|
1904 In Paleontology
Dinosaurs Newly named dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Plesiosaurs * Plesiosaur gastroliths documented.Brown (1904). Williston (1904). Sanders, Manley, and Carpenter (2001), "Table 12.1" page 167. Synapsids Non-mammalian Metatherians Eutherians Cetaceans Even-toed Ungulates References {{reflist * Brown, B. (1904) Stomach stones and food of plesiosaurs, Science, n.s. 20, (501): 184-185 * Sanders F, Manley K, Carpenter K. Gastroliths from the Lower Cretaceous sauropod Cedarosaurus weiskopfae. In: Tanke D.H, Carpenter K, editors. Mesozoic vertebrate life: new research inspired by the paleontology of Philip J. Currie. Indiana University Press; Bloomington, IN: 2001. pp. 166–180. * Williston, Samuel Wendel; 1904; The stomach stones of the plesiosaurs; Science; 20 pp. 565; American Association for the Advancement of Science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
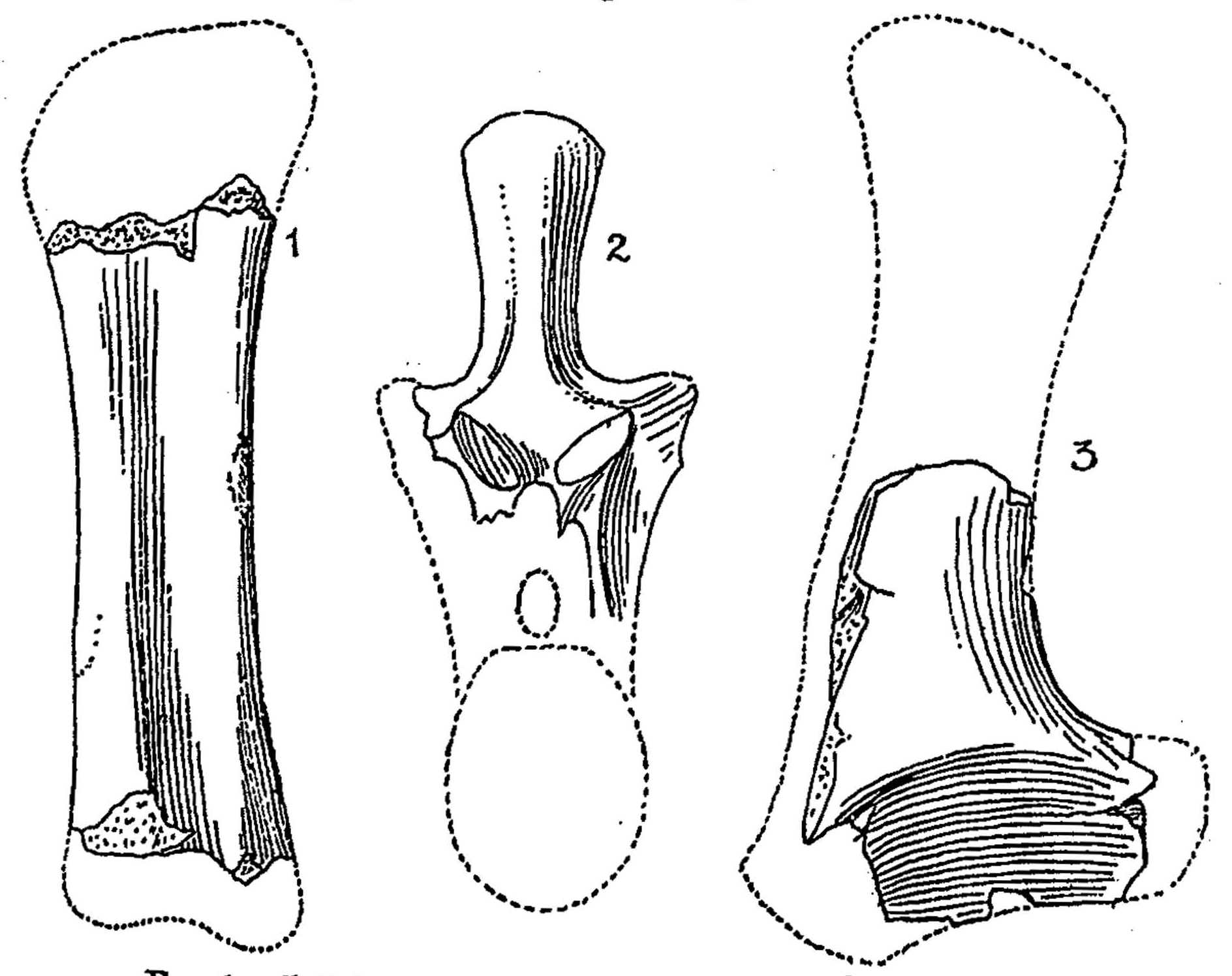
Algoasaurus
''Algoasaurus'' (; "Algoa Bay reptile") is a genus of sauropod dinosaur from the Berriasian- early Valanginian-age Early Cretaceous Upper Kirkwood Formation of Cape Province, South Africa, specifically near a town called Despatch. Discovery and naming The holotype, a cervical vertebra, femur, an ungual phalanx and a scapula, was recovered in 1903 from a quarry in Despatch, Eastern Cape which exposed part of the Upper Kirkwood Formation by workmen who did not recognize them as dinosaur specimens, so many of the bones, probably including the rest of the once near-complete holotype, were made into bricks and thus destroyed;Broom, R. (1904)On the occurrence of an opisthocoelian dinosaur (''Algoasaurus Bauri'') in the Cretaceous beds of South Africa.''Geological Magazine'', decade 5, 1(483):445-447. it is possible that bricks in the Nelson Mandela Bay Metropolitan Municipality may still contain parts of the ''Algoasaurus'' holotype. According to Broom (1904), the Port Elizabeth Mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinle Formation
The Chinle Formation is an Upper Triassic continental geological formation of fluvial, lacustrine, and palustrine to eolian deposits spread across the U.S. states of Nevada, Utah, northern Arizona, western New Mexico, and western Colorado. In New Mexico, it is often raised to the status of a geological group, the Chinle Group. Some authors have controversially considered the Chinle to be synonymous to the Dockum Group of eastern Colorado and New Mexico, western Texas, the Oklahoma panhandle, and southwestern Kansas. The Chinle Formation is part of the Colorado Plateau, Basin and Range, and the southern section of the Interior Plains.GEOLEX database entry for Chinle USGS (viewed 19 March 2006) A probable separate depositional basin within the Chinle is found in northwestern Colorado and northeastern Ut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosthennops
''Prosthennops'' is a genus of extinct peccaries that lived in North and Central America between the middle Miocene and lower Pliocene (around 15-5 million years ago). Description This animal was very similar to present-day peccaries, both in appearance and size. ''Prosthennops'' had a shoulder height of about 76 cm. Individuals in the northern part of its range were larger than those in southern Central America. It possessed a robust skull, with a depressed and elongated snout (but to a lesser extent than other extinct peccaries such as Mylohyus). The orbits were set back on the skull, above the glenoid cavity. The malar/zygomatic bones were prominent like those of African warthogs, developing laterally in massive tubercles.The premaxillary bones were well-developed and bore only two pairs of incisors, of which the second pair was often vestigial. The fangs were pointed downwards, rather than forwards as in modern boars. The highly developed canines had an elliptical cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutetian
The Lutetian is, in the geologic timescale, a stage or age in the Eocene. It spans the time between . The Lutetian is preceded by the Ypresian and is followed by the Bartonian. Together with the Bartonian it is sometimes referred to as the Middle Eocene Subepoch. Stratigraphic definition The Lutetian was named after Lutetia, the Latin name for the city of Paris. The Lutetian Stage was introduced in scientific literature by French geologist Albert de Lapparent in 1883 and revised by A. Blondeau in 1981. The base of the Lutetian Stage is at the first appearance of the nanofossil ''Blackites inflatus'', according to an official reference profile (GSSP) established in 2011. Of two candidates located in Spain, the Gorrondatxe section was chosen.See thwebsite of Eustoquio Molinafor these candidates. The top of the Lutetian (the base of the Bartonian) is at the first appearance of calcareous nanoplankton species ''Reticulofenestra reticulata''. The Lutetian overlaps with the Geisel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protocetus
''Protocetus atavus'' ("first whale") is an extinct species of primitive cetacean from Egypt. It lived during the middle Eocene period 45 million years ago. The first discovered protocetid, ''Protocetus atavus'' was described by based on a cranium and a number of associated vertebrae and ribs found in middle Lutetian Tethyan marine limestone from Gebel Mokattam near Cairo, Egypt. Description ''Protocetus'' are believed to have had a streamlined, whale-like body around long, but was probably primitive in some respects.Palmer D (ed.) (1999). ''The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals''. London: Marshall Editions. p. 230. . Many protocetids (like ''Maiacetus'', '' Rodhocetus'') possessed well developed innominates and hind limbs, often attached to the backbone with a sacrum. ''Protocetus'' are known to have had at least one sacral vertebrate,Gingerich P.D. (2010). "Cetacea". In Werdelin L & Sanders W.J. (eds.). ''Cenozoic mammals of africa'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesocetus
''Mesocetus'' is an extinct genus of baleen whale from the Miocene of Europe (Antwerp, Belgium and Balkans). Description ''Mesocetus'' is similar to other tranatocetids in having rostral bones that override the frontals and contact the parietals, nasals dividing the maxillae on the vertex, a dorsoventrally bent occipital shield with a more horizontal anterior portion and more vertical posterior portion, and a tympanic bulla with short, narrow anterior portion with rounded or squared anterior end and wider and higher posterior portion that is particularly swollen in the posteroventral area. Shared characters with ''Tranatocetus'' include posterior ends of premaxillae fused with the maxillae and divided on the vertex by long, narrow and high (vertical plate-like) nasals and cervical vertebrae with wide transverse foramina, almost as wide as the centra. Species * ''Mesocetus agrami'' Van Beneden, 1886; known from late Miocene (late Serravallian) of the Balkans. * ''Mesocetus aquitan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protocetid
Protocetidae, the protocetids, form a diverse and heterogeneous group of extinct cetaceans known from Asia, Europe, Africa, South America, and North America. Description There were many genera, and some of these are very well known (e.g., ''Rodhocetus''). Known protocetids had large fore- and hindlimbs that could support the body on land, and it is likely that they lived amphibiously: in the sea and on land. It is unclear at present whether protocetids had flukes (the horizontal tail fin of modern cetaceans). However, what is clear is that they are adapted even further to an aquatic life-style. In ''Rodhocetus'', for example, the sacrum – a bone that in land-mammals is a fusion of five vertebrae that connects the pelvis with the rest of the vertebral column – was divided into loose vertebrae. However, the pelvis retain a sacroiliac joint. Furthermore, the nasal openings are now halfway up the snout; a first step towards the telescoped condition in modern whales. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartonian
The Bartonian is, in the ICS's geologic time scale, a stage or age in the middle Eocene Epoch or Series. The Bartonian Age spans the time between . It is preceded by the Lutetian and is followed by the Priabonian Age. Stratigraphic definition The Bartonian Stage was introduced by Swiss stratigrapher Karl Mayer-Eymar in 1857. The name derives from the coastal village Barton-on-Sea (part of New Milton) in southern England. The Barton Group, a lithostratigraphic unit from the south English Hampshire Basin, is of Bartonian age. The distinction between group and stage was made in the second part of the 20th century, when stratigraphers saw the need to distinguish between litho- and chronostratigraphy. The base of the Bartonian is at the first appearance of the calcareous nanoplankton species ''Reticulofenestra reticulata''. In 2009, an official reference profile (GSSP) for the base of the Bartonian had not yet been established. The top of the Bartonian Stage (the base of the Pria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
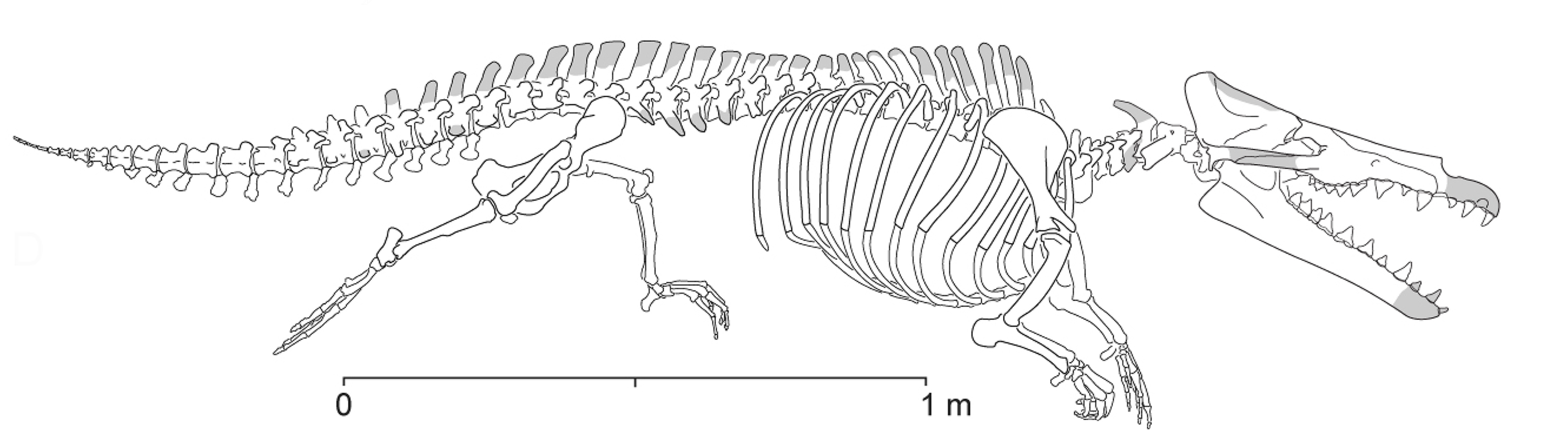
Eocetus
''Eocetus'' is an extinct protocetid early whale known from the early late Eocene (Bartonian, ) Giushi Formation in Gebel Mokattam, (, paleocoordinates ) outside Cairo, Egypt. The specimen was first named by Fraas as ''Mesocetus schweinfurthi''. However, the name ''Mesocetus'' was previously used causing a change to the species name to ''Eocetus schweinfurthi''. Since the genus was first described in the early 20th century, several other specimens, mostly isolated vertebrae, have been attributed to ''Eocetus'', but the taxonomic status of these widely distributed specimens remain disputed. Discovery and taxonomy described "''Mesocetus schweinfurthi''" based on a dorsoventrally compressed skull with only I2 ''in situ'', a specimen supposedly originating from a 40 Ma Tethyan deposit at Mokattam. Fraas also referred two isolated teeth, P4 and M1, to the skull and the most important of his specimens is not the deformed skull, but the upper molar which retains three roots and a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argyrolagus
''Argyrolagus'' is an extinct genus of South American metatherian, belonging to the order Polydolopimorpha from the Early Pliocene Monte Hermoso Formation, Patagonia, Argentina.''Argyrolagus'' at .org Description Jumping on its hind legs, the long (without tail) ''Argyrolagus'' resembled a gerbil or kultarr. It had a long tail for balance, and a narrow head with a pointed snout. Judging from its huge eyes, ''Argyrolagus'' was nocturnal. The form of its teeth suggest that it ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanosuchus
''Titanosuchus ferox'' ("Fierce titan crocodile") is an extinct species of dinocephalian therapsids that lived in the Middle Permian epoch in South Africa. Along with its close relatives, ''Jonkeria'' and ''Moschops'', ''Titanosuchus'' inhabited present-day South Africa around 265 million years ago, in the Late Permian. ''Titanosuchus'' was a carnivore which measured over 2.5 m long and might have eaten both ''Jonkeria'' and ''Moschops'', among other vertebrates. Its teeth included sharp incisors and fang-like canines, perfect for biting prey. ''Titanosuchus'' should not be confused with the therapsid ''Eotitanosuchus'', which belonged to a different family. ''Parascapanodon'' and ''Scapanodon'' were once thought to be distinct genera, but are now considered to be junior synonyms of ''Titanosuchus''.Boonstra, L. D., 1969, The fauna of the Tapinocephalus zone (Beaufort beds of the Karoo): Annals of the South African Museum, v. 56, part 1, p. 1-73. See also * List of therapsids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lopingian
The Lopingian is the uppermost series/last epoch of the Permian. It is the last epoch of the Paleozoic. The Lopingian was preceded by the Guadalupian and followed by the Early Triassic. The Lopingian is often synonymous with the informal terms late Permian or upper Permian. The name was introduced by Amadeus William Grabau in 1931 and derives from Leping, Jiangxi in China. It consists of two stages/ ages. The earlier is the Wuchiapingian and the later is the Changhsingian. The International Chronostratigraphic Chart (v2018/07) provides a numerical age of 259.1 ±0.5 Ma. If a Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) has been approved, the lower boundary of the earliest stage determines numerical age of an epoch. The GSSP for the Wuchiapingian has a numerical age of 259.8 ± 0.4 Ma. Evidence from Milankovitch cycles suggests that the length of an Earth day during this epoch was approximately 22 hours. The Lopingian ended with the Permian–Triassic extinction event. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |