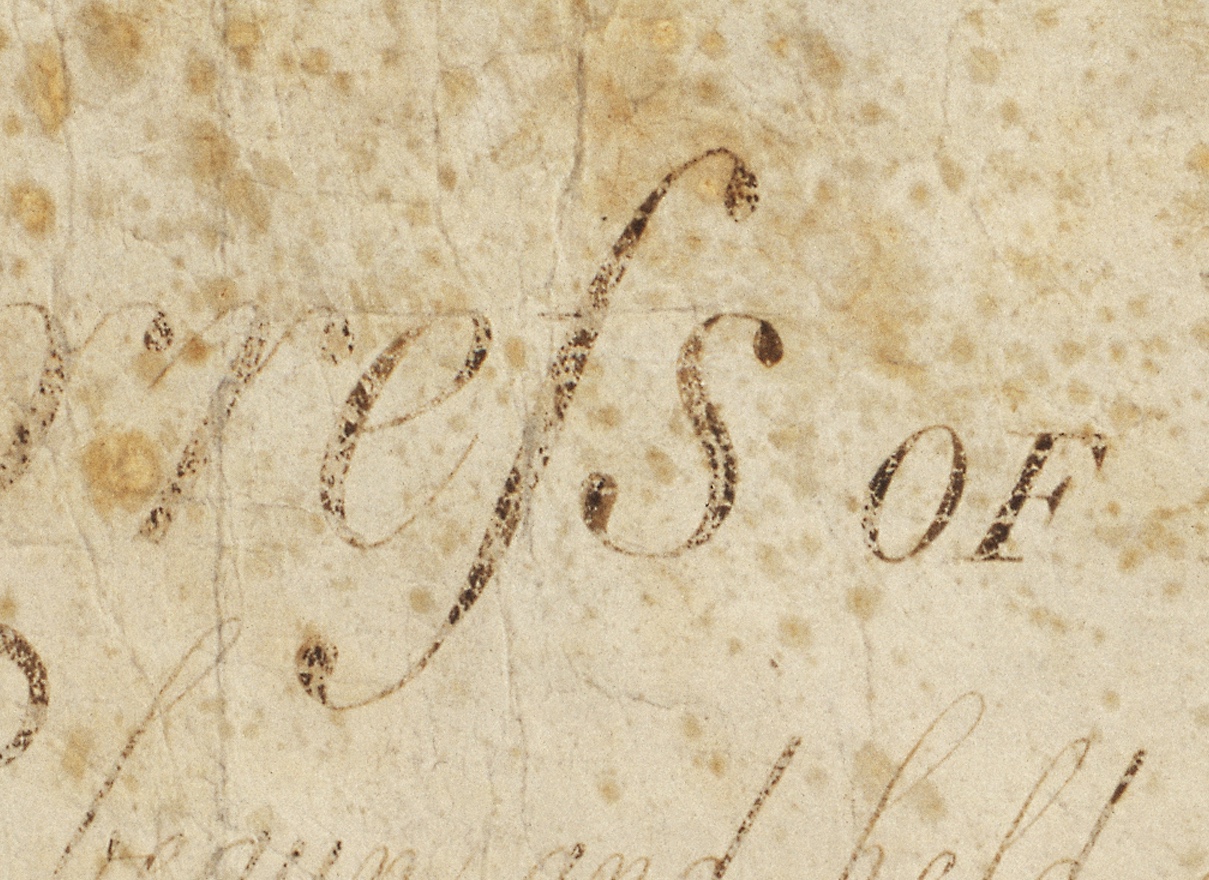|
2000s Sports Drama Films
S, or s, is the nineteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ess'' (pronounced ), plural ''esses''. History Origin Northwest Semitic šîn represented a voiceless postalveolar fricative (as in 'ip'). It originated most likely as a pictogram of a tooth () and represented the phoneme via the acrophonic principle. Ancient Greek did not have a phoneme, so the derived Greek letter sigma () came to represent the voiceless alveolar sibilant . While the letter shape Σ continues Phoenician ''šîn'', its name ''sigma'' is taken from the letter ''samekh'', while the shape and position of ''samekh'' but name of ''šîn'' is continued in the '' xi''. Within Greek, the name of ''sigma'' was influenced by its association with the Greek word (earlier ) "to hiss". The original name of the letter "sigma" may have been ''san'', but due to the complica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long S
The long s , also known as the medial s or initial s, is an archaism, archaic form of the lowercase letter . It replaced the single ''s'', or one or both of the letters ''s'' in a 'double ''s''' sequence (e.g., "ſinfulneſs" for "sinfulness" and "poſſeſs" or "poſseſs" for "possess"—but never asterisk#Ungrammaticality, *"poſſeſſ"). The modern letterform is known as the 'short', 'terminal', or 'round' s. In typography, it is known as a type of swash letter, commonly referred to as a "swash s". The long s is the basis of the first half of the grapheme of the German alphabet Orthographic ligature, ligature letter , (''eszett'' or [sharp s]). Rules This list of rules for the long s is not exhaustive, and it applies only to books printed during the 17th and 18th centuries in English-speaking countries. Similar rules exist for other European languages. * A round s is always used at the end of a word ending with s: "his", "complains", "ſucceſs" ** However, long s is m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sh (digraph)
Sh is a digraph of the Latin alphabet, a combination of S and H. European languages Albanian In Albanian, sh represents . It is considered a distinct letter, named shë, and placed between S and T in the Albanian alphabet. Breton In Breton, sh represents . It is not considered a distinct letter and it is a variety of zh (e. g. ("older"). It is not considered as a diphthong in compound words, such as ''kroashent'' ("roundabout": ''kroaz'' ("cross") + ''hent'' ("way", "ford"). English In English, usually represents . The exception is in compound words, where the and are not a digraph, but pronounced separately, e.g. ''hogshead'' is ''hogs-head'' , not ''*hog-shead'' . ''Sh'' is not considered a distinct letter for collation purposes. American Literary braille includes a single-cell contraction for the digraph with the dot pattern (1 4 6). In isolation it stands for the word "shall". In Old English orthography, the sound was written . In Middle English it cam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiceless Alveolar Sibilant
The voiceless alveolar fricatives are a type of fricative consonant pronounced with the tip or blade of the tongue against the alveolar ridge (gum line) just behind the teeth. This refers to a class of sounds, not a single sound. There are at least six types with significant perceptual differences: *The voiceless alveolar sibilant has a strong hissing sound, as the ''s'' in English ''sink''. It is one of the most common sounds in the world. *The voiceless denti-alveolar sibilant (an ''ad hoc'' notation), also called apico-dental, has a weaker lisping sound like English ''th'' in ''thin''. It occurs in Spanish dialects in southern Spain (eastern Andalusia). *The voiceless alveolar retracted sibilant Voiceless_alveolar_fricative#Voiceless_alveolar_retracted_sibilant.html" ;"title="nowiki/> .html" ;"title="Voiceless alveolar fricative#Voiceless alveolar retracted sibilant">">Voiceless alveolar fricative#Voiceless alveolar retracted sibilant"> and the subform apico-alveolar , or cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigma (letter)
Sigma (; uppercase Σ, lowercase σ, lowercase in word-final position ς; grc-gre, σίγμα) is the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 200. In general mathematics, uppercase Σ is used as an operator for summation. When used at the end of a letter-case word (one that does not use all caps), the final form (ς) is used. In ' (Odysseus), for example, the two lowercase sigmas (σ) in the center of the name are distinct from the word-final sigma (ς) at the end. The Latin letter S derives from sigma while the Cyrillic letter Es derives from a lunate form of this letter. History The shape (Σς) and alphabetic position of sigma is derived from the Phoenician letter ( ''shin''). Sigma's original name may have been ''san'', but due to the complicated early history of the Greek epichoric alphabets, ''san'' came to be identified as a separate letter in the Greek alphabet, represented as Ϻ. Herodotus reports that "san" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to |