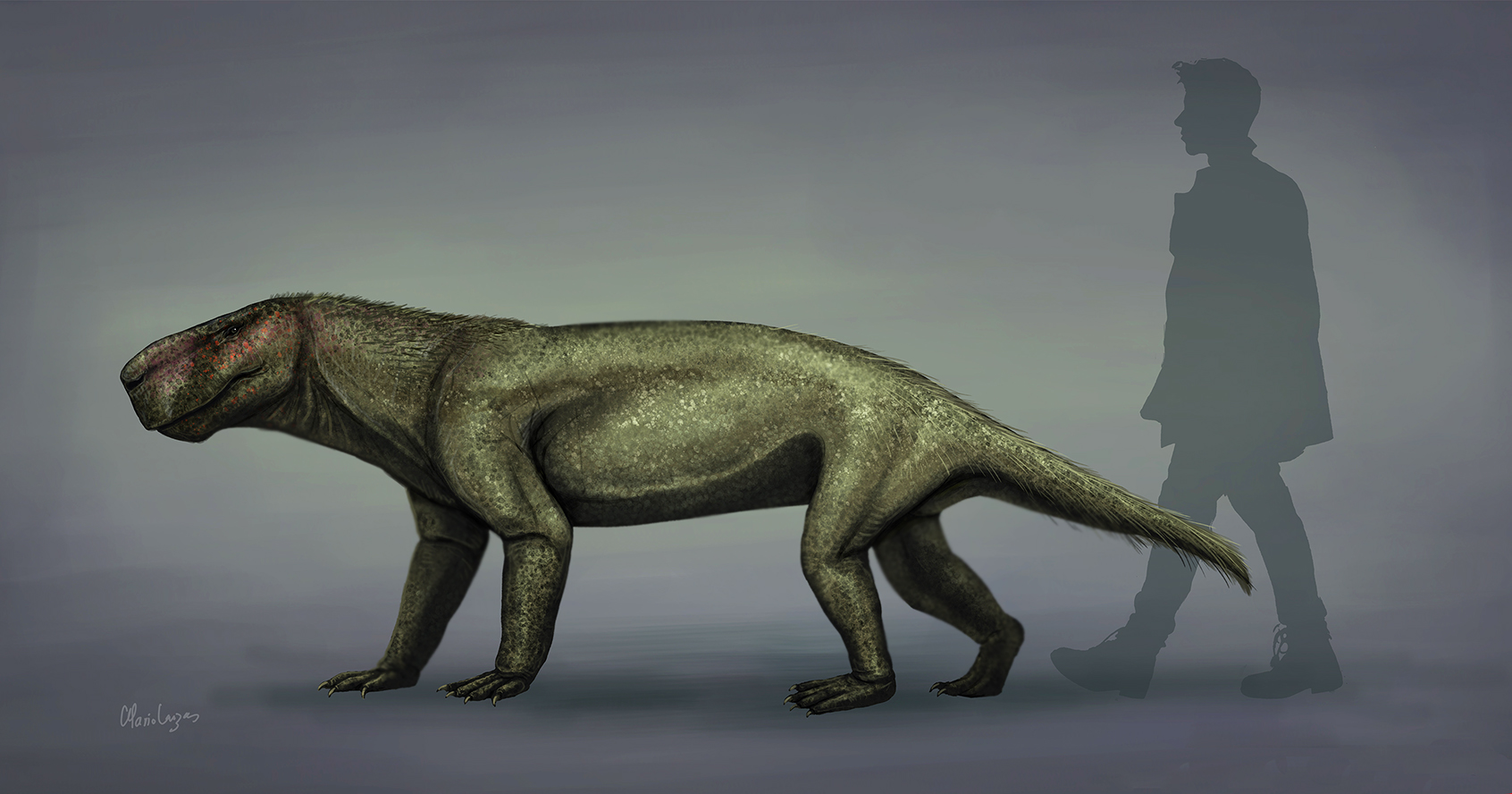|
1955 In Paleontology
Plants Pteridophyta Dinosaurs * ''Massospondylus'' gastroliths are documented.Bond (1955). Sanders, Manley, and Carpenter (2001), "Table 12.1" page 167. Newly named dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Synapsids Theriodonts Eutherians Cetaceans References {{portal, Paleontology * Bond, G. 1955. A note on dinosaur remains from the Forest Sandstone (Upper Karoo). Occasional Papers of the National Museum of Rhodesia 2: 795–800. * Sanders F, Manley K, Carpenter K. Gastroliths from the Lower Cretaceous sauropod Cedarosaurus weiskopfae. In: Tanke D.H, Carpenter K, editors. Mesozoic vertebrate life: new research inspired by the paleontology of Philip J. Currie. Indiana University Press; Bloomington, IN: 2001. pp. 166–180. 1950s in paleontology Paleontology Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azolla Primaeva
''Azolla primaeva'' is an extinct species of "water fern" in the family Salviniaceae known from Eocene fossils from the Ypresian stage (), found in southern British Columbia. The species was first described from poorly preserved material collected in the Similkameen River area near Princeton, British Columbia and later noted from outcrops at Stump Lake northeast of Princeton. The fossils were described by David P. Penhallow in the 1890 volume ''On Fossil Plants from the Smilkameen Valley and Other Places in the Southern Interior of British Columbia''. Though the volume only lists John William Dawson as author, Dawson notes that the ''A primaevum'' description had been written by Penhallow. Due to the poor nature of the type specimen the species was placed in the form genus '' Azollophyllum'' as ''Azollophyllum primaevum'' indicating its similarity to the modern genus, but at the same time acknowledging lack of detail needed to confirm its placement in the genus. Placement of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evgeny Maleev
Evgeny Aleksandrovich Maleev (, ; 25 February 1915 – 12 April 1966) was a Soviet and Russian paleontologist who did most of his research on reptiles and Asian fossils, such as the naming of the ankylosaur ''Talarurus'' and theropods ''Tarbosaurus'' and ''Therizinosaurus'' along with the family Therizinosauridae. Biography Evgeny Aleksandrovich Maleev was born on February 25, 1915, in the Russian Empire. After being a member on the Eastern Front (World War II) he started his scientific career at the Moscow State University. In 1947 he graduated from the Faculty of Biology, also in that year, he started to work at the Paleontological Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences. In 1950 Maleev presented his PhD thesis, "Morphofunctional analysis of the occipital region of the skull and skeleton of the neck of mammals", being awarded the Candidate of Sciences. Later on, he worked as the deputy manager from 1956 to 1962. He also was the leader of an expedition conducted in 1962 to In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liolithax
''Liolithax'' is an extinct genus of dolphin from the Middle Miocene (Serravallian) Temblor Formation of California. Taxonomy ''Liolithax kernensis'', described by Remington Kellogg Arthur Remington Kellogg (5 October 1892 – 8 May 1969) was an American naturalist and a director of the United States National Museum. His work focused on marine mammals. Early life and career Kellogg was born in Davenport, Iowa, and quic ... on the basis of the periotic CAS 4370 in 1931, was considered the only species of the genus until Barnes (1978) reassigned ''"Lophocetus" pappus'' to ''Liolithax'' based on similarities between the holotype periotic of ''L. kernensis'' and the periotic of ''L. pappus''. ''Liolithax'' was grouped in Kampholophinae with ''Kampholophos'' by Barnes (1978, 1985). The discovery of a skull from middle Miocene deposits in Baja California, Mexico cast doubt on the congenericity of ''"Lophocetus" pappus'' with the ''Liolithax'' type species by including a petros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traversodontid
Traversodontidae is an extinct family of herbivorous cynodonts. Traversodonts were primarily Gondwanan, with many species known from Africa and South America. Recently, traversodonts have also been found from Europe and eastern North America. Traversodonts first appeared in the Middle Triassic and diversified in the Late Triassic before going extinct at the end of the epoch. The family Traversodontidae was erected by Friedrich von Huene in 1936 for cynodonts first found in São Pedro do Sul in Paleorrota, Brazil. Description Traversodonts are members of Gomphodontia, a group of herbivorous cynognathian cynodonts. As an adaptation toward eating plants, they have wide postcanine teeth behind large canines. These postcanines are closely spaced with their crowns touching each other. Each is usually wider than it is long and is covered in several cusps. Because of their complexity, postcanine teeth are the primary means of identifying and distinguishing different species of traverso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manda Formation
The Manda Formation (also known as the Manda Beds) is a Middle Triassic (Anisian?) or possibly Late Triassic (Carnian?) geologic formation in Tanzania. It preserves fossils of many terrestrial vertebrates from the Triassic, including some of the earliest dinosauromorph archosaurs. The formation is often considered to be Anisian in age according to general tetrapod biochronology hypotheses and correlations to the ''Cynognathus'' Assemblage Zone of South Africa. However, some recent studies cast doubt to this age, suggesting that parts deposits may actually be younger (Carnian) in age. History of study One of the first to study rocks of the Manda Formation was British geologist G. M. Stockley. In 1932, Stockley explored the geology of the Ruhuhu Basin in Tanzania. He called a series of layers dating from the Late Carboniferous to the Middle Triassic the Songea Series and divided it into eight units labelled K1-K8. Stockley was also the first to describe fossils from these rocks, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalenodon
''Scalenodon'' is an extinct genus of traversodontid cynodonts from the Middle Triassic of Africa and possibly Russia. The type species ''S. angustifrons'' was named in 1946 and several other species were named in the following years. Most of the species from Africa are now thought to belong to different genera than ''Scalenodon''. History and species The first fossils belonging to ''Scalenodon'' were found in the Manda Formation of Zambia and assigned to '' Trirachodon angustifrons'' in 1946. In 1955, the species was given its own genus, ''Scalenodon''. In 1963, a second species called ''S. drysdalli'' was named from the Ntawere Formation in the Luangwa Valley of Zambia. Later that year ''S. drysdalli'' was placed in its own genus, '' Luangwa''. Three additional species, ''S. attridgei'', ''S. charigi'', and ''S. hirschoni'', were named from the Manda Formation in 1972. In 1973, a Russian species of ''Scalenodon'' was named ''S. boreus''. ''S. boreus'' is known from the southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorgonopsia
Gorgonopsia (from the Greek Gorgon, a mythological beast, and 'aspect') is an extinct clade of sabre-toothed therapsids from the Middle to Upper Permian roughly 265 to 252 million years ago. They are characterised by a long and narrow skull, as well as elongated upper and sometimes lower canine teeth and incisors which were likely used as slashing and stabbing weapons. Postcanine teeth are generally reduced or absent. For hunting large prey, they possibly used a bite-and-retreat tactic, ambushing and taking a debilitating bite out of the target, and following it at a safe distance before its injuries exhausted it, whereupon the gorgonopsian would grapple the animal and deliver a killing bite. They would have had an exorbitant gape, possibly in excess of 90°, without having to unhinge the jaw. They markedly increased in size as time went on, growing from small skull lengths of in the Middle Permian to bear-like proportions of up to in the Upper Permian. The latest gorgonopsia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lopingian
The Lopingian is the uppermost series/last epoch of the Permian. It is the last epoch of the Paleozoic. The Lopingian was preceded by the Guadalupian and followed by the Early Triassic. The Lopingian is often synonymous with the informal terms late Permian or upper Permian. The name was introduced by Amadeus William Grabau in 1931 and derives from Leping, Jiangxi in China. It consists of two stages/ ages. The earlier is the Wuchiapingian and the later is the Changhsingian. The International Chronostratigraphic Chart (v2018/07) provides a numerical age of 259.1 ±0.5 Ma. If a Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) has been approved, the lower boundary of the earliest stage determines numerical age of an epoch. The GSSP for the Wuchiapingian has a numerical age of 259.8 ± 0.4 Ma. Evidence from Milankovitch cycles suggests that the length of an Earth day during this epoch was approximately 22 hours. The Lopingian ended with the Permian–Triassic extinction event. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauroctonus
''Sauroctonus'' (from el, σαῦρος , 'lizard' and el, κτόνος , 'murderer') is an extinct genus of therapsids. ''Sauroctonus progressus'' was a large (2 m long) gorgonopsid that lived in the Late Permian epoch before the Permian-Triassic extinction event that wiped out many life forms on Earth (259-254 million years ago). Its fossils have been found in the Usili Formation ( Songea Group) of Tanzania and the Sokolki Assemblage Zone of the Volga Basin of Russia. Description ''Sauroctonus's'' flattened, triangular skull was about long, with a parietal eye, a primitive character, on the crown. The upper and lower jaw each contained one pair of massive canine teeth (the upper pair was larger); the other teeth were smaller, but were also sharp and pointed. In addition, minute, blunt teeth were present on the palatine bones. The lower jaw was widened to form a kind of chin. The long, lightly built, five-toed limbs bore a resemblance to mammals' limbs, but despite its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrannosaurid
Tyrannosauridae (or tyrannosaurids, meaning "tyrant lizards") is a family of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs that comprises two subfamilies containing up to thirteen genera, including the eponymous ''Tyrannosaurus''. The exact number of genera is controversial, with some experts recognizing as few as three. All of these animals lived near the end of the Cretaceous Period and their fossils have been found only in North America and Asia. Although descended from smaller ancestors, tyrannosaurids were almost always the largest predators in their respective ecosystems, putting them at the apex of the food chain. The largest species was ''Tyrannosaurus rex'', one of the largest and most massive known land predators, which measured over in length and according to most modern estimates to in weight. Tyrannosaurids were bipedal carnivores with massive skulls filled with large teeth. Despite their large size, their legs were long and proportioned for fast movement. In contrast, their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrannosaurus
''Tyrannosaurus'' is a genus of large theropoda, theropod dinosaur. The species ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' (''rex'' meaning "king" in Latin), often called ''T. rex'' or colloquially ''T-Rex'', is one of the best represented theropods. ''Tyrannosaurus'' lived throughout what is now western North America, on what was then an island continent known as Laramidia. ''Tyrannosaurus'' had a much wider range than other Tyrannosauridae, tyrannosaurids. Fossils are found in a variety of geologic formation, rock formations dating to the Maastrichtian Age (geology), age of the Upper Cretaceous Period (geology), period, 68 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago. It was the last known member of the tyrannosaurids and among the last non-aves, avian dinosaurs to exist before the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. Like other tyrannosaurids, ''Tyrannosaurus'' was a bipedal carnivore with a massive skull balanced by a long, heavy tail. Relative to its large and powerful hind limbs, the foreli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |