|
1906 Pensacola Hurricane
The 1906 Mississippi hurricane was a deadly and destructive hurricane during the 1906 Atlantic hurricane season. The fourth hurricane of the season, the system was originally observed in the western Caribbean on September 22; however, modern research revealed that the system became a tropical depression on September 19. The system slowly intensified, eventually becoming a major hurricane by September 24. The system made landfall near Pascagoula, Mississippi, during the evening of September 27, devastating the cities of Pensacola and Mobile and the state of Mississippi. Damage totaled to at least $19,221,000, and more than 134 people were killed. Meteorological history The first documented information on the storm places it in the western Caribbean Sea on September 22, although modern reanalysis of this storm identifies it as a tropical depression on September 19. The storm drifted north from the Yucatán Channel on September 24, while it was a weak hurricane with winds of . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southeastern United States
The Southeastern United States, also referred to as the American Southeast or simply the Southeast, is a geographical region of the United States. It is located broadly on the eastern portion of the southern United States and the southern portion of the eastern United States. It comprises at least a core of states on the lower East Coast of the United States and eastern Gulf Coast. Expansively, it reaches as far north as West Virginia and Maryland (bordered to north by the Ohio River and Mason–Dixon line), and stretching as far west as Arkansas and Louisiana. There is no official U.S. government definition of the region, though various agencies and departments use different definitions. Geography The U.S. Geological Survey considers the Southeast region to be the states of Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Arkansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Tennessee, plus Puerto Rico and the United States Virgin Islands. There is no official Census Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louisville And Nashville Railroad
The Louisville and Nashville Railroad , commonly called the L&N, was a Class I railroad that operated freight and passenger services in the southeast United States. Chartered by the Commonwealth of Kentucky in 1850, the road grew into one of the great success stories of American business. Operating under one name continuously for 132 years, it survived civil war and economic depression and several waves of social and technological change. Under Milton H. Smith, president of the company for 30 years, the L&N grew from a road with less than of track to a system serving fourteen states. As one of the premier Southern railroads, the L&N extended its reach far beyond its namesake cities, stretching to St. Louis, Memphis, Atlanta, and New Orleans. The railroad was economically strong throughout its lifetime, operating freight and passenger trains in a manner that earned it the nickname, "The Old Reliable." Growth of the railroad continued until its purchase and the tumultuous rail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apalachicola Bay
Apalachicola may refer to: * Apalachicola people, a group of Native Americans who lived along the Apalachicola River in present-day Florida Places *Apalachicola, Florida *Apalachicola River *Apalachicola Bay *Apalachicola National Forest *Apalachicola Regional Airport *Port of Apalachicola Railroad *Apalachicola and Alabama Railroad *Apalachicola Northern Railroad The Apalachicola Northern Railroad was a short-line railroad which operated in the Florida Panhandle. It owned and operated a between Port Saint Joe, Florida, and Chattahoochee, Florida, with a short spur to Apalachicola, Florida. It was founde ... Ships *, a tugboat in the United States Navy. {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Bay (Santa Rosa County, Florida)
East Bay is a bay located in the far western Florida Panhandle. Unusually, East Bay is connected to open waters via Pensacola Bay to its southwest. The bay is fed primarily by the Blackwater River and the East Bay River. East Lagoon The east side of East Bay is pinched into a wide river-like shape (often referred to as East Lagoon on historical maps, though the name is no longer commonly used) until eventually becoming an actual river at East Bay River. The Lagoon starts where the bay is met by Axelson Point and Miller Point. History European exploration of the bay likely occurred as early as Pensacola's establishment in the early 16th century. The bay has been included in most major maps of the bay system and harbor, dating back to that era. Between its first mapping and the present day, the bay has been listed under several different names, primarily Oyster Cove, Galvez Bay, and East Bay. During Hurricane Ivan's landfall in September 2004, the storm surge from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
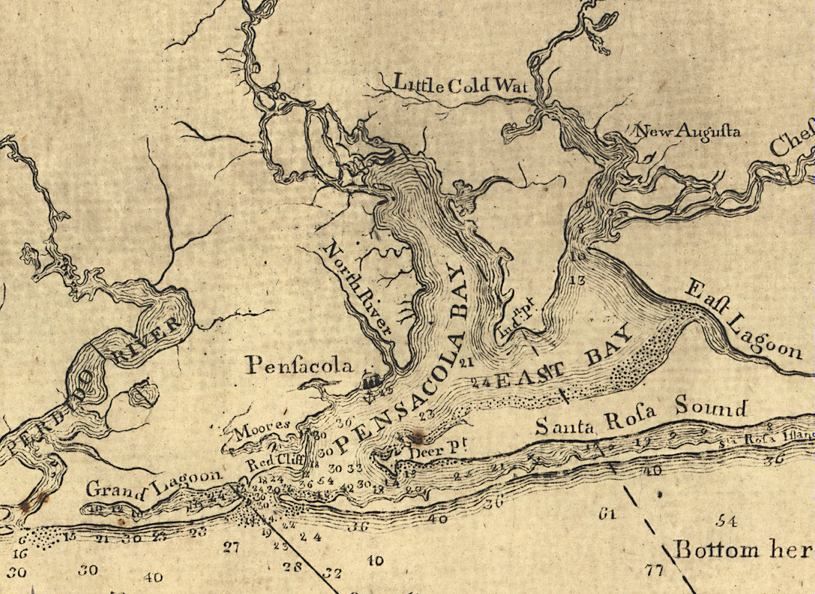
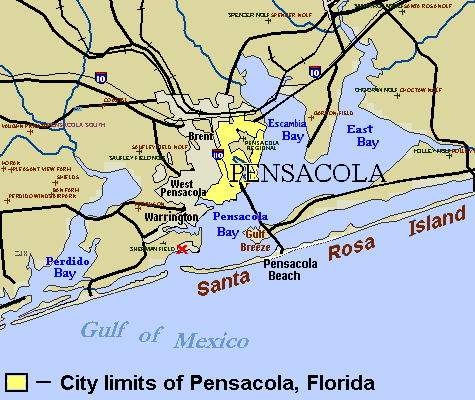
Pensacola Bay
Pensacola Bay is a bay located in the northwestern part of Florida, United States, known as the Florida Panhandle. The bay, an inlet of the Gulf of Mexico, is located in Escambia County and Santa Rosa County, adjacent to the city of Pensacola, Florida, and is about 13 miles (21 km) long and 2.5 miles (4 km) wide. The Pensacola Bay estuarine system including Escambia Bay, Pensacola Bay, Blackwater Bay, East Bay, and Santa Rosa Sound, and four rivers—the Escambia,’ Blackwater,’ Yellow and East Rivers is 144 square miles, and it is the fourth largest estuarine system in Florida. Pensacola Bay is formed and protected by Fairpoint Peninsula and the barrier island of Santa Rosa. The Pensacola Bay Bridge crosses the bay, connecting Pensacola to Gulf Breeze on the western end of the peninsula. The Gulf Islands National Seashore includes Santa Rosa Island, and encloses part of the bay. The Gulf Intracoastal Waterway runs through a section of the bay. Pensacola Bay le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warrington, Florida
Warrington is a census-designated place (CDP) in Escambia County, Florida, United States. Warrington is located between downtown Pensacola and the state line with Alabama; it is away from both. The population was 14,531 at the 2010 census. It is part of the Pensacola– Ferry Pass– Brent Metropolitan Statistical Area. A failed referendum was held in 1975 to incorporate Warrington as a town. Despite falling outside of city limits and having a post office explicitly named "Warrington", mail going to the addresses in the Warrington ZIP code (32507) falls under the jurisdiction of Pensacola. Naval Air Station Pensacola is located in Warrington (albeit with their own ZIP code, 32508, which corresponds to the mailing city "Naval Air Station Pensacola, FL"). History Warrington is named for Lewis Warrington, who served as Secretary of the Navy, and who helped choose the area that became Naval Air Station Pensacola. He served as the first commandant of the newly created Navy Yard, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Air Station Pensacola
Naval Air Station Pensacola or NAS Pensacola (formerly NAS/KNAS until changed circa 1970 to allow Nassau International Airport, now Lynden Pindling International Airport, to have IATA code NAS), "The Cradle of Naval Aviation", is a United States Navy base located next to Warrington, Florida, a community southwest of the Pensacola city limits. It is best known as the initial primary training base for all U.S. Navy, Marine Corps and Coast Guard officers pursuing designation as naval aviators and naval flight officers, the advanced training base for most naval flight officers, and as the home base for the United States Navy Flight Demonstration Squadron, the precision-flying team known as the Blue Angels. Because of contamination by heavy metals and other hazardous materials during its history, it is designated as a Superfund site needing environmental cleanup. The air station also hosts the Naval Education and Training Command (NETC) and the Naval Aerospace Medical Institute (NAM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
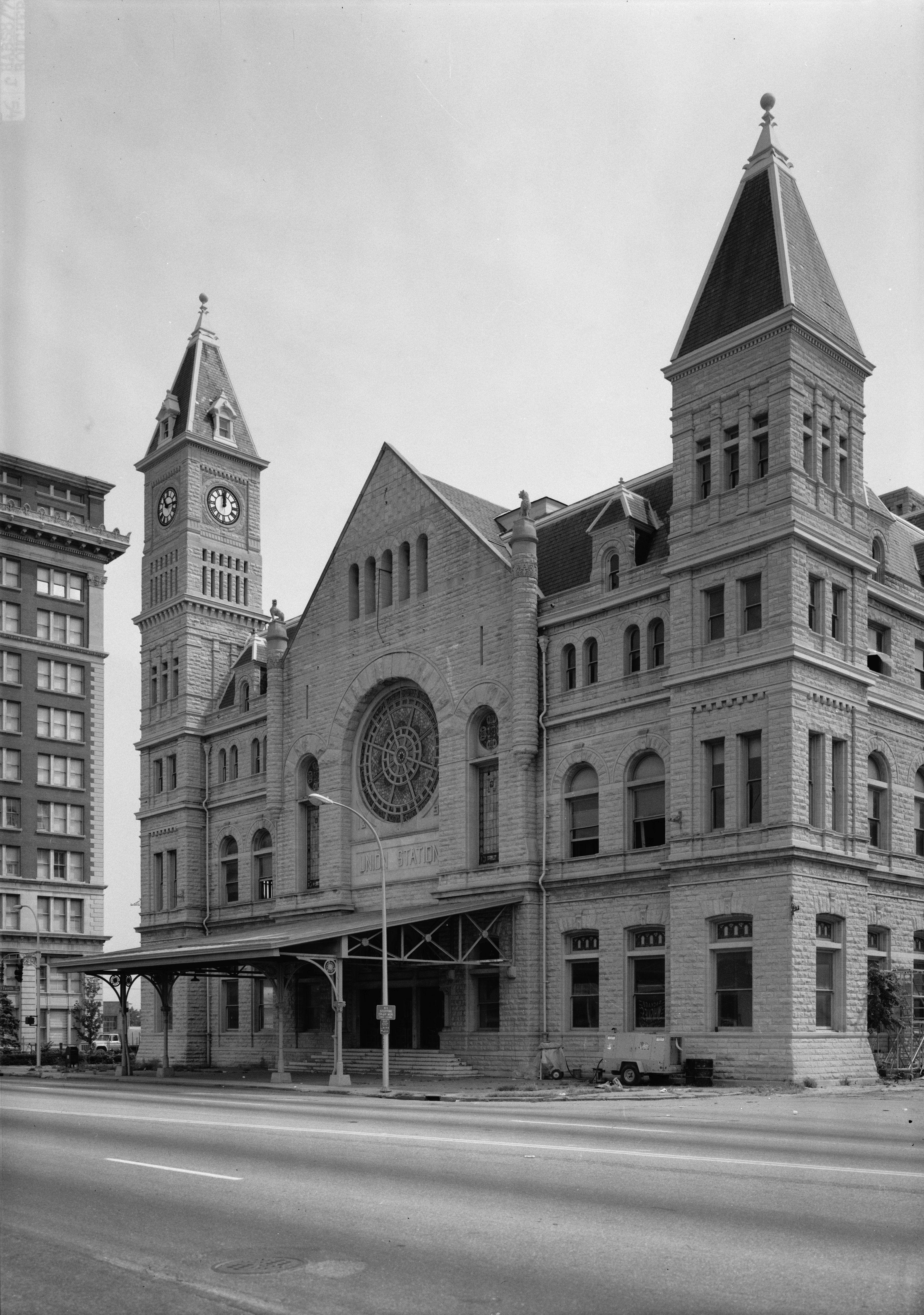
Pensacola 1906 Hurricane Damage
Pensacola () is the westernmost city in the Florida Panhandle, and the county seat and only incorporated city of Escambia County, Florida, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 54,312. Pensacola is the principal city of the Pensacola Metropolitan Area, which had an estimated 502,629 residents . Pensacola is the site of the first Spanish settlement within the borders of the continental United States in 1559, predating the establishment of St. Augustine by 6 years, although the settlement was abandoned due to a hurricane and not re-established until 1698. Pensacola is a seaport on Pensacola Bay, which is protected by the barrier island of Santa Rosa and connects to the Gulf of Mexico. A large United States Naval Air Station, the first in the United States, is located southwest of Pensacola near Warrington; it is the base of the Blue Angels flight demonstration team and the National Naval Aviation Museum. The main campus of the University of West Flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schooner
A schooner () is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than the mainmast. A common variant, the topsail schooner also has a square topsail on the foremast, to which may be added a topgallant. Differing definitions leave uncertain whether the addition of a fore course would make such a vessel a brigantine. Many schooners are gaff-rigged, but other examples include Bermuda rig and the staysail schooner. The origins of schooner rigged vessels is obscure, but there is good evidence of them from the early 17th century in paintings by Dutch marine artists. The name "schooner" first appeared in eastern North America in the early 1700s. The name may be related to a Scots word meaning to skip over water, or to skip stones. The schooner rig was used in vessels with a wide range of purposes. On a fast hull, good ability to windward was useful for priv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barque
A barque, barc, or bark is a type of sailing ship, sailing vessel with three or more mast (sailing), masts having the fore- and mainmasts Square rig, rigged square and only the mizzen (the aftmost mast) Fore-and-aft rig, rigged fore and aft. Sometimes, the mizzen is only partly fore-and-aft rigged, bearing a square-rigged sail above. Etymology The word "barque" entered English via the French term, which in turn came from the Latin language, Latin ''barca'' by way of Occitan language, Occitan, Catalan language, Catalan, Spanish, or Italian. The Latin ''barca'' may stem from Celtic language, Celtic ''barc'' (per Rudolf Thurneysen, Thurneysen) or Greek ''baris'' (per Friedrich Christian Diez, Diez), a term for an Egyptian boat. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'', however, considers the latter improbable. The word ''barc'' appears to have come from Celtic languages. The form adopted by English, perhaps from Irish language, Irish, was "bark", while that adopted by Latin as ''barca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
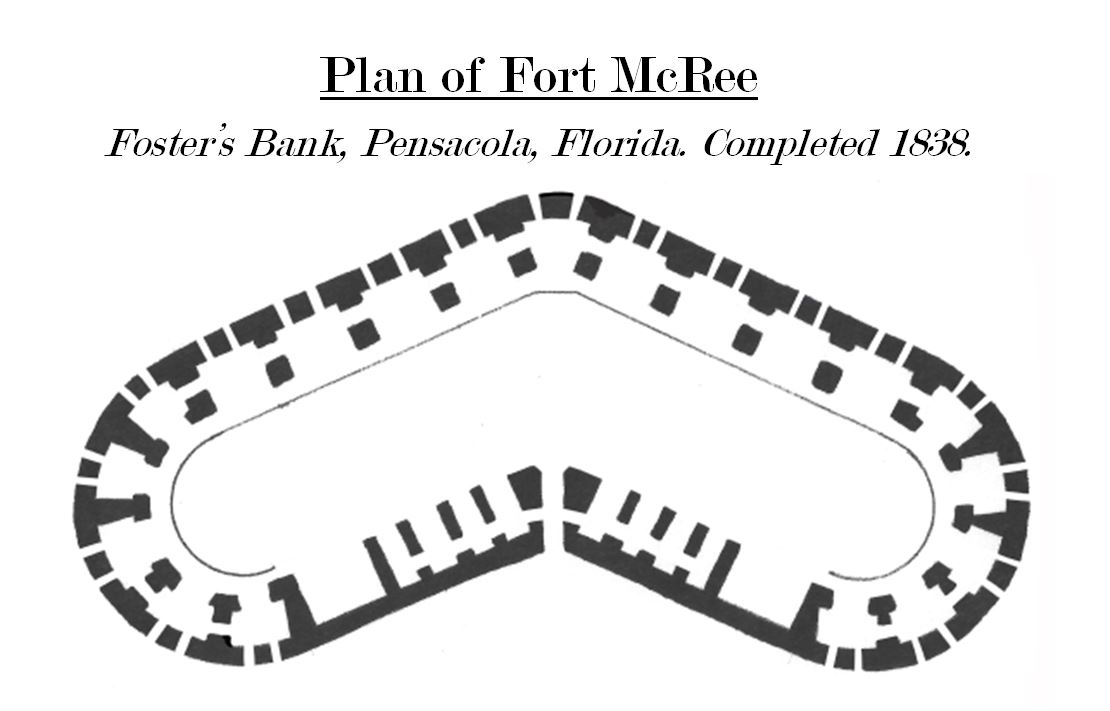
Fort McRee
Fort McRee was a historic military fort constructed by the United States on the eastern tip of Perdido Key to defend Pensacola and its important natural harbor. In the defense of Pensacola Bay, Fort McRee was accompanied by Fort Pickens, located across Pensacola Pass on Santa Rosa Island, and Fort Barrancas, located across Pensacola Bay on the grounds of what is now Naval Air Station (NAS) Pensacola. Fort Pickens was the largest of these. Very little remains of Fort McRee today. History Design and Construction Fort McRee was one of three major installations constructed by the United States to strengthen defenses at Pensacola Bay following the War of 1812. Its construction lasted from 1834 to 1839; the facility was a three-tiered fort and a detached water battery close to sea level. It was located on the eastern tip of Perdido Key on a stretch of beach known as Foster's Bank. It had a highly unusual shape because of its position on a small, narrow barrier island. Fort McRee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Pickens
Fort Pickens is a pentagonal historic United States military fort on Santa Rosa Island in the Pensacola, Florida, area. It is named after American Revolutionary War hero Andrew Pickens. The fort was completed in 1834 and was one of the few forts in the South that remained in Union hands throughout the American Civil War. It remained in use until 1947. Fort Pickens is included within the Gulf Islands National Seashore, and as such, is administered by the National Park Service. Design Fort Pickens was part of the Third System of Fortifications, meant to enhance the old earthworks and simple, obsolete designs of the First and Second System of Fortifications. Fort Pickens was of a Pentagonal design, with broader western walls to provide a wide range of fire over the bay. The fort had a counterscarp to the east side exclusively, to create a defensive moat in the event that a land invasion came from the west. The westernmost Bastions were also equipped with mine chambers, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |