|
1551 In Science
Astronomy * Publication of Erasmus Reinhold's ephemeris, the '' Tabulae prutenicae'', helping to disseminate Copernican methods of astronomical calculation. Botany * Bolognese naturalist Ulisse Aldrovandi begins to collect plants for a herbarium. * William Turner publishes the first part of '' in London. Mathematics * Georg Joachim Rheticus publishes ''Canon of the Science of Triangles''. Medicine * By July – Fifth and last outbreak of sweating sickness in England. Dr. John Caius writes the first full contemporary account of the symptoms of the disease. * Conrad Gessner is the first to describe adipose tissue. Zoology * Pierre Belon publishes ''Histoire naturelle des estranges poissons''. * Conrad Gessner begins publication of his encyclopedic illustrated '' Historiae animalium'' in Zurich. Publications * Martín Cortés de Albacar publishes ''Breve compendio de la esfera y del arte de navegar'' in Spain, an influential work in cosmography, proposing spherical charts an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erasmus Reinhold
Erasmus Reinhold (22 October 1511 – 19 February 1553) was a German astronomer and mathematician, considered to be the most influential astronomical pedagogue of his generation. He was born and died in Saalfeld, Saxony. He was educated, under Jacob Milich, at the University of Wittenberg, where he was first elected dean and later became rector. In 1536 he was appointed professor of higher mathematics by Philipp Melanchthon. In contrast to the limited modern definition, "mathematics" at the time also included applied mathematics, especially astronomy. His colleague, Georg Joachim Rheticus, also studied at Wittenberg and was appointed professor of lower mathematics in 1536. Reinhold catalogued a large number of stars. His publications on astronomy include a commentary (1542, 1553) on Georg Purbach's ''Theoricae novae planetarum''. Reinhold knew about Copernicus and his heliocentric ideas prior to the publication of his ''De revolutionibus'', and made a favourable reference t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford Dictionary Of National Biography
The ''Dictionary of National Biography'' (''DNB'') is a standard work of reference on notable figures from British history, published since 1885. The updated ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' (''ODNB'') was published on 23 September 2004 in 60 volumes and online, with 50,113 biographical articles covering 54,922 lives. First series Hoping to emulate national biographical collections published elsewhere in Europe, such as the '' Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie'' (1875), in 1882 the publisher George Smith (1824–1901), of Smith, Elder & Co., planned a universal dictionary that would include biographical entries on individuals from world history. He approached Leslie Stephen, then editor of the ''Cornhill Magazine'', owned by Smith, to become the editor. Stephen persuaded Smith that the work should focus only on subjects from the United Kingdom and its present and former colonies. An early working title was the ''Biographia Britannica'', the name of an earlier eightee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physician
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the study, diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of disease, injury, and other physical and mental impairments. Physicians may focus their practice on certain disease categories, types of patients, and methods of treatment—known as specialities—or they may assume responsibility for the provision of continuing and comprehensive medical care to individuals, families, and communities—known as general practice. Medical practice properly requires both a detailed knowledge of the academic disciplines, such as anatomy and physiology, underlying diseases and their treatment—the ''science'' of medicine—and also a decent competence in its applied practice—the art or ''craft'' of medicine. Both the role of the physician and the meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English People
The English people are an ethnic group and nation native to England, who speak the English language in England, English language, a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language, and share a common history and culture. The English identity is of History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon origin, when they were known in Old English as the ('race or tribe of the Angles'). Their ethnonym is derived from the Angles, one of the Germanic peoples who migrated to Great Britain around the 5th century AD. The English largely descend from two main historical population groups the West Germanic tribes (the Angles, Saxons, Jutes and Frisians) who settled in southern Britain following the withdrawal of the Ancient Rome, Romans, and the Romano-British culture, partially Romanised Celtic Britons already living there.Martiniano, R., Caffell, A., Holst, M. et al. Genomic signals of migration and continuity in Britain before the Anglo-Saxons. Nat Commun 7, 10326 (2016). https://doi.org/10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timothy Bright
Timothie Bright, M.D. (1551?–1615) was an Early Modern English physician and clergyman, the inventor of modern shorthand. Early life Bright was born in or about 1551, probably in the neighbourhood of Sheffield. He matriculated as a sizar at Trinity College, Cambridge, 'impubes, æt. 11,' on 21 May 1561, and graduated B.A. in 1567–8. In 1572 he was at Paris, probably pursuing his medical studies, when he narrowly escaped the St Bartholomew's Day massacre by taking refuge in the house of Francis Walsingham. In his dedication of ''Animadversions on Scribonius'' (1584) to Sir Philip Sidney (1584), Bright remarks that he had only seen him once, on that occasion. Physician Bright graduated M.B. at Cambridge in 1574, received a licence to practise medicine in the following year, and was created M.D. in 1579. For some years after this, he appears to have lived at Cambridge, but was living at Ipswich in 1584. He was one of those who, on 1 October 1585, witnessed the statutes of Emmanu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Deviation
Magnetic deviation is the error induced in a compass by ''local'' magnetic fields, which must be allowed for, along with magnetic declination, if accurate bearings are to be calculated. (More loosely, "magnetic deviation" is used by some to mean the same as "magnetic declination". This article is about the former meaning.) Compass readings Compasses are used to determine the direction of true North. However, the compass reading must be corrected for two effects. The first is magnetic declination or variation—the angular difference between ''magnetic North'' (the local direction of the Earth's magnetic field) and true North.Admiralty Manual of Navigation Vol 1 1964 p12 The second is ''magnetic deviation''—the angular difference between magnetic North and the compass needle due to nearby sources of interference such as magnetically permeable bodies, or other magnetic fields within the field of influence. Sources In navigation manuals, ''magnetic deviation'' refers specificall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmography
The term cosmography has two distinct meanings: traditionally it has been the protoscience of mapping the general features of the cosmos, heaven and Earth; more recently, it has been used to describe the ongoing effort to determine the large-scale features of the observable universe. Traditional usage The 14th-century work '' 'Aja'ib al-makhluqat wa-ghara'ib al-mawjudat'' by Persian physician Zakariya al-Qazwini is considered to be an early work of cosmography. Traditional Hindu, Buddhist and Jain cosmography schematize a universe centered on Mount Meru surrounded by rivers, continents and seas. These cosmographies posit a universe being repeatedly created and destroyed over time cycles of immense lengths. In 1551, Martín Cortés de Albacar, from Zaragoza, Spain, published ''Breve compendio de la esfera y del arte de navegar''. Translated into English and reprinted several times, the work was of great influence in Britain for many years. He proposed spherical charts and menti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg , image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg , national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond") , national_anthem = (English: "Royal March") , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Madrid , coordinates = , largest_city = Madrid , languages_type = Official language , languages = Spanish language, Spanish , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = , ethnic_groups_ref = , religion = , religion_ref = , religion_year = 2020 , demonym = , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Parliamentary system, parliamentary constitutional monarchy , leader_title1 = Monarchy of Spain, Monarch , leader_name1 = Felipe VI , leader_title2 = Prime Minister of Spain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martín Cortés De Albacar
Martín Cortés de Albacar (1510–1582) was a Spanish cosmographer.p131 Antonio Barrera-Osorio ''Experiencing nature: the Spanish American empire and the early scientific revolution;'' University of Texas Press, 2006 In 1551 he published the standard navigational textbook ''Arte de navegar'' (also known as ''Breve compendio'') Cortés was born in Bujaraloz, province of Zaragoza, Aragon. From 1530, in Cádiz, he taught cosmography and the art of navigation to pilots. ''Art of Navigation'' Cortés' book, ''Breve compendio,''...''Arte de navegar'' was promoted by Steven Borough who had it translated into English by Richard Eden and published in 1561 entitled ''The Art of Navigation.'' As such it became the first English manual of navigationAndrew Hadfield, ‘Eden, Richard (c.1520–1576)’, ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, Sept 2004 and the primary text for European navigation throughout the early 17thC, enjoyed by such as Martin Frobisher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historiae Animalium (Gesner)
''Historia animalium'' ("History of the Animals"), published at Zurich in 1551–1558 and 1587, is an encyclopedic "inventory of renaissance zoology" by Conrad Gessner (1516–1565). Gessner was a medical doctor and professor at the Carolinum in Zürich, the precursor of the University of Zurich. The ''Historia animalium'', after Aristotle's work of the same name. is the first modern zoological work that attempts to describe all the animals known, and the first bibliography of natural history writings. The five volumes of natural history of animals cover more than 4500 pages. Overview The ''Historia animalium'' was Gessner's magnum opus, and was the most widely read of all the Renaissance natural histories. The generously illustrated work was so popular that Gessner's abridgement, ''Thierbuch'' ("Animal Book"), was published in Zurich in 1563, and in England Edward Topsell translated and condensed it as a ''Historie of foure-footed beastes'' (London: William Jaggard, 1607). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
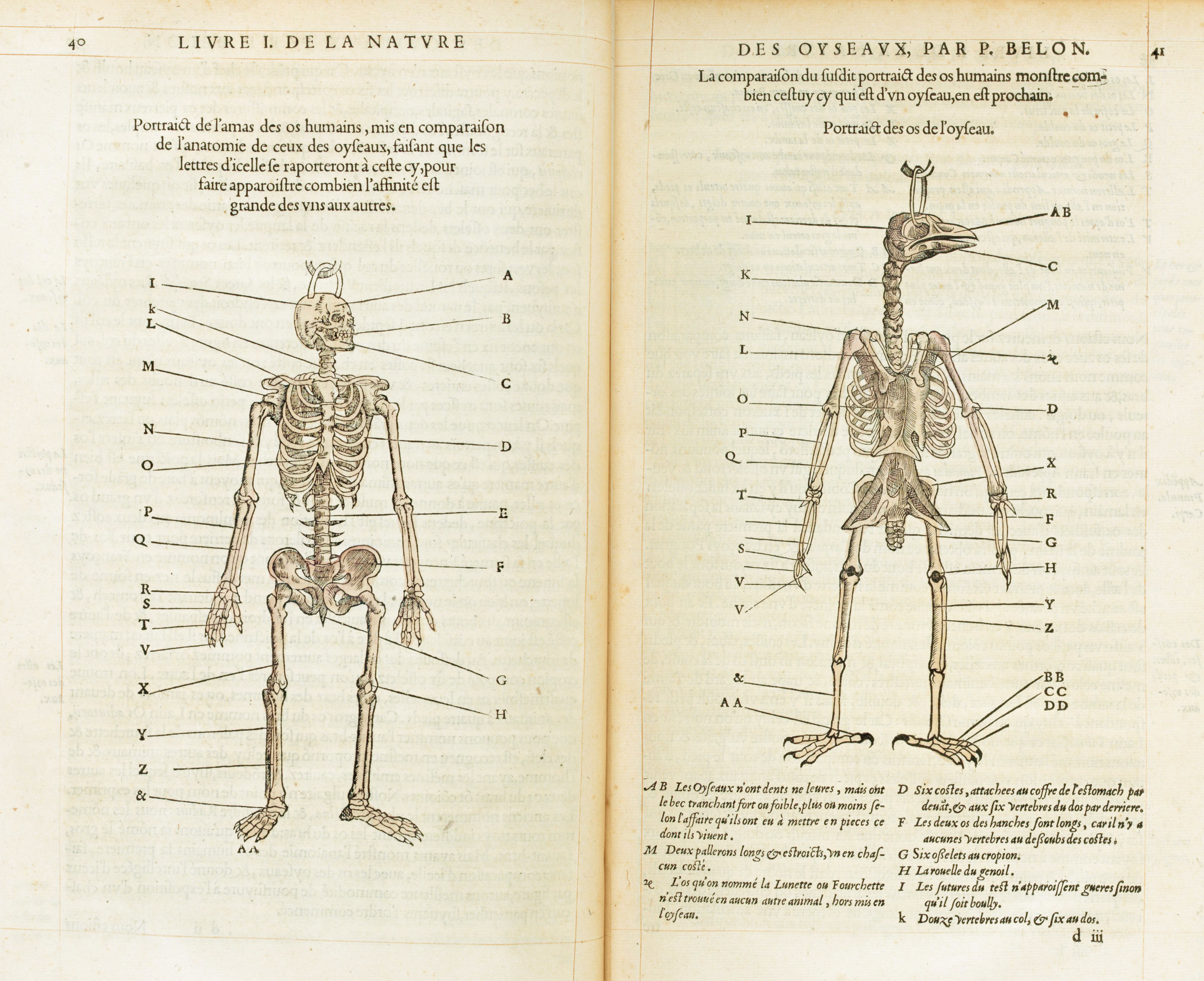
Pierre Belon
Pierre Belon (1517–1564) was a French traveller, naturalist, writer and diplomat. Like many others of the Renaissance period, he studied and wrote on a range of topics including ichthyology, ornithology, botany, comparative anatomy, architecture and Egyptology. He is sometimes known as Pierre Belon du Mans, or, in the Latin in which his works appeared, as Petrus Bellonius Cenomanus. The Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov (known for Pavlov's dogs) called him the "prophet of comparative anatomy". Life Belon was born in 1517 at the hamlet of Souletière near Cérans-Foulletourte in the Pays de la Loire. Nothing is known about his descent. Somewhere between 1532 and 1535 he started working as an apprentice to René des Prez, born in Foulletourte but by then an apothecary to the bishop of Clermont, Guillaume Duprat. Between 1535 and 1538 he entered the service of René du Bellay, bishop of Le Mans, who allowed him to study medicine at the University of Wittenberg with the botanist Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |