|
1522 In Science
The year 1522 in science and technology included a number of events, some of which are listed here. Exploration * September 6 – The ''Victoria (ship), Victoria'' (Carrack, nau ''Vittoria''), one of the surviving ships of the Magellan expedition, returns to Sanlúcar de Barrameda in Spain under the command of Juan Sebastián Elcano, becoming the first ship to Circumnavigation, circumnavigate the world. It carries the first (dead) examples of the bird-of-paradise ever to be seen in Europe. Venetian cardinal Gasparo Contarini, in Spain at this time, is the first European to give a correct explanation of the one-day discrepancy in dates observed by the crew on their return. Mathematics * Adam Ries publishes his popular arithmetical text '. * Johannes Werner's original work on conic sections is published. Medicine * Publication in Seville, by Juan Varela and under the title of ''Metaphora medicinae'', of a manual of medicine and pharmacy by Bernardino de Laredo. Births * Septembe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for scientific reasoning is tens of thousands of years old. The earliest written records in the history of science come from Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but was preserved in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age and later by the efforts of Byzantine Greek scholars who brought Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Werner
Johann(es) Werner ( la, Ioannes Vernerus; February 14, 1468 – May 1522) was a German mathematician. He was born in Nuremberg, Germany, where he became a parish priest. His primary work was in astronomy, mathematics, and geography, although he was also considered a skilled instrument maker. Mathematics His mathematical works were in the areas of spherical trigonometry, as well as conic sections. He published an original work on conic sections in 1522 and is one of several mathematicians sometimes credited with the invention of prosthaphaeresis, which simplifies tedious computations by the use of trigonometric formulas, sometimes called Werner's formulas. Astronomy In 1500 he observed a comet, and kept observations of its movements from June 1 until the 24th. This work further developed the suggestion of Regiomontanus that the occurrences of eclipses and cometary orbits could be used to find longitude, giving a practical approach for this method by means of the cross-staff. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1522 In Science
The year 1522 in science and technology included a number of events, some of which are listed here. Exploration * September 6 – The ''Victoria (ship), Victoria'' (Carrack, nau ''Vittoria''), one of the surviving ships of the Magellan expedition, returns to Sanlúcar de Barrameda in Spain under the command of Juan Sebastián Elcano, becoming the first ship to Circumnavigation, circumnavigate the world. It carries the first (dead) examples of the bird-of-paradise ever to be seen in Europe. Venetian cardinal Gasparo Contarini, in Spain at this time, is the first European to give a correct explanation of the one-day discrepancy in dates observed by the crew on their return. Mathematics * Adam Ries publishes his popular arithmetical text '. * Johannes Werner's original work on conic sections is published. Medicine * Publication in Seville, by Juan Varela and under the title of ''Metaphora medicinae'', of a manual of medicine and pharmacy by Bernardino de Laredo. Births * Septembe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymath
A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific problems. In Western Europe, the first work to use the term polymathy in its title () was published in 1603 by Johann von Wowern, a Hamburg philosopher. Von Wowern defined polymathy as "knowledge of various matters, drawn from all kinds of studies ... ranging freely through all the fields of the disciplines, as far as the human mind, with unwearied industry, is able to pursue them". Von Wowern lists erudition, literature, philology, philomathy, and polyhistory as synonyms. The earliest recorded use of the term in the English language is from 1624, in the second edition of ''The Anatomy of Melancholy'' by Robert Burton; the form ''polymathist'' is slightly older, first appearing in the ''Diatribae upon the first part of the late History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1605 In Science
The year 1605 in science and technology involved some significant events. Exploration * Habitation at Port-Royal established by France under Pierre Dugua, Sieur de Mons, the first European colonization of Nova Scotia in North America (at this time part of Acadia); the Gregorian calendar is adopted. Chemistry * First recorded use of the word ''Chemistry'' ("Chymistrie") in English, in Thomas Tymme's ''The Practice of Chymicall and Hermeticall Physicke'', translated from Joseph Duchesne. * The phenomenon of mechanoluminescence is first discovered by Sir Francis Bacon from scratching sugar with a knife. * Michal Sedziwój publishes the alchemical treatise ''A New Light of Alchemy'' which proposes the existence of the "food of life" within air, much later recognized as oxygen. Technology * Chartreuse is invented, a liqueur still made by Carthusian monks, named for the great charterhouse (''la grande Chartreuse''). Births * October 19 – Thomas Browne, English physici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulisse Aldrovandi
Ulisse Aldrovandi (11 September 1522 – 4 May 1605) was an Italian naturalist, the moving force behind Bologna's botanical garden, one of the first in Europe. Carl Linnaeus and the comte de Buffon reckoned him the father of natural history studies. He is usually referred to, especially in older scientific literature in Latin, as Aldrovandus; his name in Italian is equally given as Aldroandi. Life Aldrovandi was born in Bologna to Teseo Aldrovandi and his wife, a noble but poor family. His father was a lawyer, and Secretary to the Senate of Bologna, but died when Ulisse was seven years old. His widowed mother wanted him to become a jurist. Initially he was sent to apprentice with merchants as a scribe for a short time when he was 14 years old, but after studying mathematics, Latin, law, and philosophy, initially at the University of Bologna, and then at the University of Padua in 1545, he became a notary. His interests successively extended to philosophy and logic, which he c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernardino De Laredo
Fray Bernardino de Laredo (1482 in Seville – 1540 in San Francisco del Monte, Sevilla) was a physician and Franciscan mystical writer. Life Of noble birth, Bernardino grew up in Seville and became a page to an exiled Portuguese nobleman (Duke Álvaro of Portugal) in that city. He then left the nobleman's service at age thirteen to apply himself seriously to school. He studied medicine, possibly graduating from the University of Seville, and began to practice as a physician around 1507. In 1510, though, a close friend of entered the Order of St Francis as a lay brother, and he did the same.Bernardino de Laredo, ''The ascent of Mount Sion: being the third book of the treatise of that name'', translated with an introd. and notes by E. Allison Peers, (London: Faber & Faber, 1952), p12 He remained a lay brother in the Franciscan order for the next thirty years, for most of that time living in the friary of San Francisco del Monte, near Villaverde del Río, a town about eighteen miles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula. Seville has a municipal population of about 685,000 , and a metropolitan population of about 1.5 million, making it the largest city in Andalusia, the fourth-largest city in Spain and the 26th most populous municipality in the European Union. Its old town, with an area of , contains three UNESCO World Heritage Sites: the Alcázar palace complex, the Cathedral and the General Archive of the Indies. The Seville harbour, located about from the Atlantic Ocean, is the only river port in Spain. The capital of Andalusia features hot temperatures in the summer, with daily maximums routinely above in July and August. Seville was founded as the Roman city of . Known as ''Ishbiliyah'' after the Islamic conquest in 711, Seville became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
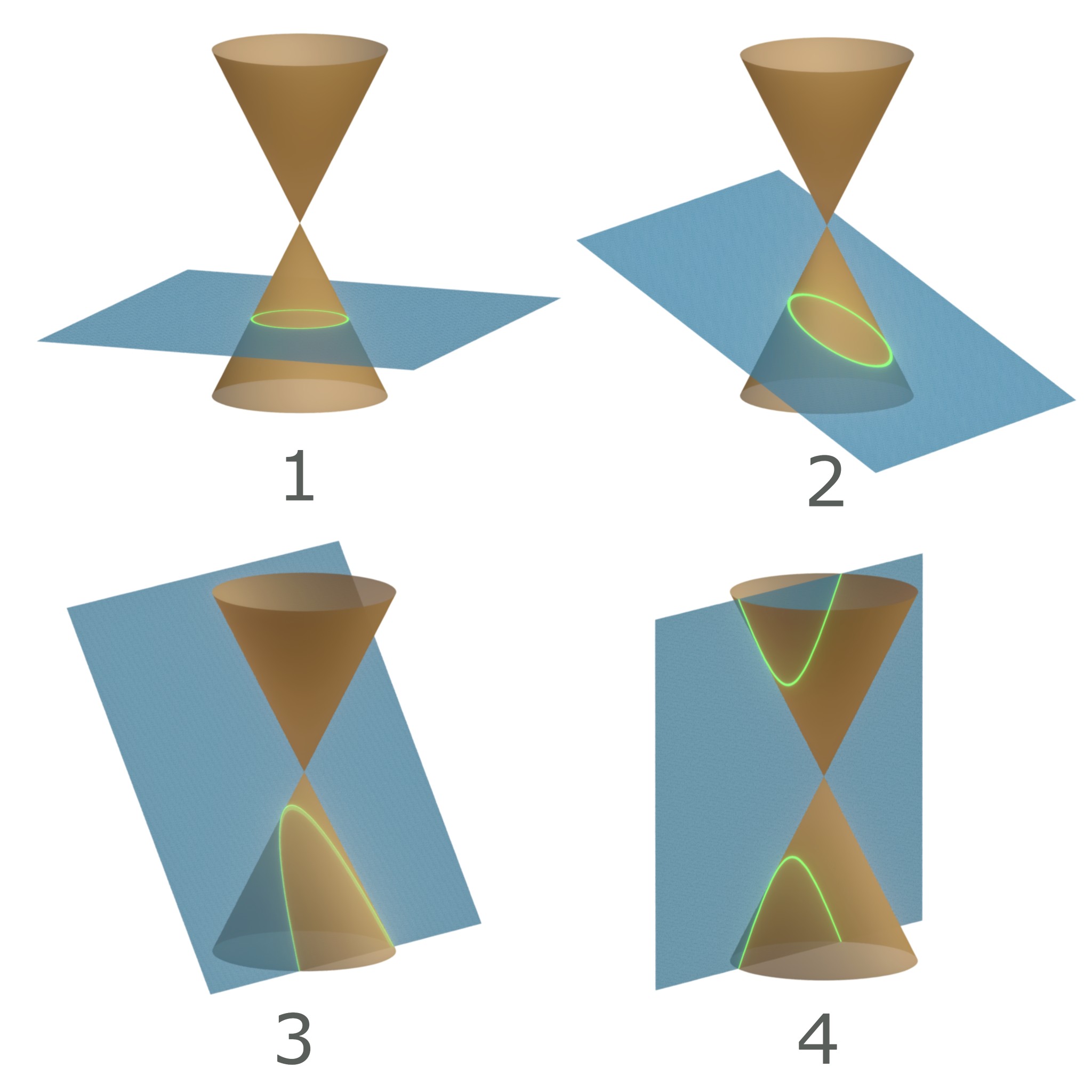
Conic Section
In mathematics, a conic section, quadratic curve or conic is a curve obtained as the intersection of the surface of a cone with a plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a special case of the ellipse, though historically it was sometimes called a fourth type. The ancient Greek mathematicians studied conic sections, culminating around 200 BC with Apollonius of Perga's systematic work on their properties. The conic sections in the Euclidean plane have various distinguishing properties, many of which can be used as alternative definitions. One such property defines a non-circular conic to be the set of those points whose distances to some particular point, called a ''focus'', and some particular line, called a ''directrix'', are in a fixed ratio, called the ''eccentricity''. The type of conic is determined by the value of the eccentricity. In analytic geometry, a conic may be defined as a plane algebraic curve of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Ries
Adam Ries (17 January 1492 – 30 March 1559) was a German mathematician. He is also known by the name Adam Riese. Life Almost nothing is known about Ries' childhood, youth and education. The exact year of his birth is not known. The caption on the only known contemporary portrait of the mathematician reads: ANNO 1550 ADAM RIES SEINS ALTERS IM LVIII. So apparently he was in his 58th year of age at the time of the picture, which was made in 1550. From this it can be deduced that he was born in 1492 or 1493. The location of his birth, Staffelstein, can be determined with certainty, since he gives information about himself in the preface to his book, ''Coß''. His father was the owner of the mill there, Contz Ries, and his mother, Eva Kittler, was his father's second wife. The first decades after Ries' birth are not documented, so it is not known which schools he attended. There is also no information about his studies in the matriculation registers of the universities. The firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, science, industry, communication, transportation, and daily life. Technologies include physical objects like utensils or machines and intangible tools such as software. Many technological advancements have led to societal changes. The earliest known technology is the stone tool, used in the prehistoric era, followed by fire use, which contributed to the growth of the human brain and the development of language in the Ice Age. The invention of the wheel in the Bronze Age enabled wider travel and the creation of more complex machines. Recent technological developments, including the printing press, the telephone, and the Internet have lowered communication barriers and ushered in the knowledge economy. While technology contributes to econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |