|
1987 In Spaceflight
The following is an outline of 1987 in spaceflight. Launches Deep-space rendezvous There were no deep-space rendezvous in 1987. References Footnotes {{Orbital launches in 1987 Spaceflight by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas H
The Atlas H was an American expendable launch system derived from the SM-65 Atlas missile. It was a member of the Atlas family of rockets, and was used to launch five clusters of NOSS satellites for the US National Reconnaissance Office. Two flights also carried LiPS satellites, as secondary payloads for the United States Naval Research Laboratory. The Atlas H was a stage and a half rocket, using the enhanced Atlas rocket designed for use as the first stage of the Atlas G rocket, which differed from the Atlas H in having a Centaur upper stage. This stage was later reused as the first stage of the Atlas I. In practice, an MSD upper stage was flown on all five launches. Atlas H could put a payload of 3,630 kg (8,000 lb) into low Earth orbit, or a payload of 2,255 kg (4,971 lb) into a geostationary transfer orbit A geosynchronous transfer orbit or geostationary transfer orbit (GTO) is a type of geocentric orbit. Satellite, Satellites that are destined for g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Data System
The Satellite Data System (SDS) is a system of United States military communications satellites. At least three generations have been used: SDS-1 from 1976 to 1987; SDS-2 from 1989 to 1996; SDS-3 from 1998 to the present. It is believed that these satellites were known by the code name ''Quasar''. The first generation was named simply 'SDS', the second generation was named 'Quasar' and the third generation each had their own designations. Orbital characteristics SDS satellites have a highly elliptical orbit, going from about 300 kilometers at perigee to roughly 39,000 km at apogee in order to allow communications with polar stations that cannot contact geosynchronous satellites. The high apogee meant that the polar regions were visible for long amounts of time, and only two satellites were required in order to achieve constant communications ability. In addition, two geostationary satellites appear to be part of the system. The SDS satellites were constructed by Hughes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kvant-1
Kvant-1 (russian: Квант-1; English: Quantum-I/1) (37KE) was the first module to be attached in 1987 to the Mir Core Module, which formed the core of the Soviet space station ''Mir''. It remained attached to ''Mir'' until the entire space station was deorbited in 2001. The Kvant-1 module contained scientific instruments for astrophysical observations and materials science experiments. It was used to conduct research into the physics of active galaxies, quasars and neutron stars and it was uniquely positioned for studies of the Supernova SN 1987A. Furthermore, it supported biotechnology experiments in anti-viral preparations and fractions. Some additions to Kvant-1 during its lifetime were solar arrays and the ''Sofora'' and ''Rapana'' girders. The Kvant-1 module was based on the TKS spacecraft and was the first, experimental version of a planned series of '37K' type modules. The 37K modules featured a jettisonable TKS-E type propulsion module, also called the Functional Servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baikonur Cosmodrome Site 200
Site 200 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome is a launch site used by Proton rockets. It consists of two launch pads, areas 39 and 40. Area 39 is currently (as of 2021) used for Proton-M launches, including commercial flights conducted by International Launch Services. Area 40 is currently (as of 2021) inactive, as it was slated to be rebuilt as a launch site for the Angara rocket. Although the project was relocated to Site 250, Area 40 was not put back into service. A number of planetary probes have been launched from Site 200. Venera 14, Venera 15, Vega 1, Fobos 1, the failed Mars-96, and ExoMars were launched from area 39. Venera 13, Venera 16, Vega 2, Fobos 2 were launched from Area 40. Area 39 was also the launch site for the core of the Mir space station, along with both Kvant modules, and the Kristall module. Salyut 7 and Granat The International Astrophysical Observatory "GRANAT" (usually known as Granat; russian: Гранат, lit. ''pomegranate''), was a Soviet (later Russi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
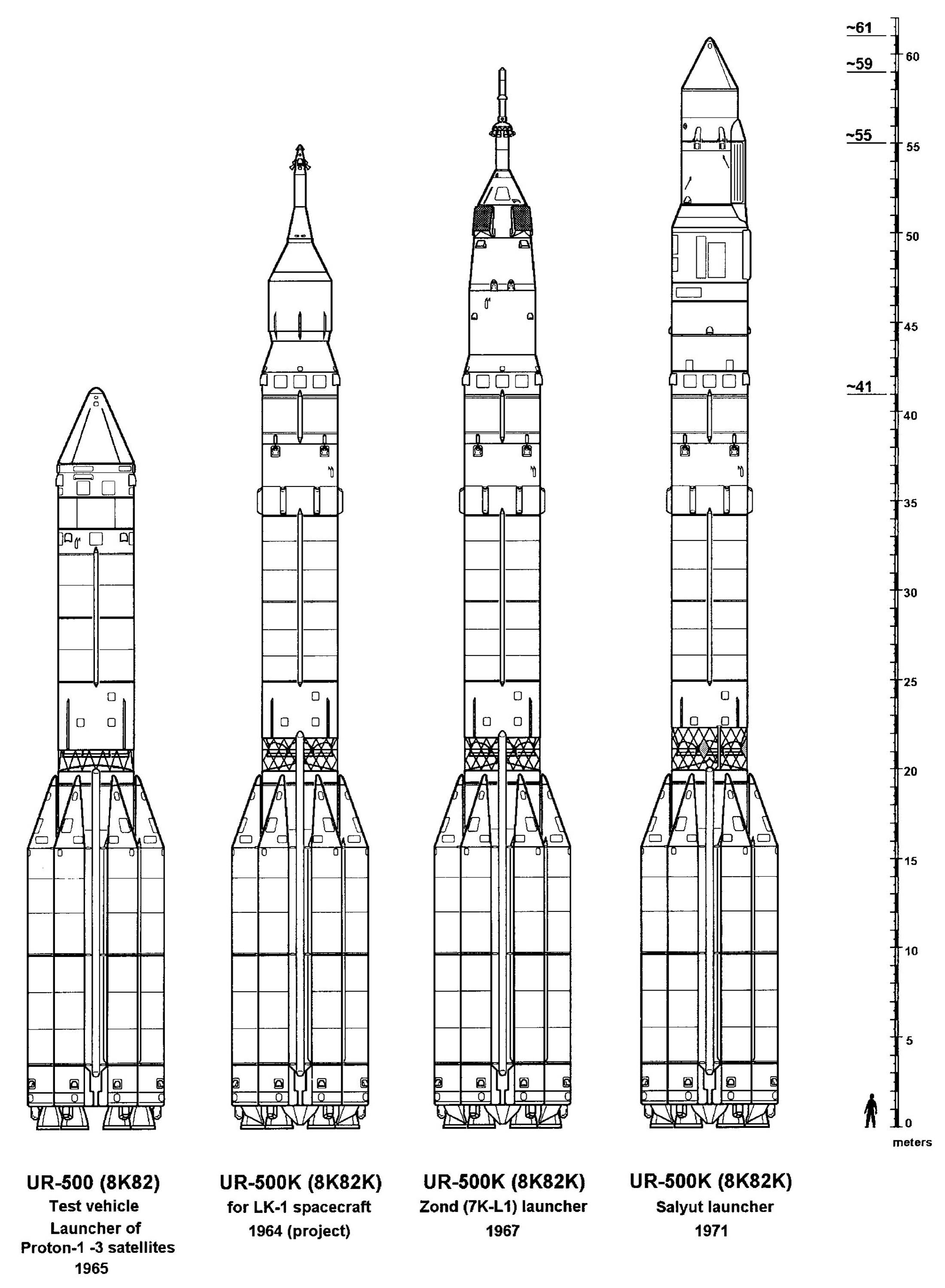
Proton-K
The Proton-K, also designated Proton 8K82K after its GRAU index or SL-12 after its model number, 8K82K, was a Russian, previously Soviet, carrier rocket derived from the earlier Proton. It was built by Khrunichev, and launched from sites 81 and 200 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The maiden flight on 10 March 1967 carried a Soyuz 7K-L1 as part of the Zond program. During the so-called Moon Race these Proton/Soyuz/Zond flights consisted of several uncrewed test flights of Soyuz spacecraft to highly elliptical or circumlunar orbits with the unrealized aim of landing Soviet cosmonauts on the Moon. It was retired from service in favour of the modernised Proton-M, making its 310th and final launch on 30 March 2012. Vehicle description The baseline Proton-K was a three-stage rocket. Thirty were launched in this configuration, with payloads including all of the Soviet Union's ''Salyut'' space stations, all Mir modules with the exception of the Docking Module, which was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palapa B2-P
Agila-1 or Mabuhay was launched on March 20, 1987, under the name Palapa B2-P in Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. It was originally under Indonesian company, PT Pasifik Satelit Nusantara until it was acquired by Philippine company, Mabuhay Satellite Corporation which is under PLDT in 1996. Upon its acquisition by Mabuhay, it became the first Philippine satellite through acquisition while in orbit. Palapa B2-P was later renamed to "Agila-1", the local name for the Philippine eagle. The satellite's operation ended in January 1998 and was deorbit Atmospheric entry is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. There are two main types of atmospheric entry: ''uncontrolled entry'', such as the entr ...ed. References {{Orbital launches in 1987 Telecommunications in the Philippines First artificial satellites of a country Spacecraft launched in 1987 Satellites of the Philippines S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geostationary Orbit
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit''Geostationary orbit'' and ''Geosynchronous (equatorial) orbit'' are used somewhat interchangeably in sources. (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit in altitude above Earth's equator ( in radius from Earth's center) and following the direction of Earth's rotation. An object in such an orbit has an orbital period equal to Earth's rotational period, one sidereal day, and so to ground observers it appears motionless, in a fixed position in the sky. The concept of a geostationary orbit was popularised by the science fiction writer Arthur C. Clarke in the 1940s as a way to revolutionise telecommunications, and the first satellite to be placed in this kind of orbit was launched in 1963. Communications satellites are often placed in a geostationary orbit so that Earth-based satellite antennas do not have to rotate to track them but can be pointed permanently at the position in the sky where the sat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Satellite
A weather satellite or meteorological satellite is a type of Earth observation satellite that is primarily used to monitor the weather and climate of the Earth. Satellites can be polar orbiting (covering the entire Earth asynchronously), or geostationary (hovering over the same spot on the equator). While primarily used to detect the development and movement of storm systems and other cloud patterns, meteorological satellites can also detect other phenomena such as city lights, fires, effects of pollution, auroras, sand and dust storms, snow cover, ice mapping, boundaries of ocean currents, and energy flows. Other types of environmental information are collected using weather satellites. Weather satellite images helped in monitoring the volcanic ash cloud from Mount St. Helens and activity from other volcanoes such as Mount Etna. Smoke from fires in the western United States such as Colorado and Utah have also been monitored. El Niño and its effects on weather are monitored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Oceanic And Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditions, charts the seas, conducts deep sea exploration, and manages fishing and protection of marine mammals and endangered species in the U.S. exclusive economic zone. Purpose and function NOAA's specific roles include: * ''Supplying Environmental Information Products''. NOAA supplies to its customers and partners information pertaining to the state of the oceans and the atmosphere, such as weather warnings and forecasts via the National Weather Service. NOAA's information services extend as well to climate, ecosystems, and commerce. * ''Providing Environmental Stewardship Services''. NOAA is a steward of U.S. coastal and marine environments. In coordination with federal, state, local, tribal and international authorities, NOAA manages the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GOES 7
GOES-7, known as GOES-H before becoming operational, is an American satellite. It was originally built as a weather satellite, and formed part of the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite system. Originally built as a ground spare, GOES-H was launched in 1987 due to delays with the next series of satellites. It was operated by NOAA until 1999, before being leased to Peacesat, who use it as a communications satellite. As of 2009, it was operational over the Pacific Ocean, providing communications for the Pacific Islands. On April 12, 2012, the spacecraft was finally decommissioned and moved to a graveyard orbit. Launch GOES-H was launched aboard a McDonnell Douglas Delta 3914 rocket, flying from Launch Complex 17A at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The launch occurred at 23:05 GMT on 26 February 1987. The launch had originally been scheduled for late 1986, but was delayed after GOES-G failed to achieve orbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Space Launch Complex 17
Space Launch Complex 17 (SLC-17), previously designated Launch Complex 17 (LC-17), was a launch site at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), Florida used for Thor and Delta launch vehicles launches between 1958 and 2011. It was built in 1956 for use with the PGM-17 Thor missile, the first operational ballistic missile in the arsenal of the United States. More recently the launch complex has been used for vehicles in the Delta launch vehicle family, derived from the Thor missile, to launch probes to the Moon and planets, solar observatories and weather satellites. SLC-17 features two expendable launch vehicle (ELV) launch pads, 17A and 17B. The pads were operated by the 45th Space Wing and have supported more than 300 Department of Defense, NASA and commercial missile and rocket launches. Following the last military launch, in August 2009, SLC-17A was withdrawn from use, and LC-17B was transferred to NASA (SLC-17B) for two remaining launches. Pad 17A supported its first T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida. Headquartered at the nearby Patrick Space Force Base, the station is the primary launch site for the Space Force's Eastern RangeCAST 1999, p. 1-12. with three launch pads currently active (Space Launch Complexes 37B, 40, and 41). The facility is south-southeast of NASA's Kennedy Space Center on adjacent Merritt Island, with the two linked by bridges and causeways. The Cape Canaveral Space Force Station Skid Strip provides a runway close to the launch complexes for military airlift aircraft delivering heavy and outsized payloads to the Cape. A number of American space exploration pioneers were launched from CCSFS, including the first U.S. Earth satellite (1958), first U.S. astronaut (1961), first U.S. astronaut in orbit (1962), first two-man U.S. spacecraft (1965), first U.S. unmanned lunar lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |