|
1957 Birthday Honours (New Zealand)
The 1957 Queen's Birthday Honours in New Zealand, celebrating the official birthday of Elizabeth II, were appointments made by the Queen on the advice of the New Zealand government to various orders and honours to reward and highlight good works by New Zealanders. They were announced on 13 June 1957. The recipients of honours are displayed here as they were styled before their new honour. Order of Saint Michael and Saint George Knight Commander (KCMG) * The Honourable William Sullivan – lately Minister of Labour, Mines and Housing. File:Bill Sullivan.jpg, Sir William Sullivan Companion (CMG) * The Most Reverend Alfred Walter Averill – a former archbishop of New Zealand. For services to the community as bishop and archbishop. * Gordon Graham Gibbes Watson – of Lower Hutt. For services to the legal profession. Order of the British Empire Commander (CBE) ;Civil division * Percy William Burbidge – professor of physics, Auckland University College, 1921–1957. * A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states during her lifetime, and was head of state of 15 realms at the time of her death. Her reign of 70 years and 214 days was the longest of any British monarch and the longest verified reign of any female monarch in history. Elizabeth was born in Mayfair, London, as the first child of the Duke and Duchess of York (later King George VI and Queen Elizabeth The Queen Mother). Her father acceded to the throne in 1936 upon the abdication of his brother Edward VIII, making the ten-year-old Princess Elizabeth the heir presumptive. She was educated privately at home and began to undertake public duties during the Second World War, serving in the Auxiliary Territorial Service. In November 1947, she married Philip Mountbatten, a former prince ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori People
The Māori (, ) are the indigenous Polynesian people of mainland New Zealand (). Māori originated with settlers from East Polynesia, who arrived in New Zealand in several waves of canoe voyages between roughly 1320 and 1350. Over several centuries in isolation, these settlers developed their own distinctive culture, whose language, mythology, crafts, and performing arts evolved independently from those of other eastern Polynesian cultures. Some early Māori moved to the Chatham Islands, where their descendants became New Zealand's other indigenous Polynesian ethnic group, the Moriori. Initial contact between Māori and Europeans, starting in the 18th century, ranged from beneficial trade to lethal violence; Māori actively adopted many technologies from the newcomers. With the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi in 1840, the two cultures coexisted for a generation. Rising tensions over disputed land sales led to conflict in the 1860s, and massive land confiscations, to which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
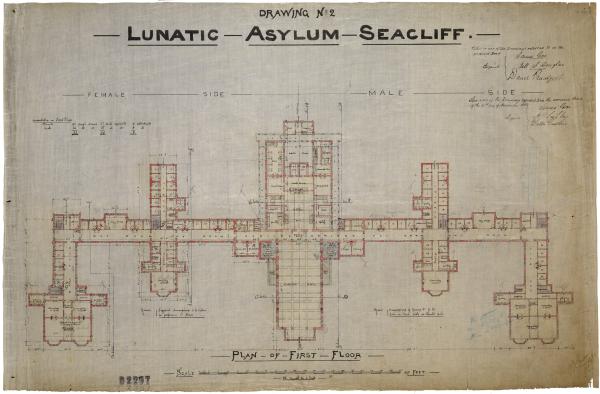
Seacliff Lunatic Asylum
Seacliff Lunatic Asylum (often Seacliff Asylum, later Seacliff Mental Hospital) was a psychiatric hospital in Seacliff, New Zealand. When built in the late 19th century, it was the largest building in the country, noted for its scale and extravagant architecture. It became infamous for construction faults resulting in partial collapse, as well as a 1942 fire which destroyed a wooden outbuilding, claiming 37 lives (39 in other sources), because the victims were trapped in a locked ward.Fire: Seacliff Mental Hospital (from the website) The asylum was less than 20 miles north of |
William Rodger (accountant)
William Wallace Rodger (13 January 1847 – 23 October 1888), known from 1887 William Wallace Rodger-Cunliffe, was an English lawyer, billiards player and first-class cricketer who played for Kent County Cricket Club. Early life Rodger was born in 1847 at Gloucester Place, Marylebone in London. He was the son of Sir Robert Rodger and his wife Sophia and was educated at Eton College and Exeter College, Oxford. His father was a Justice of the Peace and High Sheriff of Kent who bought Hadlow Castle in Kent where the family lived.Carlaw D (2020) ''Kent County Cricketers A to Z. Part One: 1806–1914'' (revised edition), pp. 470–471.Available onlineat the Association of Cricket Statisticians and Historians. Retrieved 2020-12-21.) Cricket Rodger did not play cricket for the school XI or for the university, but made his first-class cricket debut for the Gentlemen of Kent in 1865 after graduating from Oxford. He played for the side during the 1865 and 1866 Canterbury Cricket Weeks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal New Zealand Foundation Of The Blind
The Royal New Zealand Foundation of the Blind or Blind Foundation, now publicly branded as Blind Low Vision NZ, is a provider of services to blind, deafblind and people with vision-impairment in New Zealand. History The Foundation began in 1890 as the Jubilee Institute for the Blind with a school and residence in Parnell, Auckland. Sheltered workshops and hostels were provided for many years. These were phased out at the end of the twentieth century in favour of mainstreaming, members' greater integration into the community. A school run by the Foundation became part of the public school system. The ''Royal New Zealand Foundation of the Blind Act 2002'' allows for the Foundation to become an incorporated society. After a rebranding consultation process, the public name of the Royal New Zealand Foundation of the Blind, changed to Blind Foundation in December 2013. Services Blind Low Vision NZ's website lists the following services: emotional support, equipment, financial a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tauranga
Tauranga () is a coastal city in the Bay of Plenty region and the fifth most populous city of New Zealand, with an urban population of , or roughly 3% of the national population. It was settled by Māori late in the 13th century, colonised by Europeans in the early 19th century, and was constituted as a city in 1963. The city lies in the north-western corner of the Bay of Plenty, on the south-eastern edge of Tauranga Harbour. The city extends over an area of , and encompasses the communities of Bethlehem, New Zealand, Bethlehem, on the south-western outskirts of the city; Greerton, on the southern outskirts of the city; Matua, west of the central city overlooking Tauranga Harbour; Maungatapu; Mount Maunganui, located north of the central city across the harbour facing the Bay of Plenty; Otūmoetai; Papamoa, Tauranga's largest suburb, located on the Bay of Plenty; Tauranga City; Tauranga South; and Welcome Bay. Tauranga is one of New Zealand's main centres for business, interna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invercargill
Invercargill ( , mi, Waihōpai is the southernmost and westernmost city in New Zealand, and one of the southernmost cities in the world. It is the commercial centre of the Southland region. The city lies in the heart of the wide expanse of the Southland Plains to the east of the Ōreti or New River some north of Bluff, which is the southernmost town in the South Island. It sits amid rich farmland that is bordered by large areas of conservation land and marine reserves, including Fiordland National Park covering the south-west corner of the South Island and the Catlins coastal region. Many streets in the city, especially in the centre and main shopping district, are named after rivers in Scotland. These include the main streets Dee and Tay, as well as those named after the Tweed, Forth, Tyne, Esk, Don, Ness, Yarrow, Spey, Eye and Ythan rivers, amongst others. The 2018 census showed the population was 54,204, up 2.7% on the 2006 census number and up 4.8% on the 2013 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fred Hall-Jones
Frederick George Hall-Jones (4 July 1891 – 28 January 1982) was a New Zealand lawyer, historian and community leader. Biography Hall-Jones was born in Scarborough just south of Timaru, South Canterbury, New Zealand, on 4 July 1891, the son of William Hall-Jones and Rosalind Lucy Hall-Jones (née Purss). He took over the legal practice of R. H. Rattray at Invercargill in 1917, it later being known as Hall-Jones & Sons. At the 1938 general election he stood as the National Party candidate for the seat of , but lost to Labour's William Denham. Hall-Jones was appointed an Officer of the Order of the British Empire in the 1957 Queen's Birthday Honours, for services in community affairs and as an historian in Southland. His son, John Hall-Jones John Hall-Jones (14 September 1927 – 19 November 2015) was a New Zealand historian, otolaryngologist and outdoorsman. Jones concentrated on the history of Southland and Otago, New Zealand's southernmost regions, as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ōkato
Ōkato is a small town in rural Taranaki, New Zealand. It is situated about 25 minutes drive around the coast from New Plymouth on State Highway 45. Oakura is 12 km to the north-east, and Warea is 9 km to the south-west. The place offers popular rocky surfing spots around coastal beaches. The town was established as a military settlement in the 1860s. The New Zealand Ministry for Culture and Heritage gives a translation of "place of Kato" for . While "Kato" was probably a personal name, an alternative translation is "place of full tide/tsunami". In July 2020, the name of the locality was officially gazetted as Ōkato by the New Zealand Geographic Board. Ōkato has all the elements of a New Zealand rural community with sporting facilities (rugby grounds, bowling club, squash courts, tennis courts and swimming pool), Coastal Taranaki School, a police station, and a volunteer fire brigade. Ōkato was also notable as the home of Okato Cheese which was manufactured by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Canterbury
The University of Canterbury ( mi, Te Whare Wānanga o Waitaha; postnominal abbreviation ''Cantuar.'' or ''Cant.'' for ''Cantuariensis'', the Latin name for Canterbury) is a public research university based in Christchurch, New Zealand. It was founded in 1873 as Canterbury College, the first constituent college of the University of New Zealand. It is New Zealand's second-oldest university, after the University of Otago, itself founded four years earlier in 1869. Its original campus was in the Christchurch Central City, but in 1961 it became an independent university and began moving out of its original neo-gothic buildings, which were re-purposed as the Christchurch Arts Centre. The move was completed on 1 May 1975 and the university now operates its main campus in the Christchurch suburb of Ilam. The university is well known for its Engineering and Science programmes, with its Civil Engineering programme ranked 9th in the world (Academic Ranking of World Universities, 2021). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of New Zealand
The University of New Zealand was New Zealand's sole degree-granting university from 1874 to 1961. It was a collegiate university embracing several constituent institutions at various locations around New Zealand. After it was dissolved in 1961 New Zealand had four independent degree-granting universities and two associated agricultural colleges: the University of Otago (Dunedin), University of Canterbury (Christchurch), University of Auckland (Auckland), Victoria University of Wellington (Wellington), Canterbury Agricultural College (Lincoln) and Massey Agricultural College (Palmerston North). History The University of New Zealand Act set up the university in 1870. At that time, the system's headquarters was in Christchurch, Canterbury Province. The University of Otago negotiated to keep its title of "university" when it joined the University of New Zealand in 1874, but it agreed to award degrees of the University of New Zealand. The colleges in Christchurch, Auckland and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |