|
1905 In Aviation
This is a list of aviation-related events from 1905: Events * In Santa Clara, California, Daniel J. Maloney flies for 20 minutes with a glider after starting from a balloon at a height of 4,000 ft (1,220 m). * The engineer Maurice Stanislas Léger's helicopter lifts a person vertically into the air in Monaco. * U.S. Army Signal Corps transferred all balloon school activities to Fort Omaha, Nebraska. January–December *18 January – The Wright brothers begin discussions with the United States Government about selling it an airplane. *16–20 March – Daniel Maloney is launched by balloon in a tandem-wing glider designed by John MontgomeryJohnsen, Frederick A., "Mother Ships," ''Aviation History'', January 2018, p. 48. and makes three successful flights at Aptos, California, the highest launch being at 3,000 feet (914 meters) with an 18-minute descent to a predetermined landing location. *27 April – Sapper Moreton of the British Army's balloon section is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot air balloons and airships. Aviation began in the 18th century with the development of the hot air balloon, an apparatus capable of atmospheric displacement through buoyancy. Some of the most significant advancements in aviation technology came with the controlled gliding flying of Otto Lilienthal in 1896; then a large step in significance came with the construction of the first powered airplane by the Wright brothers in the early 1900s. Since that time, aviation has been technologically revolutionized by the introduction of the jet which permitted a major form of transport throughout the world. Etymology The word ''aviation'' was coined by the French writer and former naval officer Gabriel La Landelle in 1863. He derived the term from the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabriel Voisin
Gabriel Voisin (5 February 1880 – 25 December 1973) was a French aviation pioneer and the creator of Europe's first manned, engine-powered, heavier-than-air aircraft capable of a sustained (1 km), circular, controlled flight, which was made by Henry Farman on 13 January 1908 near Paris, France. During World War I the company founded by Voisin became a major producer of military aircraft, notably the Voisin III. Subsequently, he switched to the design and production of luxury automobiles under the name Avions Voisin. Early life Gabriel Voisin was born on 5 February 1880 in Belleville-sur-Saône, France, and his brother Charles Voisin, two years younger than him, was his main childhood companion. When his father abandoned the family his mother, Amélie, took her sons to Neuville-sur-Saône, where they settled near her father's factory. Their grandfather, Charles Forestier, took charge of the boys' education with military rigor. The boys also went for expeditions along the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The state's capital and largest city is Columbus, with the Columbus metro area, Greater Cincinnati, and Greater Cleveland being the largest metropolitan areas. Ohio is bordered by Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the west, and Michigan to the northwest. Ohio is historically known as the "Buckeye State" after its Ohio buckeye trees, and Ohioans are also known as "Buckeyes". Its state flag is the only non-rectangular flag of all the U.S. states. Ohio takes its name from the Ohio River, which in turn originated from the Seneca word ''ohiːyo'', meaning "good river", "great river", or "large creek". The state arose from the lands west of the Appalachian Mountai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
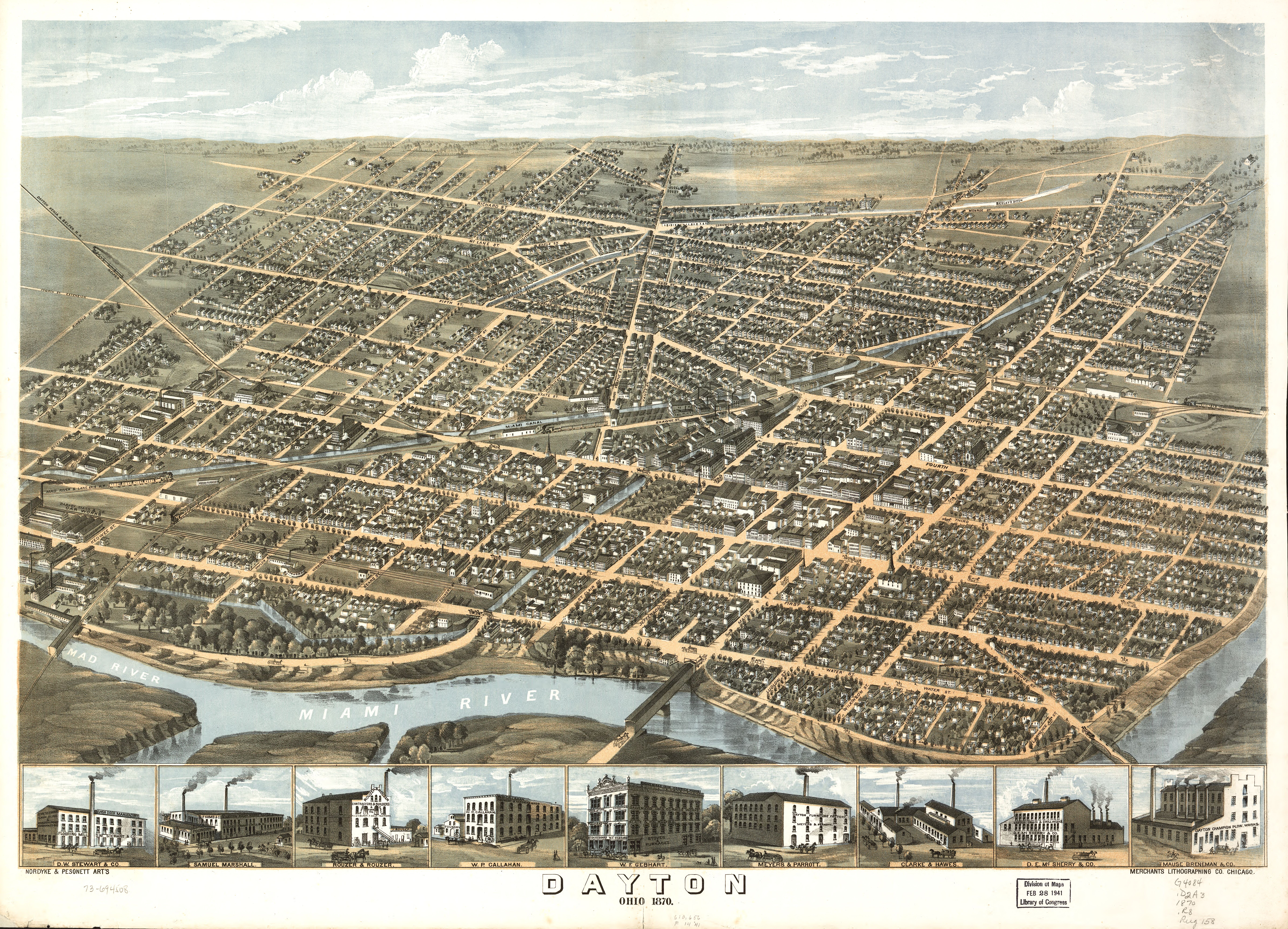
Dayton, Ohio
Dayton () is the sixth-largest city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Montgomery County. A small part of the city extends into Greene County. The 2020 U.S. census estimate put the city population at 137,644, while Greater Dayton was estimated to be at 814,049 residents. The Combined Statistical Area (CSA) was 1,086,512. This makes Dayton the fourth-largest metropolitan area in Ohio and 73rd in the United States. Dayton is within Ohio's Miami Valley region, north of the Greater Cincinnati area. Ohio's borders are within of roughly 60 percent of the country's population and manufacturing infrastructure, making the Dayton area a logistical centroid for manufacturers, suppliers, and shippers. Dayton also hosts significant research and development in fields like industrial, aeronautical, and astronautical engineering that have led to many technological innovations. Much of this innovation is due in part to Wright-Patterson Air Force Base and its place in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
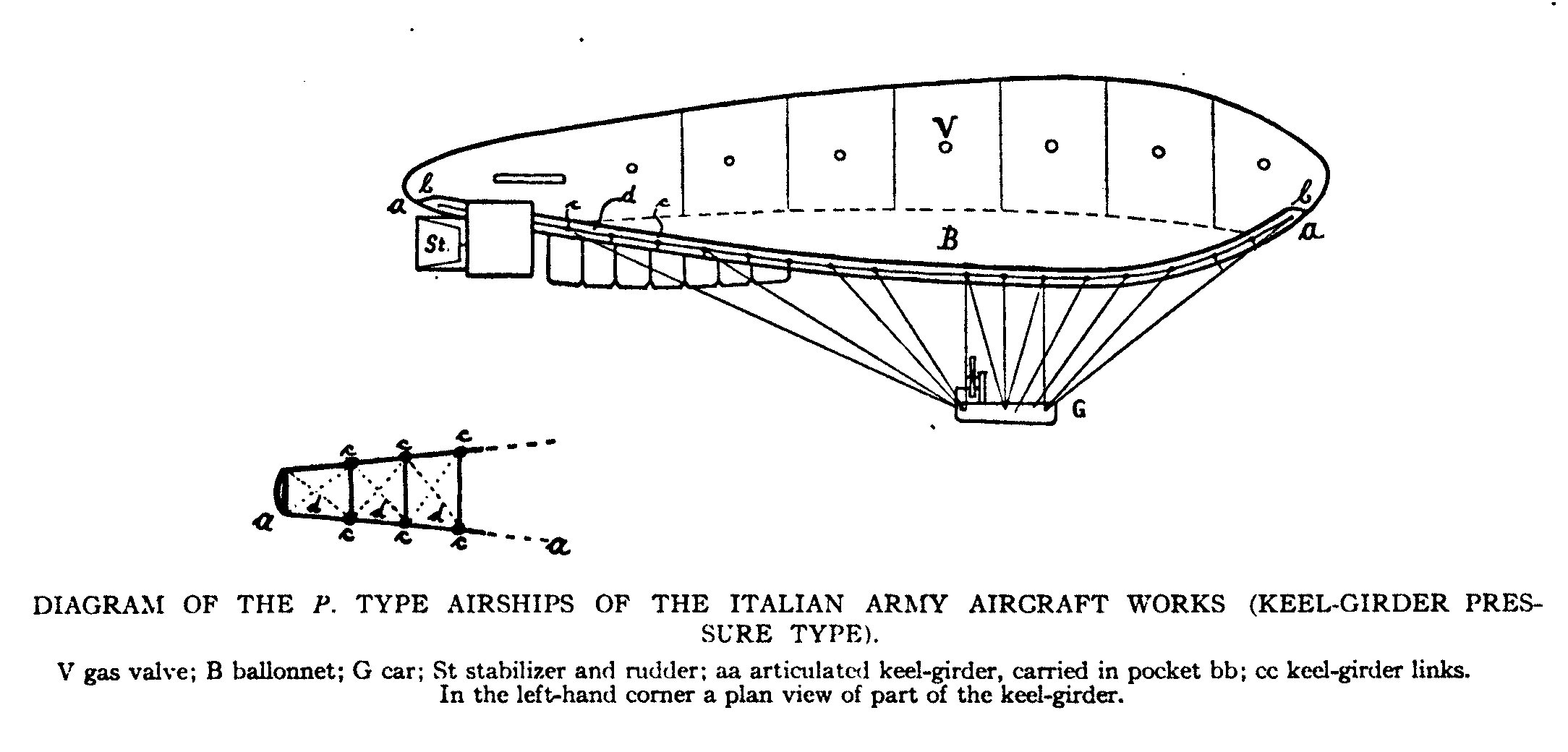
Semi-rigid Airship
A semi-rigid airship is an airship which has a stiff keel or truss supporting the main envelope along its length. The keel may be partially flexible or articulated and may be located inside or outside the main envelope. The outer shape of the airship is maintained by gas pressure, as with the non-rigid "blimp". Semi-rigid dirigibles were built in significant quantity from the late 19th century but in the late 1930s they fell out of favour along with rigid airships. No more were constructed until the semi-rigid design was revived by the Zeppelin NT in 1997. Semi-rigid construction is lighter-weight than the outer framework of a rigid airship, while it allows greater loading than a non-rigid type. Principle More or less integrally attached to the hull are the gondola, engines and sometimes the empennage (tail). The framework has the task of distributing the suspension loads of these attachments and the lifting gas loads evenly throughout the whole hull's surface and may also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willows Airships
The Willows airships were a series of pioneering non-rigid airships designed and built in Wales by Ernest Thompson Willows in the first decade of the 20th century. The first airship Willows No. 1 flew in 1905, and the last, the Willows No. 5 in 1913. Design and development Willows No. 1 First flown for 85 minutes by the nineteen-year-old Willows from East Moors, Cardiff in Wales on 5 August 1905, the No. 1 was a small semi-rigid of 12,600 cubic feet (354 m³). The 74 ft (22.55 m) long and 18 ft (5.5 m) diameter envelope was made from silk and had a framework gondola suspended beneath it. At the rear of the framework was a twin-cylinder Peugeot motorcycle engine fitted with a two-bladed 10 ft (3 m) pusher propeller. The Willows No. 1 undertook six flights with the longest lasting two hours. Willows No. 2 Willows next airship the Willows No. 2 first flew on 26 November 1909. No. 2 was 86 ft (26.2 m) long and 22 ft (6.7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest Willows
Ernest Thompson Willows (1886–1926) was a pioneer Welsh aviator and airship builder. He became the first person in the United Kingdom to hold a pilots certificate for an airship when the Royal Aero Club awarded him ''Airship Pilots Certificate No. 1''. Willows was born in Cardiff, Wales on 11 July 1886. He was educated at Clifton College in Bristol, entering the school in 1896 and leaving in 1901 aged 15 to train as a dentist. He built his first airship, the Willows No. 1, in 1905 when he was 19. It was first flown from East Moors, Cardiff on 5 August 1905, the flight lasting 85 minutes. This was soon followed by an improved ''Willows No. 2'', in which he landed outside Cardiff City Hall on 4 June 1910. No. 2 was re-built as No. 3 which he named the ''City of Cardiff'' before he flew it from London to Paris in 1910. This was the first airship crossing of the English Channel at night and the first from England to France. The journey was not without incident, including droppi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percy Pilcher
Percy Sinclair Pilcher (16 January 1867 – 2 October 1899) was a British inventor and pioneer aviator who was his country's foremost experimenter in unpowered flight near the end of the nineteenth century. After corresponding with Otto Lilienthal, Pilcher had considerable success with developing hang gliders. In 1895, he made repeated flights in the ''Bat'', and in 1896–1897 many flights in the ''Hawk'' culminated in a world distance record. By 1899, Pilcher had produced a motor-driven triplane, which he planned to test at Stanford Hall in Leicestershire on September 30, 1899; however, the attempt was delayed by mechanical problems. When he substituted a flight of ''Hawk'', it suffered structural failure in mid-air and he was fatally injured in the resulting crash, with his powered aircraft never having been tested. Research carried out by Cranfield University in the early 2000s concluded that Pilcher's triplane was more or less workable, and would have been capable of fli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
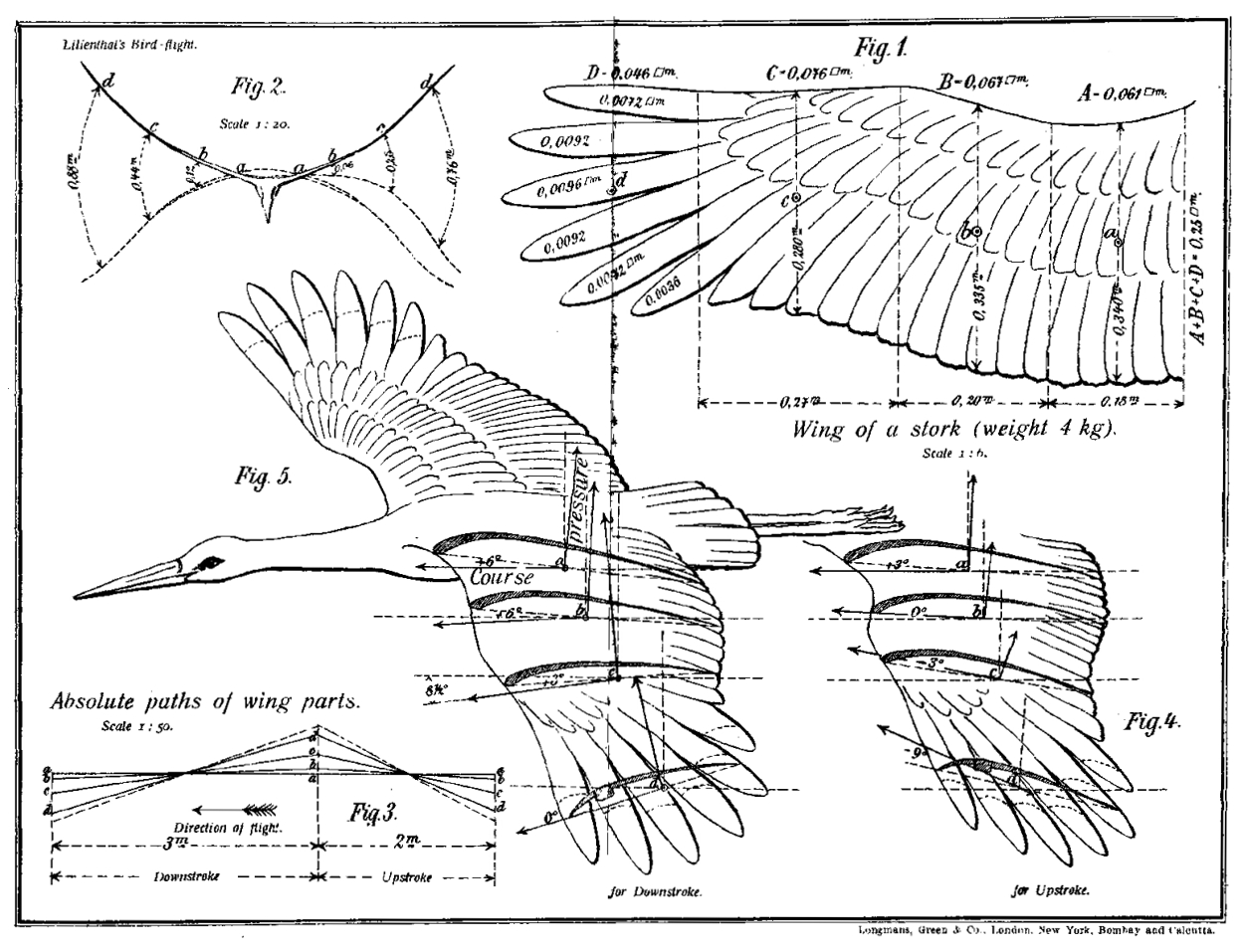
Otto Lilienthal
Karl Wilhelm Otto Lilienthal (23 May 1848 – 10 August 1896) was a German pioneer of aviation who became known as the "flying man". He was the first person to make well-documented, repeated, successful flights with gliders, therefore making the idea of "heavier than air" a reality. Newspapers and magazines published photographs of Lilienthal gliding, favourably influencing public and scientific opinion about the possibility of flying machines becoming practical. Lilienthal's work led to him developing the concept of the modern wing. His flight attempts in 1891 are seen as the beginning of human flight and the "Lilienthal Normalsegelapparat" is considered to be the first airplane in series production, making the ''Maschinenfabrik Otto Lilienthal'' the first air plane production company in the world. Otto Lilienthal is often referred to as either the "father of aviation" or "father of flight". On 9 August 1896, his glider stalled and he was unable to regain control. Falling f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavier-than-air
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, helicopters, airships (including blimps), gliders, paramotors, and hot air balloons. The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called ''aeronautics.'' Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard pilot, but unmanned aerial vehicles may be remotely controlled or self-controlled by onboard computers. Aircraft may be classified by different criteria, such as lift type, aircraft propulsion, usage and others. History Flying model craft and stories of manned flight go back many centuries; however, the first manned ascent — and safe descent — in modern times took place by larger hot-air ball ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
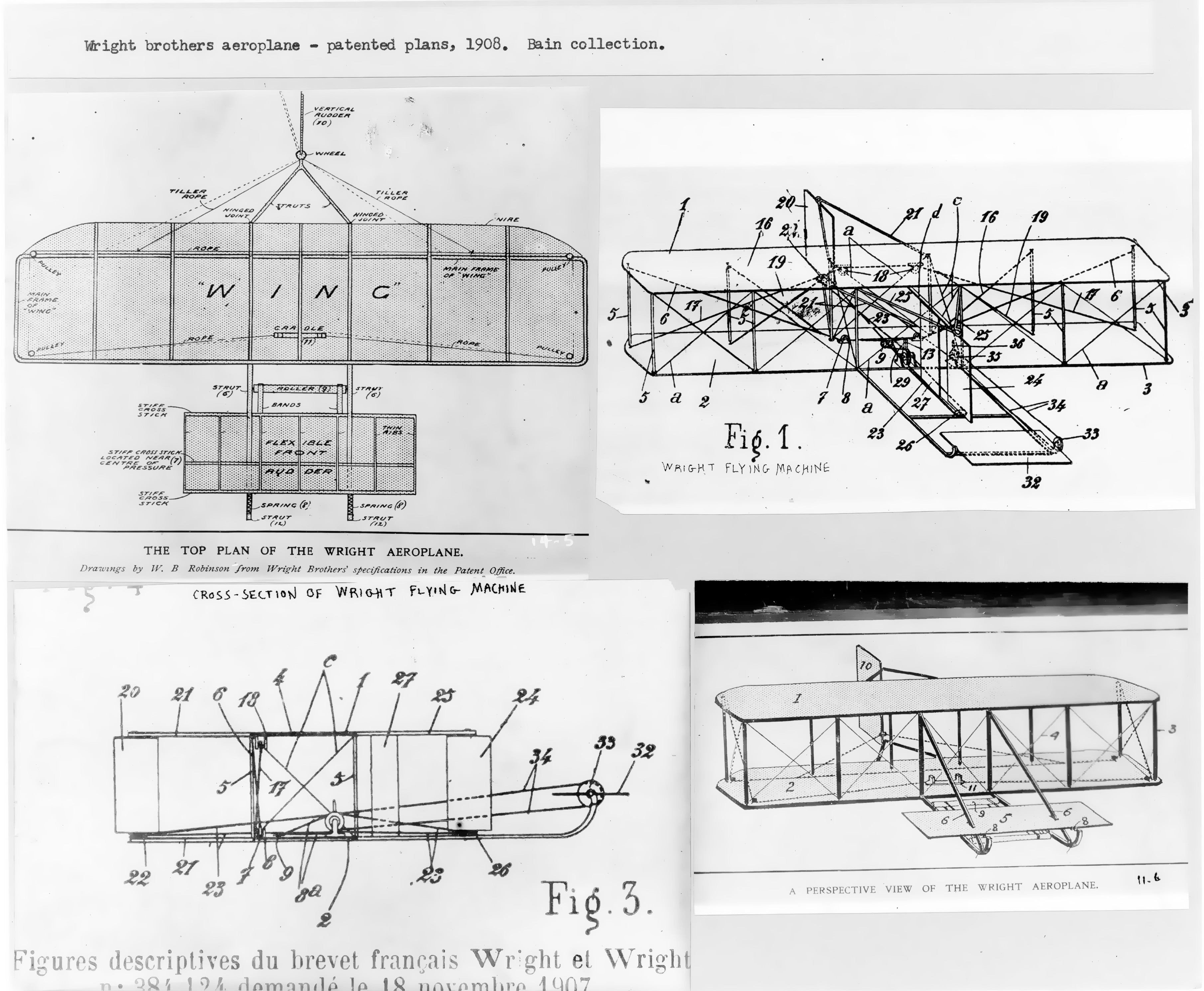
Wright Flyer
The ''Wright Flyer'' (also known as the ''Kitty Hawk'', ''Flyer'' I or the 1903 ''Flyer'') made the first sustained flight by a manned heavier-than-air powered and controlled aircraft—an airplane—on December 17, 1903. Invented and flown by Orville and Wilbur Wright, it marked the beginning of the pioneer era of aviation. The Wright brothers flew the ''Wright Flyer'' four times that day on land now part of the town of Kill Devil Hills, about south of Kitty Hawk, North Carolina. The aircraft was preserved and is now exhibited in the National Air and Space Museum in Washington, D.C. Design and construction The ''Flyer'' was based on the Wrights' experience testing gliders at Kitty Hawk between 1900 and 1902. Their last glider, the 1902 Glider, led directly to the design of the ''Wright Flyer''. The Wrights built the aircraft in 1903 using spruce for straight members of the airframe (such as wing spars) and ash wood for curved components (wing ribs). The wings were desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wright Flyer III
The Wright Flyer III was the third powered aircraft by the Wright Brothers, built during the winter of 1904–05. Orville Wright made the first flight with it on June 23, 1905. The Flyer III had an airframe of spruce construction with a wing camber of 1-in-20 as used in 1903, rather than the less effective 1-in-25 used in 1904. The new machine was equipped with the engine and other hardware from the scrapped Flyer II and, after major modifications, achieved much greater performance than Flyers I and II. Design and development The 1905 flyer was made stronger, more durable, and with a longer tail to provide better directional stability and control. A larger cylinder bore engine provided more power, while a more effective leading edge, and efficient propellers, improved performance. The propeller blades were made wider and thinner, while according to Harry Combs, "...adding a backward sweep to the blades, calculated precisely to avoid the pressures of flight and to keep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)