|
1517 In Science
{{Science year nav, 1517 The year 1517 in science and technology included a number of events, some of which are listed here. Medicine * A third epidemic of sweating sickness in England hits Oxford and Cambridge. * German surgeon Hans von Gersdorff publishes his ''Feldbuch der Wundarzney'' ("Field book of surgery"). Births * June 29 – Rembert Dodoens, Flemish physician and botanist (died 1585) * October 5 – Leonardo Fioravanti, Bolognese physician (died 1588) * Pierre Belon, French naturalist (died 1564) * Jacques Pelletier du Mans, French mathematician (died 1582) Deaths * Luca Pacioli Fra Luca Bartolomeo de Pacioli (sometimes ''Paccioli'' or ''Paciolo''; 1447 – 19 June 1517) was an Italian mathematician, Franciscan friar, collaborator with Leonardo da Vinci, and an early contributor to the field now known as accounting ..., Florentine mathematician (b. c.1447) 16th century in science 1510s in science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonardo Fioravanti (doctor)
Leonardo Fioravanti (151788) was a noted doctor, surgeon and alchemist active in Italy in the 16th century. Biography Born in Bologna on October 5, 1517 to Gabriele and Margarite Fioravanti, Leonardo was baptised at the Metropolitan Cathedral of Saint Peter. His family had ties to the celebrated architects Aristotele Fioravanti, Bartolomeo et Aristote. He received his first degree in medicine at Naples, and his second on March 27, 1568 at Bologna. He was elevated into the nobility by the king of Spain. He lived for a time in Rome and in Venice, and also in other important Italian cities. In Palermo, he performed the first recorded splenectomy A splenectomy is the surgical procedure that partially or completely removes the spleen. The spleen is an important organ in regard to immunological function due to its ability to efficiently destroy encapsulated bacteria. Therefore, removal of ... on Italian soil. Historians "have long portrayed Leonardo Fioravanti as the epitom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1517 In Science
{{Science year nav, 1517 The year 1517 in science and technology included a number of events, some of which are listed here. Medicine * A third epidemic of sweating sickness in England hits Oxford and Cambridge. * German surgeon Hans von Gersdorff publishes his ''Feldbuch der Wundarzney'' ("Field book of surgery"). Births * June 29 – Rembert Dodoens, Flemish physician and botanist (died 1585) * October 5 – Leonardo Fioravanti, Bolognese physician (died 1588) * Pierre Belon, French naturalist (died 1564) * Jacques Pelletier du Mans, French mathematician (died 1582) Deaths * Luca Pacioli Fra Luca Bartolomeo de Pacioli (sometimes ''Paccioli'' or ''Paciolo''; 1447 – 19 June 1517) was an Italian mathematician, Franciscan friar, collaborator with Leonardo da Vinci, and an early contributor to the field now known as accounting ..., Florentine mathematician (b. c.1447) 16th century in science 1510s in science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico anno 2013, datISTAT/ref> Florence was a centre of medieval European trade and finance and one of the wealthiest cities of that era. It is considered by many academics to have been the birthplace of the Renaissance, becoming a major artistic, cultural, commercial, political, economic and financial center. During this time, Florence rose to a position of enormous influence in Italy, Europe, and beyond. Its turbulent political history includes periods of rule by the powerful Medici family and numerous religious and republican revolutions. From 1865 to 1871 the city served as the capital of the Kingdom of Italy (established in 1861). The Florentine dialect forms the base of Standard Italian and it became the language of culture throughout Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luca Pacioli
Fra Luca Bartolomeo de Pacioli (sometimes ''Paccioli'' or ''Paciolo''; 1447 – 19 June 1517) was an Italian mathematician, Franciscan friar, collaborator with Leonardo da Vinci, and an early contributor to the field now known as accounting. He is referred to as the father of accounting and bookkeeping and he was the first person to publish a work on the double-entry system of book-keeping on the continent. He was also called Luca di Borgo after his birthplace, Borgo Sansepolcro, Tuscany. Several of his works were plagiarised from Piero della Francesca, in what has been called "probably the first full-blown case of plagiarism in the history of mathematics". Life Luca Pacioli was born between 1446 and 1448 in the Tuscan town of Sansepolcro where he received an abbaco education. This was education in the vernacular (''i.e.'', the local tongue) rather than Latin and focused on the knowledge required of merchants. His father was Bartolomeo Pacioli; however, Luca Pacioli was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1582 In Science
The year 1582 in science and technology included a number of events, some of which are listed here. This year sees the introduction of the Gregorian calendar, promulgated by Pope Gregory XIII in the Papal bull ''Inter gravissimas'' on February 24 and based largely on the work of Christopher Clavius. Under the Habsburg monarchy in Spain, Portugal and Italy, together with the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the year continues under the Julian calendar as normal until Thursday October 4, the next day becoming Friday October 15; France follows two months later, letting Sunday December 9 be followed by Monday December 20. Other countries switch in later years. Astronomy * Giovanni Antonio Magini publishes the ephemerides ''Ephemerides coelestium motuum''. Exploration * Richard Hakluyt publishes ''Divers Voyages Touching the Discoverie of America and the Ilands Adjacent unto the Same, Made First of all by our Englishmen''. Medicine * Urbain Hémard investigates the anatomy of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems. Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, structure, space, models, and change. History One of the earliest known mathematicians were Thales of Miletus (c. 624–c.546 BC); he has been hailed as the first true mathematician and the first known individual to whom a mathematical discovery has been attributed. He is credited with the first use of deductive reasoning applied to geometry, by deriving four corollaries to Thales' Theorem. The number of known mathematicians grew when Pythagoras of Samos (c. 582–c. 507 BC) established the Pythagorean School, whose doctrine it was that mathematics ruled the universe and whose motto was "All is number". It was the Pythagoreans who coined the term "mathematics", and with whom the study of mathematics for its own sake begins. The first woman mathematician recorded by history was Hypati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Pelletier Du Mans
Jacques Pelletier du Mans, also spelled Peletier ( la, Iacobus Peletarius Cenomani, 25 July 1517 – 17 July 1582) was a humanist, poet and mathematician of the French Renaissance. Born in Le Mans into a bourgeois family, he studied at the Collège de Navarre in Paris, where his brother Jean was a professor of mathematics and philosophy. He subsequently studied law and medicine, frequented the literary circle around Marguerite de Navarre and from 1541 to 1543 he was secretary to René du Bellay. In 1541 he published the first French translation of Horace's '' Ars Poetica'' and during this period he also published numerous scientific and mathematical treatises. In 1547 he produced a funeral oration for Henry VIII of England and published his first poems (''Œuvres poétiques''), which included translations from the first two cantos of Homer's ''Odyssey'' and the first book of Virgil's ''Georgics'', twelve Petrarchian sonnets, three Horacian odes and a Martial-like epigra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1564 In Science
The year 1564 in science and technology included many events, some of which are listed here. Medicine * Ambroise Paré publishes his treatise on surgery, ''Dix livres de la chirurgie: avec le magasin des instrumens necessaires à icelle'', in French. Births * February 15 – Galileo Galilei, Pisan astronomer (died 1642). * March 9 – David Fabricius, Frisian astronomer (died 1617). * ''approx. date'' – Pierre Richer de Belleval, French botanist (died 1632). Deaths * April – Pierre Belon, French naturalist (born 1517) (murdered) * October 15 – Vesalius, Flemish anatomist (born 1514) * October 18 – Johannes Acronius Frisius, German physician and mathematician (born 1520) * Charles Estienne, French anatomist (born 1504 __NOTOC__ Year 1504 (Roman numerals, MDIV) was a leap year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events January–June * January 1 – Kingdom of France, French troops of King Louis XII .. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
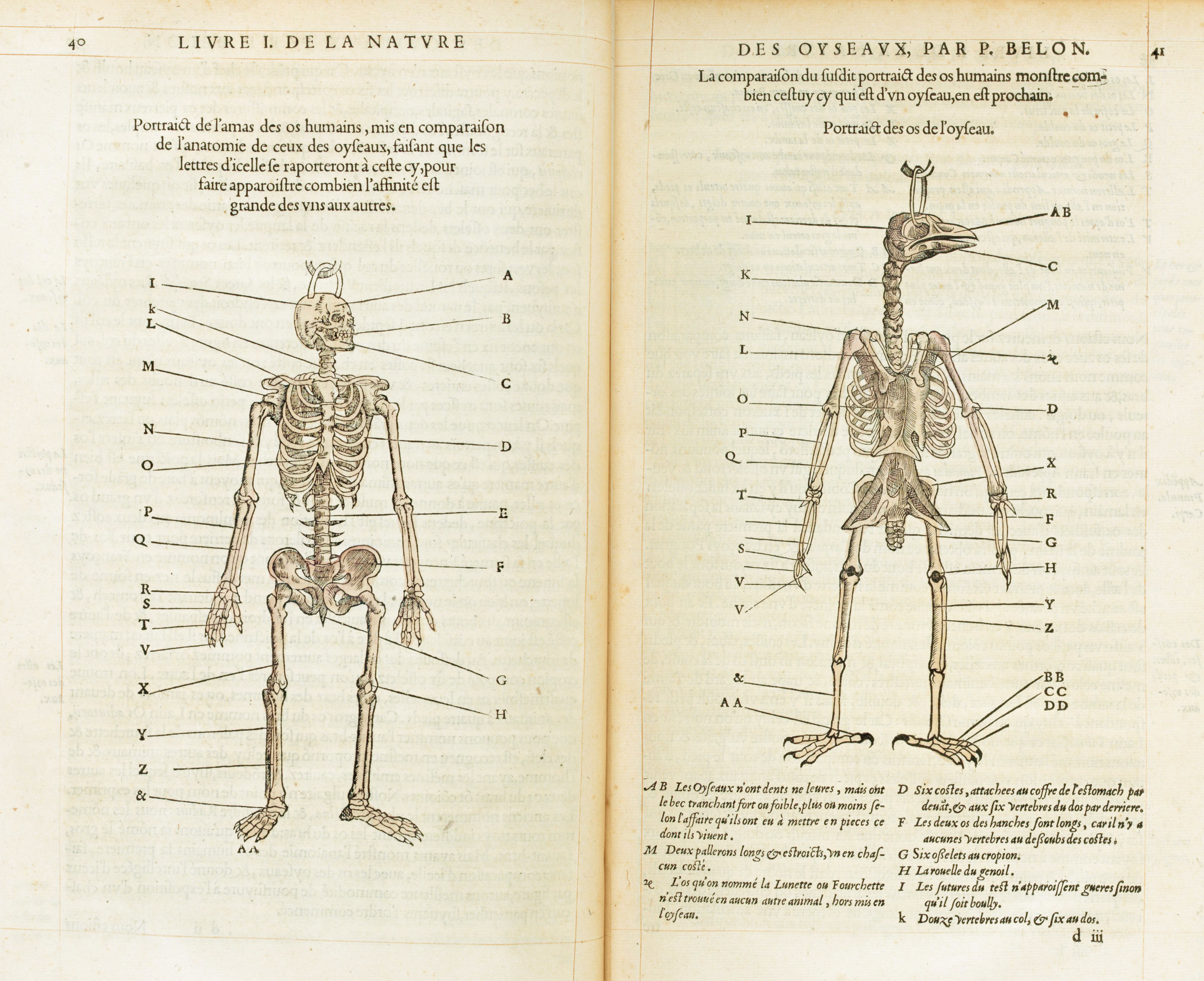
Pierre Belon
Pierre Belon (1517–1564) was a French traveller, naturalist, writer and diplomat. Like many others of the Renaissance period, he studied and wrote on a range of topics including ichthyology, ornithology, botany, comparative anatomy, architecture and Egyptology. He is sometimes known as Pierre Belon du Mans, or, in the Latin in which his works appeared, as Petrus Bellonius Cenomanus. The Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov (known for Pavlov's dogs) called him the "prophet of comparative anatomy". Life Belon was born in 1517 at the hamlet of Souletière near Cérans-Foulletourte in the Pays de la Loire. Nothing is known about his descent. Somewhere between 1532 and 1535 he started working as an apprentice to René des Prez, born in Foulletourte but by then an apothecary to the bishop of Clermont, Guillaume Duprat. Between 1535 and 1538 he entered the service of René du Bellay, bishop of Le Mans, who allowed him to study medicine at the University of Wittenberg with the botanist Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1588 In Science
The year 1588 in science and technology, Armada year, included a number of events, some of which are listed here. Astronomy * Tycho Brahe publishes ''De mundi aetheri recentioribus phaenomenis'' in Uraniborg. * Giovanni Paolo Gallucci publishes his star atlas ''Theatrum Mundi et Temporis'' (Theater of the world and time). History of science * October 7 – The first biography of Nicolaus Copernicus (died 1543) is completed by Bernardino Baldi. Mathematics * Pietro Cataldi discovers the sixth and seventh Mersenne primes by this year. * Giovanni Antonio Magini Giovanni Antonio Magini (in Latin, Maginus) (13 June 1555 – 11 February 1617) was an Italian astronomer, astrologer, cartographer, and mathematician. His Life He was born in Padua, and completed studies in philosophy in Bologna in 1579. Hi ... is chosen over Galileo Galilei, Galileo to occupy the chair of mathematics at the University of Bologna after the death of Egnatio Danti. * Ferdinando I de Medici, Grand Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |