elections for the Assembly of French Polynesia (''Assemblée de la Polynésie française''), the territorial assembly of French Polynesia, held. A progressive coalition led by pro-independence Oscar Temaru wins 26 (27 respectively) seats and forms a coali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Election
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office. Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operated since the 17th century. Elections may fill offices in the legislature, sometimes in the executive and judiciary, and for regional and local government. This process is also used in many other private and business organisations, from clubs to voluntary associations and corporations. The global use of elections as a tool for selecting representatives in modern representative democracies is in contrast with the practice in the democratic archetype, ancient Athens, where the elections were considered an oligarchic institution and most political offices were filled using sortition, also known as allotment, by which officeholders were chosen by lot. Electoral reform describes the process of introducing fair electoral systems wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commune In France
The () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, ' in Germany, ' in Italy, or ' in Spain. The United Kingdom's equivalent are civil parishes, although some areas, particularly urban areas, are unparished. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the municipal arrondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2004 In French Polynesia
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures. In mathematics Four is the smallest composite number, its proper divisors being and . Four is the sum and product of two with itself: 2 + 2 = 4 = 2 x 2, the only number b such that a + a = b = a x a, which also makes four the smallest squared prime number p^. In Knuth's up-arrow notation, , and so forth, for any number of up arrows. By consequence, four is the only square one more than a prime number, specifically three. The sum of the first four prime numbers two + three + five + seven is the only sum of four consecutive prime numbers that yields an odd prime number, seventeen, which is the fourth super-prime. Four lies between the first proper pair of twin primes, three and five, which are the first two Fermat primes, like seventeen, which is the third. On the other hand, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2004 In France
Events from the year 2004 in France. Incumbents * President – Jacques Chirac * Prime Minister – Jean-Pierre Raffarin Events *3 January – Flash Airlines Flight 604 headed for Cairo crashes into the Red Sea. All 148 people on board are killed, of whom more than 120 were French tourists. *30 January – Former Prime Minister and current Mayor of Bordeaux, Alain Juppe, is convicted of a party funding scam in the 1980s and early 1990s. *31 January – Air France and British Airways cancel five upcoming US flights to Washington, D.C. and Miami, Florida amid fears of Al-Qaida. *10 February – The French National Assembly votes to pass a law banning religious items and clothing from schools. *20 February – The insecticide Regent ( fipronil), from BASF, is banned in France for its implication in pollinator decline. *1 March – French troops are deployed to Haiti. *21–28 March – Regional elections held, in which the government of Prime Minister Jean-Pierre Raffarin suffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2004 Elections In Oceania
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures. In mathematics Four is the smallest composite number, its proper divisors being and . Four is the sum and product of two with itself: 2 + 2 = 4 = 2 x 2, the only number b such that a + a = b = a x a, which also makes four the smallest squared prime number p^. In Knuth's up-arrow notation, , and so forth, for any number of up arrows. By consequence, four is the only square one more than a prime number, specifically three. The sum of the first four prime numbers two + three + five + seven is the only sum of four consecutive prime numbers that yields an odd prime number, seventeen, which is the fourth super-prime. Four lies between the first proper pair of twin primes, three and five, which are the first two Fermat primes, like seventeen, which is the third. On the other hand, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2004 Elections In France
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures. In mathematics Four is the smallest composite number, its proper divisors being and . Four is the sum and product of two with itself: 2 + 2 = 4 = 2 x 2, the only number b such that a + a = b = a x a, which also makes four the smallest squared prime number p^. In Knuth's up-arrow notation, , and so forth, for any number of up arrows. By consequence, four is the only square one more than a prime number, specifically three. The sum of the first four prime numbers two + three + five + seven is the only sum of four consecutive prime numbers that yields an odd prime number, seventeen, which is the fourth super-prime. Four lies between the first proper pair of twin primes, three and five, which are the first two Fermat primes, like seventeen, which is the third. On the other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elections In French Polynesia
French Polynesia elects the Assembly of French Polynesia (''Assemblée de la Polynésie française''), the unicameral legislature on the territorial level. The Assembly of French Polynesia has 57 members, elected for a five-year term by proportional representation in multi-seat constituencies. French Polynesia has a two-party system, which means that there are two dominant political parties, with extreme difficulty for anybody to achieve electoral success under the banner of any other party. In June 2011, the electoral law will likely be changed again, with a two-round proportional system including a bonus of a third of the seats for the winning list in the second round, with the rest of the seats distributed proportionally; the electoral threshold to advance to the second round will be 12.5%. Last elections 2004 elections The elections in 2004 produced a close result leading to unstable majorities in the assembly. In addition, the election was invalidated in districts in Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
No Oe E Te Nunaa
The No Oe E Te Nunaa ( en, This Country is Yours) is a political party in French Polynesia. The party was established in April 2003 by former tourism minister Nicole Bouteau. The party supports autonomy for French Polynesia. The party won six percent of the vote and a single seat at the 2004 French Polynesian legislative election. In the subsequent 2005 by-elections it was part of the Alliance for a New Democracy (''Alliance pour une Démocratie Nouvelle''), that won 3 out of 57 seats. See also *List of political parties in French Polynesia *Elections in French Polynesia *Assembly of French Polynesia *Politics of French Polynesia Politics of French Polynesia takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic French overseas collectivity, whereby the President of French Polynesia is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power i ... References Political parties in French Polynesia {{Oceania-party-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fetia Api
The Fetia Api or Nouvelle Étoile ( en, New Star) was a centre-right political party in French Polynesia from 1996 to 2016, advocating for the autonomy of French Polynesia. The party was led by Boris Léontieff, former mayor of Arue since 1989, and then subsequently led by Philip Schyle after 2002. The party was once one of the oldest in French Polynesia, spanning over 20 years. Originally the party was first associated with the french Union for French Democracy (UDF) party, but in 2007 it was part of dissidents who split away from the UDF and created the New Centre (NC). Philip Schyle was elected the Foreign Minister for the NC, and Fetia Api helped with public financial contributions. In 2016, the party was dissolved, with the members becoming part of the newly formed Tapura Huiraatira (TAPURA) party. History 1996 Election Creation of the Fetia Api party by Boris Léontieff, mayor of Arue since 1989. Territorial elections of 1996 in French Polynesia: Boris Léonti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapura Amui No Raromatai
The Tapura Amui No Raromatai is a political party in French Polynesia. At the last legislative elections on May 23, 2004, and by-elections on February 13, 2005, the party was part of the Union for the Democracy (''Union pour la Démocratie''), that won 27 out of 57 seats. See also * List of political parties in French Polynesia *Elections in French Polynesia *Assembly of French Polynesia *Politics of French Polynesia Politics of French Polynesia takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic French overseas collectivity, whereby the President of French Polynesia is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power i ... Political parties in French Polynesia {{Oceania-party-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapura Amui No Te Faatereraa Manahune – Tuhaa Pae
The Tapura Amui No Te Faatereraa Manahune – Tuhaa Pae was a short lived political coalition in French Polynesia for the 2004 French Polynesian legislative election, specifically for the Austral Islands. The coalition was between the parties of Tapura Amui no Tuhaa Pae, Union for the Democracy (''Union pour la Démocratie''), Heiura-Les Verts, and Fetia Api. The coalition organised a political advertisement campaign for the 2004. The dates for broadcasts in 2004 took place at an unknown date, but occurred on the Austral Islands. All members of the coalition had separate broadcasts outside the coalition in 2004. In the results, the coalition took 1 seat for the Austral Islands, electing Tapura Amui no Tuhaa Pae's Chantal Florès-Tahiata, who will sit on the UPLD group. See also * List of political parties in French Polynesia * Elections in French Polynesia * Assembly of French Polynesia * Politics of French Polynesia Politics of French Polynesia takes place in a framewor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Here Ai'a
Here Ai’a ( en, Love of the Land), also known as Te Pupu Here Ai'a Te Nunaa ia Ora ( en, Patriotic Group for an Autonomous Polity), is a pro-independence political party in French Polynesia. It was founded by John Teariki and Henri Bouvier in 1965 following the banning of the pro-independence Democratic Rally of the Tahitian People (RDPT) by the colonial French government. Supported mainly by rural Polynesians, the party was a significant force in French Polynesian politics from its foundation until the early 1980's, before entering a decline following Teariki's death in 1983. The party is currently led by Gustave Taputu. The party was founded on 9 February 1965. In order to avoid being seen as an illegal re-establishment of the RDPT, the party avoided placing former RDPT leaders in leadership positions, and stated that its objective was "a democratic development of French Polynesia in close collaboration with the French people and according to the preamble of the Constitution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |