|
1878 In Science
The year 1878 in science and technology involved many significant events, listed below. Astronomy * English astronomer Richard A. Proctor describes the Zone of Avoidance, the area of the night sky that is obscured by our own galaxy, for the first time. Biology * Death of last confirmed Cape Lion. Chemistry * The rare earth element holmium is identified in erbium by Marc Delafontaine and Jacques-Louis Soret in Geneva and by Per Teodor Cleve in Sweden. Conservation * An Act of Parliament in the United Kingdom places Epping Forest in the care of the City of London Corporation to remain unenclosed. Exploration * June 22 – Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld sets out on the year-long first navigation of the Northern Sea Route, the shipping lane from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean along the Siberian coast. Geology * Clarence King publishes ''Systematic Geology''. * Charles Lapworth publishes his analysis of the change in graptolite fossils through sequences of exposed shales in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for scientific reasoning is tens of thousands of years old. The earliest written records in the history of science come from Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but was preserved in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age and later by the efforts of Byzantine Greek scholars who brought Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
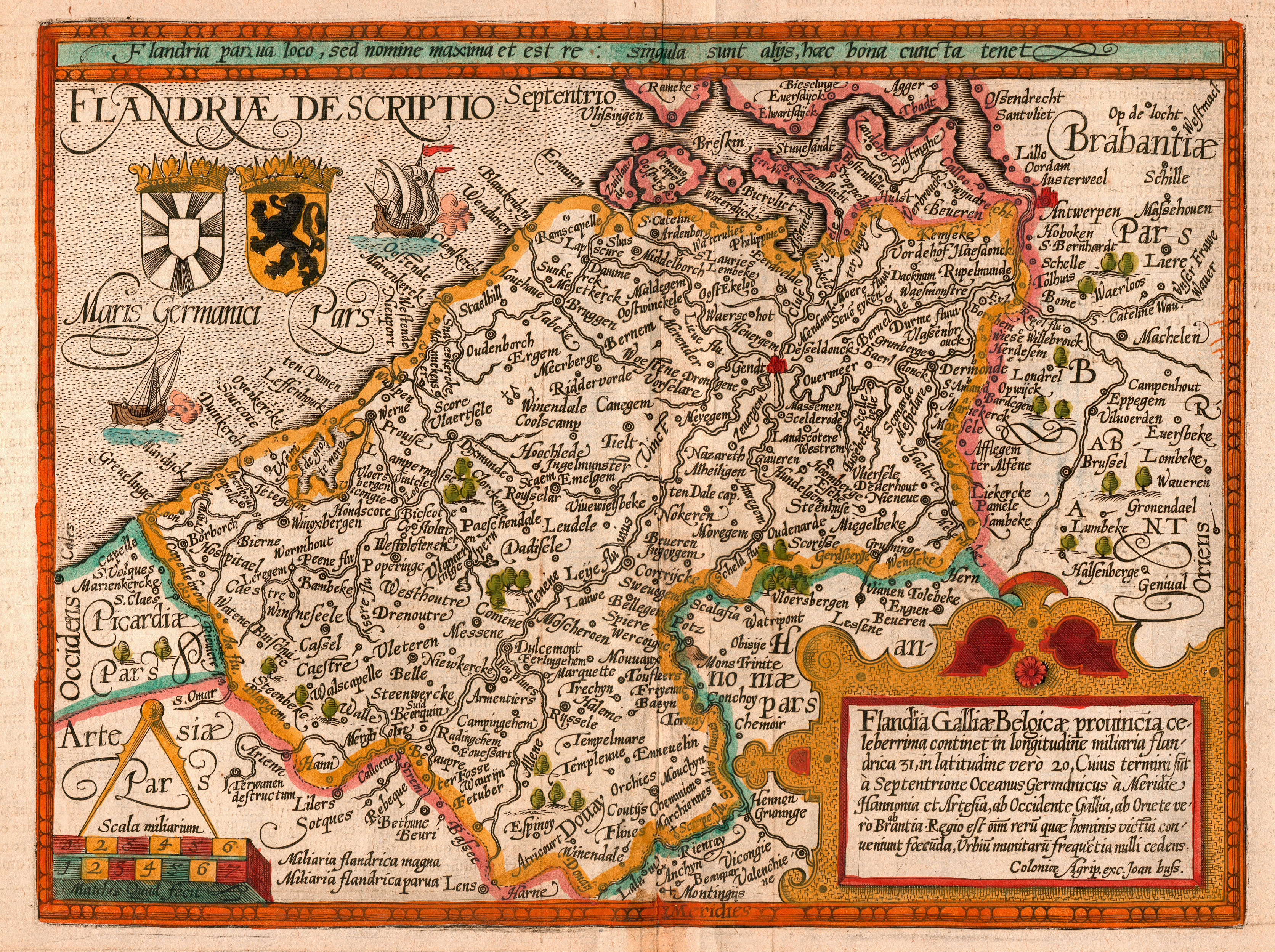
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N. Scientific explorations of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Allen Whitworth
William Allen Whitworth (1 February 1840 – 12 March 1905) was an English mathematician and a priest in the Church of England.. Education and mathematical career Whitworth was born in Runcorn; his father, William Whitworth, was a school headmaster, and he was the oldest of six siblings. He was schooled at the Sandicroft School in Northwich and then at St John's College, Cambridge, earning a B.A. in 1862 as 16th Wrangler. He taught mathematics at the Portarlington School and the Rossall School, and was a professor of mathematics at Queen's College in Liverpool from 1862 to 1864. He returned to Cambridge to earn a master's degree in 1865, and was a fellow there from 1867 to 1882. Mathematical contributions As an undergraduate, Whitworth became the founding editor in chief of the ''Messenger of Mathematics'', and he continued as its editor until 1880. He published works about the logarithmic spiral and about trilinear coordinates, but his most famous mathematical publication is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English People
The English people are an ethnic group and nation native to England, who speak the English language in England, English language, a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language, and share a common history and culture. The English identity is of History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon origin, when they were known in Old English as the ('race or tribe of the Angles'). Their ethnonym is derived from the Angles, one of the Germanic peoples who migrated to Great Britain around the 5th century AD. The English largely descend from two main historical population groups the West Germanic tribes (the Angles, Saxons, Jutes and Frisians) who settled in southern Britain following the withdrawal of the Ancient Rome, Romans, and the Romano-British culture, partially Romanised Celtic Britons already living there.Martiniano, R., Caffell, A., Holst, M. et al. Genomic signals of migration and continuity in Britain before the Anglo-Saxons. Nat Commun 7, 10326 (2016). https://doi.org/10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D'Hondt Method
The D'Hondt method, also called the Jefferson method or the greatest divisors method, is a method for allocating seats in parliaments among federal states, or in party-list proportional representation systems. It belongs to the class of highest-averages methods. The method was first described in 1792 by future U.S. president Thomas Jefferson. It was re-invented independently in 1878 by Belgian mathematician Victor D'Hondt, which is the reason for its two different names. Motivation Proportional representation systems aim to allocate seats to parties approximately in proportion to the number of votes received. For example, if a party wins one-third of the votes then it should gain about one-third of the seats. In general, exact proportionality is not possible because these divisions produce fractional numbers of seats. As a result, several methods, of which the D'Hondt method is one, have been devised which ensure that the parties' seat allocations, which are of whole numbers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor D'Hondt
Victor Joseph Auguste D'Hondt (; 20 November 1841 – 30 May 1901) was a Belgian lawyer and jurist of civil law at Ghent University. He devised a procedure, the D'Hondt method, which he first described in 1878, for allocating seats to candidates in party-list proportional representation elections. The method has been adopted by a number of countries, including Albania, Argentina, Armenia, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Chile, Colombia, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Ecuador, Fiji, Finland, Israel, Japan, North Macedonia, the Netherlands, Northern Ireland, Paraguay, Poland, Portugal, Scotland, Slovenia, Serbia, Spain, Switzerland, Turkey, Iceland, Uruguay and Wales. A modified D'Hondt system is used for elections to the London Assembly and the Scottish Parliament. Victor D’Hondt was an influential proponent of proportional representation in Belgium. He published several articles on proportional representation and was founding member of the ''Association Réformiste Belge p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgians
Belgians ( nl, Belgen; french: Belges; german: Belgier) are people identified with the Kingdom of Belgium, a federal state in Western Europe. As Belgium is a multinational state, this connection may be residential, legal, historical, or cultural rather than ethnic. The majority of Belgians, however, belong to two distinct ethnic groups or ''communities'' ( nl, gemeenschap, links=no; french: communauté, links=no) native to the country, i.e. its historical regions: Flemings in Flanders, who speak Dutch; and Walloons in Wallonia, who speak French or Walloon. There is also a substantial Belgian diaspora, which has settled primarily in the United States, Canada, France, and the Netherlands. Etymology The 1830 revolution led to the establishment of an independent country under a provisional government and a national congress. The name "Belgium" was adopted for the country, the word being derived from ''Gallia Belgica'', a Roman province in the northernmost part of Gaul that, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the Scott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
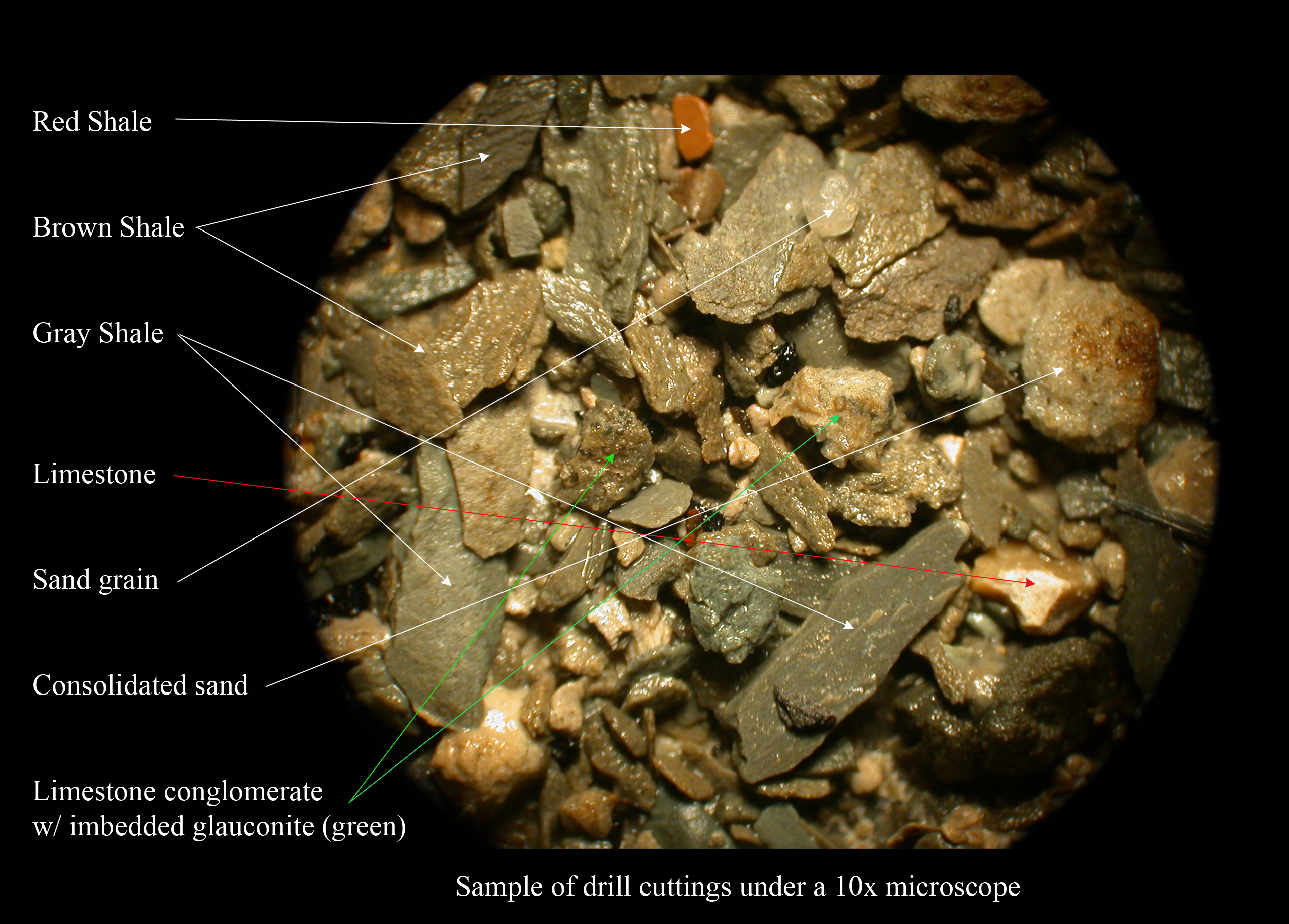
Shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especially quartz and calcite.Blatt, Harvey and Robert J. Tracy (1996) ''Petrology: Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic'', 2nd ed., Freeman, pp. 281–292 Shale is characterized by its tendency to split into thin layers ( laminae) less than one centimeter in thickness. This property is called '' fissility''. Shale is the most common sedimentary rock. The term ''shale'' is sometimes applied more broadly, as essentially a synonym for mudrock, rather than in the more narrow sense of clay-rich fissile mudrock. Texture Shale typically exhibits varying degrees of fissility. Because of the parallel orientation of clay mineral flakes in shale, it breaks into thin layers, often splintery and usually parallel to the otherwise indistinguishable beddin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
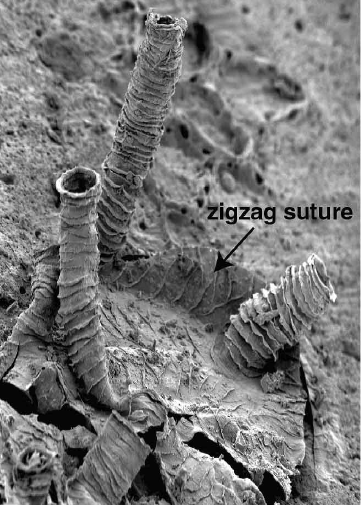
Graptolite
Graptolites are a group of colonial animals, members of the subclass Graptolithina within the class Pterobranchia. These filter-feeding Filter feeders are a sub-group of suspension feeding animals that feed by straining suspended matter and food particles from water, typically by passing the water over a specialized filtering structure. Some animals that use this method of feedin ... organisms are known chiefly from fossils found from the Middle Cambrian (Miaolingian, Wuliuan) through the Lower Carboniferous (Mississippian (geology), Mississippian). A possible early graptolite, ''Chaunograptus'', is known from the Middle Cambrian. Recent analyses have favored the idea that the living pterobranch ''Rhabdopleura'' represents an extant graptolite which diverged from the rest of the group in the Cambrian. Fossil graptolites and ''Rhabdopleura'' share a colony structure of interconnected zooids housed in organic tubes (theca) which have a basic structure of stacked half-rings (fuse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Lapworth
Charles Lapworth FRS FGS (20 September 1842 – 13 March 1920) was a headteacher and an English geologist who pioneered faunal analysis using index fossils and identified the Ordovician period. Biography Charles Lapworth was born at Faringdon in Berkshire (now Oxfordshire) the son of James Lapworth. His school in Galashiels in 2021 He trained as a teacher at the Culham Diocesan Training College near Abingdon, Oxfordshire. He moved to the Scottish border region, where he investigated the previously little-known fossil fauna of the area. He was headmaster of the school in Galashiels from 1864 to 1875. In 1869 he married Janet, daughter of Galashiels schoolmaster Walter Sanderson. Through mapping and innovative use of index fossil analysis, based on a sequence exposed at Dob's Linn, Lapworth showed that what was thought to be a thick sequence of Silurian rocks was in fact a much thinner series of rocks repeated by faulting and folding. He completed this pioneering resea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clarence King
Clarence Rivers King (January 6, 1842 – December 24, 1901) was an American geologist, mountaineer and author. He was the first director of the United States Geological Survey from 1879 to 1881. Nominated by Republican President Rutherford B. Hayes, King was noted for his exploration of the Sierra Nevada mountain range. Early life and education Clarence King was the son of James Rivers King and Florence Little King. Clarence's father was part of a family firm engaged in trade with China, which kept him away from home a great deal, and he died in 1848, so Clarence was brought up primarily by his mother. By 1848, his only two siblings had also died. Clarence developed an early interest in outdoor exploration and natural history, which was encouraged by his mother and by Reverend Dr. Roswell Park, head of the Christ Church Hall school in Pomfret, Connecticut, that Clarence attended until he was ten. He then attended schools in Boston and New Haven and, at age thirteen, was accepted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |