|
13th Infantry Brigade (United Kingdom)
The 13th Infantry Brigade was a regular infantry brigade of the British Army that saw active service during both the First and the Second World Wars. First World War The 13th Brigade was temporarily under the command of 28th Division between 23 February and 7 April 1915, when it was replaced by 84th Brigade from that Division and moved to the regular 5th Division. It served on the Western Front for most of the war except for a brief period in Italy. Order or battle Component units included: * 2nd Battalion, King's Own Scottish Borderers * 2nd Battalion, Duke of Wellington's (West Riding Regiment) ''(left January 1916)'' * 1st Battalion, Queen's Own (Royal West Kent Regiment) * 2nd Battalion, King's Own (Yorkshire Light Infantry) ''(left December 1915)'' * 1/9th (City of London) Battalion, London Regiment ''(joined November 1914, left February 1915)'' * 14th (Service) Battalion, Royal Warwickshire Regiment ''(joined December 1915, became Divisional Pioneers October 1918)'' * 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine infantry. Although disused in modern times, heavy infantry also commonly made up the bulk of many historic armies. Infantry, cavalry, and artillery have traditionally made up the core of the combat arms professions of various armies, with the infantry almost always comprising the largest portion of these forces. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets '' infant''. The individual-soldier term ''infantry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th Infantry Division (United Kingdom)
The 5th Infantry Division was a regular army infantry division of the British Army. It was established by Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington for service in the Peninsular War, as part of the Anglo-Portuguese Army, and was active for most of the period since, including the First World War and the Second World War and was disbanded soon after. The division was reformed in 1995 as an administrative division covering Wales and the English regions of West Midlands, East Midlands and East. Its headquarters were in Shrewsbury. It was disbanded on 1 April 2012. Peninsular War The 5th Division during the Peninsular War under the command of General James Leith was present at most of the major engagements including the Battle of Bussaco, the Battle of Sabugal, the Siege of Almeida, the Battle of Badajoz, the Battle of Salamanca, the Battle of Vitoria, the Siege of San Sebastian, the Battle of Nivelle and the Battle of the Nive. Peninsular War order of battle The order of battl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allied Invasion Of Sicily
The Allied invasion of Sicily, also known as Operation Husky, was a major campaign of World War II in which the Allied forces invaded the island of Sicily in July 1943 and took it from the Axis powers ( Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany). It began with a large amphibious and airborne operation, followed by a six-week land campaign, and initiated the Italian campaign. To divert some of the Axis forces to other areas, the Allies engaged in several deception operations, the most famous and successful of which was Operation Mincemeat. Husky began on the night of 9–10 July 1943 and ended on 17 August. Strategically, Husky achieved the goals set out for it by Allied planners; the Allies drove Axis air, land and naval forces from the island and the Mediterranean sea lanes were opened for Allied merchant ships for the first time since 1941. These events led to the Italian leader, Benito Mussolini, being toppled from power in Italy on 25 July, and to the Allied invasion of Italy on 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
While A Piper Plays, A Special Rum Ration Is Issued To Men Of The 2nd Royal Inniskilling Fusiliers To Mark St Patrick's Day In The Anzio Bridgehead, Italy, 17 March 1944
''While'' is a word in the English language that functions both as a noun and as a subordinating conjunction. Its meaning varies largely based on its intended function, position in the phrase and even the writer or speaker's regional dialect. As a conjunction, it is synonymous with the word ''whilst'', a form often considered archaic in American English, as well as in some style guides on both sides of the Atlantic. Usage Noun ''A while'' and ''awhile'' are often confused due to the fact that ''while'' is often accompanied by the indefinite article. The main difference is that ''a while'' means "an amount of time" or "some duration" whereas ''awhile'' is an adverb meaning "''for'' some amount of time" or "''for'' some duration". :"I slept for a while before dinner." :"I slept awhile before dinner." Both of these sentences yield the same effective meaning. ''Whilst'' is only a conjunction, and so its use here would be incorrect. Conjunction The primary function of the word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
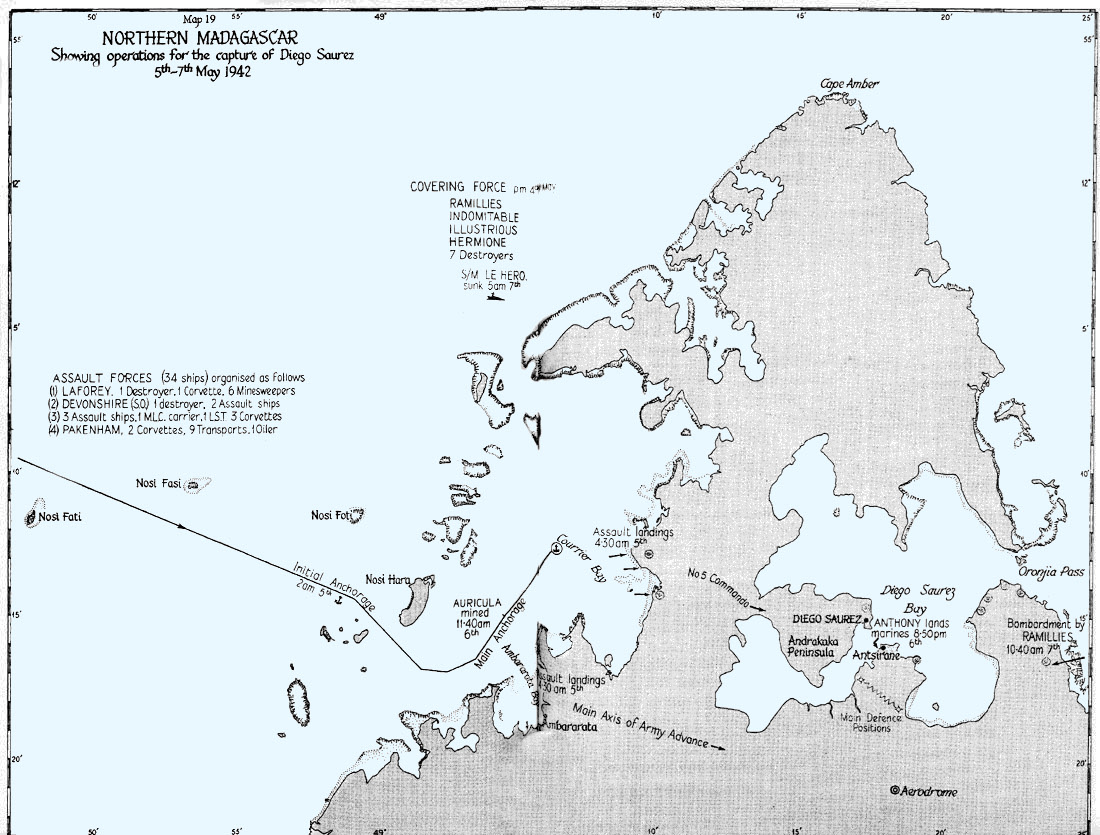
Battle Of Madagascar
The Battle of Madagascar (5 May – 6 November 1942) was a British campaign to capture the Vichy French-controlled island Madagascar during World War II. The seizure of the island by the British was to deny Madagascar's ports to the Imperial Japanese Navy and to prevent the loss or impairment of the Allied shipping routes to India, Australia and Southeast Asia. It began with Operation Ironclad, the seizure of the port of Diego-Suarez (now Antsiranana) near the northern tip of the island, on 5 May 1942. A subsequent campaign to secure the entire island, Operation Stream Line Jane, was opened on 10 September. The Allies broke into the interior, linking up with forces on the coast and secured the island by the end of October. Fighting ceased and an armistice was granted on 6 November. This was the first large-scale operation by the Allies combining sea, land and air forces. The island was placed under Free French control.Rigge p. 100 Background Geopolitical Diego-Suarez is a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vichy France
Vichy France (french: Régime de Vichy; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was the fascist French state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II. Officially independent, but with half of its territory occupied under harsh terms of the armistice, it adopted a policy of collaboration with Nazi Germany, which occupied the northern and western portions before occupying the remainder of Metropolitan France in November 1942. Though Paris was ostensibly its capital, the collaborationist Vichy government established itself in the resort town of Vichy in the unoccupied "Free Zone" (), where it remained responsible for the civil administration of France as well as its colonies. The Third French Republic had begun the war in September 1939 on the side of the Allies. On 10 May 1940, it was invaded by Nazi Germany. The German Army rapidly broke through the Allied lines by bypassing the highly fortified Maginot Line and invading through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Expeditionary Force (World War II)
The British Expeditionary Force (BEF) was the name of the contingent of the British Army sent to France in 1939 after Britain and France declared war on Nazi Germany on 3 September, beginning the Second World War. The BEF existed from 2 September 1939 when the BEF GHQ was formed until 31 May 1940, when GHQ closed down and its troops reverted to the command of Home Forces. During the 1930s, the British government had planned to deter war by abolishing the Ten Year Rule and rearming from the very low level of readiness of the early 1930s. The bulk of the extra money went to the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force but plans were made to re-equip a small number of Army and Territorial Army divisions for service overseas. General Lord Gort was appointed to the command of the BEF on 3 September 1939 and the BEF began moving to France on 4 September 1939. The BEF assembled along the Belgian–French border. The BEF took their post to the left of the French First Army under the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Warwickshire Regiment
The Royal Warwickshire Regiment, previously titled the 6th Regiment of Foot, was a line infantry regiment of the British Army in continuous existence for 283 years. The regiment saw service in many conflicts and wars, including the Second Boer War and both the First and Second World Wars. On 1 May 1963, the regiment was re-titled, for the final time, as the Royal Warwickshire Fusiliers and became part of the Fusilier Brigade. In 1968, by now reduced to a single Regular battalion, the regiment was amalgamated with the other regiments in the Fusilier Brigade – the Royal Northumberland Fusiliers, the Royal Fusiliers (City of London Regiment) and the Lancashire Fusiliers – into a new large infantry regiment, to be known as the Royal Regiment of Fusiliers, becoming the 2nd Battalion of the new regiment. History 17th century The regiment was raised in December 1673 by Sir Walter Vane, one of three 'English' units in the Dutch Anglo-Scots Brigade, a mercenary formation whose orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Regiment (1908–1938)
The London Regiment was an infantry regiment in the British Army, part of the Territorial Force (renamed the Territorial Army in 1921). The regiment saw distinguished service in the First World War and was disbanded in 1938, shortly before the Second World War, when most of its battalions were converted to other roles or transferred elsewhere. The lineage of some (but not all) of its former battalions is continued by the current regiment of the same name. History 1908 The regiment was first formed in 1908 to regiment the 26 Volunteer Force battalions in the newly formed County of London, each battalion having a distinctive uniform. The London battalions formed the London District, which consisted principally of the 1st and 2nd London Divisions. First World War Now part of the Territorial Force, the London Regiment expanded to 88 battalions in the First World War. Of these, 49 battalions saw action in the trenches of the Western Front in France and Flanders, six saw action ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King's Own (Yorkshire Light Infantry)
The King's Own Yorkshire Light Infantry (KOYLI) was a light infantry regiment of the British Army. It officially existed from 1881 to 1968, but its predecessors go back to 1755. In 1968, the regiment was amalgamated with the Somerset and Cornwall Light Infantry, the King's Shropshire Light Infantry and the Durham Light Infantry to form The Light Infantry, which in turn was merged with the Devonshire and Dorset Regiment, the Royal Gloucestershire, Berkshire and Wiltshire Regiment and the Royal Green Jackets to become The Rifles in 2007. History The 51st Foot The 53rd Regiment of Foot was raised in Leeds in 1755 and renumbered the 51st in January 1757. In 1782, in common with other regiments of the line, the 51st was given a "county" designation, becoming the 51st (2nd Yorkshire, West Riding) Regiment of Foot. The title of ''Light Infantry'' was given in honour of its former commander General Sir John Moore in 1809, and in 1821 the regiment was given royal status when ''King's Own' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen's Own (Royal West Kent Regiment)
The Queen's Own Royal West Kent Regiment was a line infantry regiment of the British Army based in the county of Kent in existence from 1881 to 1961. The regiment was created on 1 July 1881 as part of the Childers Reforms, originally as the Queen's Own (Royal West Kent Regiment), by the amalgamation of the 50th (Queen's Own) Regiment of Foot and the 97th (The Earl of Ulster's) Regiment of Foot. In January 1921, the regiment was renamed the Royal West Kent Regiment (Queen's Own) and, in April of the same year, was again renamed, this time as the Queen's Own Royal West Kent Regiment. After distinguished service in the Second Boer War, along with both the First and the Second World Wars, on 1 March 1961, the regiment was amalgamated with the Buffs (Royal East Kent Regiment) to form the Queen's Own Buffs, The Royal Kent Regiment, which was destined to be short-lived. On 31 December 1966, the Queen's Own Buffs was merged with the other regiments of the Home Counties Brigade—the Queen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Wellington's (West Riding Regiment)
The Duke of Wellington's Regiment (West Riding) was a line infantry regiment of the British Army, forming part of the King's Division. In 1702, Colonel George Hastings, 8th Earl of Huntingdon, was authorised to raise a new regiment, which he did in and around the city of Gloucester. As was the custom in those days the regiment was named Huntingdon's Regiment after its Colonel. As Colonel succeeded Colonel the name changed, but in 1751 regiments were given numbers, and the regiment was from that time officially known as the 33rd Regiment of Foot. In 1782, the regiment's title was changed to the 33rd (or First Yorkshire West Riding) Regiment, thus formalising an association with the West Riding of Yorkshire which, even then, had been long established. The first Duke of Wellington died in 1852 and in the following year Queen Victoria, in recognition of the regiment's long ties to him, ordered that the regiment's title be changed to the 33rd (or The Duke of Wellington's) Regiment. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |