|
1chipMSX
The One chip MSX, or 1chipMSX as the D4 Enterprise distributional name for the ESE MSX System 3, is a re-implementation of an MSX-2 home computer that uses a single FPGA to implement all the electronics (except the RAM) of an MSX-2, including the MSX-MUSIC and SCC+ audio extensions. The system is housed in a transparent blue plastic box, and can be used with a standard monitor (or TV) and a PC keyboard. Original MSX cartridges can be inserted, as well as SD and MMC memory cards as an external storage medium. Even though it lacks a 3.5" disk drive, disks are supported through emulation on a memory card, including support for booting MSX-DOS. Due to its VHDL programmable hardware, it's possible to give the device new hardware extensions by simply running a reconfiguration program under MSX-DOS. The "one chip-MSX" is equipped with two USB connectors, that can be used after adding some supporting VHDL code. Availability The ESE MSX System 3 is designed by ESE Artists' Fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D4 Enterprise
is a Japanese video game publisher currently specializing in content delivery services like Project EGG over the Internet. Some of the titles that have been re-released include many of Compile's titles, like the ''Madō Monogatari'' games. The company has also re-released Neo Geo and MSX titles to the Virtual Console for the Wii. Games Project EGG See also *MSX *Neo Geo *Ryu Umemoto was a Japanese video game music composer, born in Yokohama, Kanagawa Prefecture. He is known for composing soundtracks to various visual novel and shoot 'em up video games since the 1990s, for several companies including FamilySoft, C's Ware, ... * Wii Virtual Console (Japan) * Wii Virtual Console (North America) * Wii Virtual Console (PAL regions) * Wii Virtual Console (South Korea) References External linksOfficial website Amusement companies of Japan Video game companies of Japan Video game publishers Video game companies established in 2004 Japanese companies established in 2004 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCSI
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, ) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interfaces. The SCSI standard defines command sets for specific peripheral device types; the presence of "unknown" as one of these types means that in theory it can be used as an interface to almost any device, but the standard is highly pragmatic and addressed toward commercial requirements. The initial Parallel SCSI was most commonly used for hard disk drives and tape drives, but it can connect a wide range of other devices, including scanners and CD drives, although not all controllers can handle all devices. The ancestral SCSI standard, X3.131-1986, generally referred to as SCSI-1, was published by the X3T9 technical committee of the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) in 1986. SCSI-2 was published in August 1990 as X3.T9.2/86-109 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FAT16
File Allocation Table (FAT) is a file system developed for personal computers. Originally developed in 1977 for use on floppy disks, it was adapted for use on hard disks and other devices. It is often supported for compatibility reasons by current operating systems for personal computers and many mobile devices and embedded systems, allowing interchange of data between disparate systems. The increase in disk drives capacity required three major variants: FAT12, FAT16 and FAT32. The FAT standard has also been expanded in other ways while generally preserving backward compatibility with existing software. FAT is no longer the default file system for Microsoft Windows computers. FAT file systems are still commonly found on floppy disks, flash and other solid-state memory cards and modules (including USB flash drives), as well as many portable and embedded devices. FAT is the standard file system for digital cameras per the DCF specification. Overview Concepts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printed Circuit Board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a laminated sandwich structure of conductive and insulating layers: each of the conductive layers is designed with an artwork pattern of traces, planes and other features (similar to wires on a flat surface) etched from one or more sheet layers of copper laminated onto and/or between sheet layers of a non-conductive substrate. Electrical components may be fixed to conductive pads on the outer layers in the shape designed to accept the component's terminals, generally by means of soldering, to both electrically connect and mechanically fasten them to it. Another manufacturing process adds vias: plated-through holes that allow interconnections between layers. Printed circuit boards are used in nearly all electronic products. Alternatives to PCBs include wire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altera Quartus
Intel Quartus Prime is programmable logic device design software produced by Intel; prior to Intel's acquisition of Altera the tool was called Altera Quartus Prime, earlier Altera Quartus II. Quartus Prime enables analysis and synthesis of HDL designs, which enables the developer to compile their designs, perform timing analysis, examine RTL diagrams, simulate a design's reaction to different stimuli, and configure the target device with the programmer. Quartus Prime includes an implementation of VHDL and Verilog for hardware description, visual editing of logic circuits, and vector waveform simulation. Features Quartus Prime software features include: * Platform Designer (previously QSys, previously SOPC Builder), a tool that eliminates manual system integration tasks by automatically generating interconnect logic and creating a testbench to verify functionality. * SoCEDS, a set of development tools, utility programs, run-time software, and application examples to help you ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PS/2 Connector
The PS/2 port is a 6-pin mini-DIN connector used for connecting keyboards and mice to a PC compatible computer system. Its name comes from the IBM Personal System/2 series of personal computers, with which it was introduced in 1987. The PS/2 mouse connector generally replaced the older DE-9 RS-232 "serial mouse" connector, while the PS/2 keyboard connector replaced the larger 5-pin/180° DIN connector used in the IBM PC/AT design. The PS/2 keyboard port is electrically and logically identical to the IBM AT keyboard port, differing only in the type of electrical connector used. The PS/2 platform introduced a second port with the same design as the keyboard port for use to connect a mouse; thus the PS/2-style keyboard and mouse interfaces are electrically similar and employ the same communication protocol. However, unlike the otherwise similar Apple Desktop Bus connector used by Apple, a given system's keyboard and mouse port may not be interchangeable since the two device ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Graphics Array
Video Graphics Array (VGA) is a video display controller and accompanying de facto graphics standard, first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, which became ubiquitous in the PC industry within three years. The term can now refer to the computer display standard, the 15-pin D-subminiature VGA connector, or the 640×480 resolution characteristic of the VGA hardware. VGA was the last IBM graphics standard to which the majority of PC clone manufacturers conformed, making it the lowest common denominator that virtually all post-1990 PC graphics hardware can be expected to implement. IBM intended to supersede VGA with the Extended Graphics Array (XGA) standard, but failed. Instead, VGA was adapted into many extended forms by third parties, collectively known as Super VGA, then gave way to custom graphics processing units which, in addition to their proprietary interfaces and capabilities, continue to implement common VGA graphics modes and interfaces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Video
Composite video is an analog video signal format that carries standard-definition video (typically at 525 lines or 625 lines) as a single channel. Video information is encoded on one channel, unlike the higher-quality S-Video (two channels) and the even higher-quality component video (three or more channels). In all of these video formats, audio is carried on a separate connection. Composite video is also known by the initials CVBS for composite video baseband signal or color, video, blanking and sync, or is simply referred to as ''SD video'' for the standard-definition television signal it conveys. There are three dominant variants of composite video signals, corresponding to the analog color system used: NTSC, PAL, and SECAM. Usually composite video is carried by a yellow RCA connector, but other connections are used in professional settings. Signal components A composite video signal combines, on one wire, the video information required to recreate a color pic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-Video
S-Video (also known as separate video, Y/C, and erroneously Super-Video ) is an analog video signal format that carries standard-definition video, typically at 525 lines or 625 lines. It encodes video luma and chrominance on two separate channels, achieving higher image quality than composite video which encodes all video information on one channel. It also eliminates several types of visual defects such as dot crawl which commonly occur with composite video. Although it improved over composite video, S-Video has lower color resolution than component video, which is encoded over three channels. The Atari 800 was the first to introduce separate Chroma/Luma output in late 1979. However, S-Video did not get widely adopted until JVC's introduction of the S-VHS (Super-VHS) format in 1987, which is why it is sometimes incorrectly referred to as "Super-Video." Before the shift towards digital video the S-video format was widely used by consumers, but it was rarely used in profes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
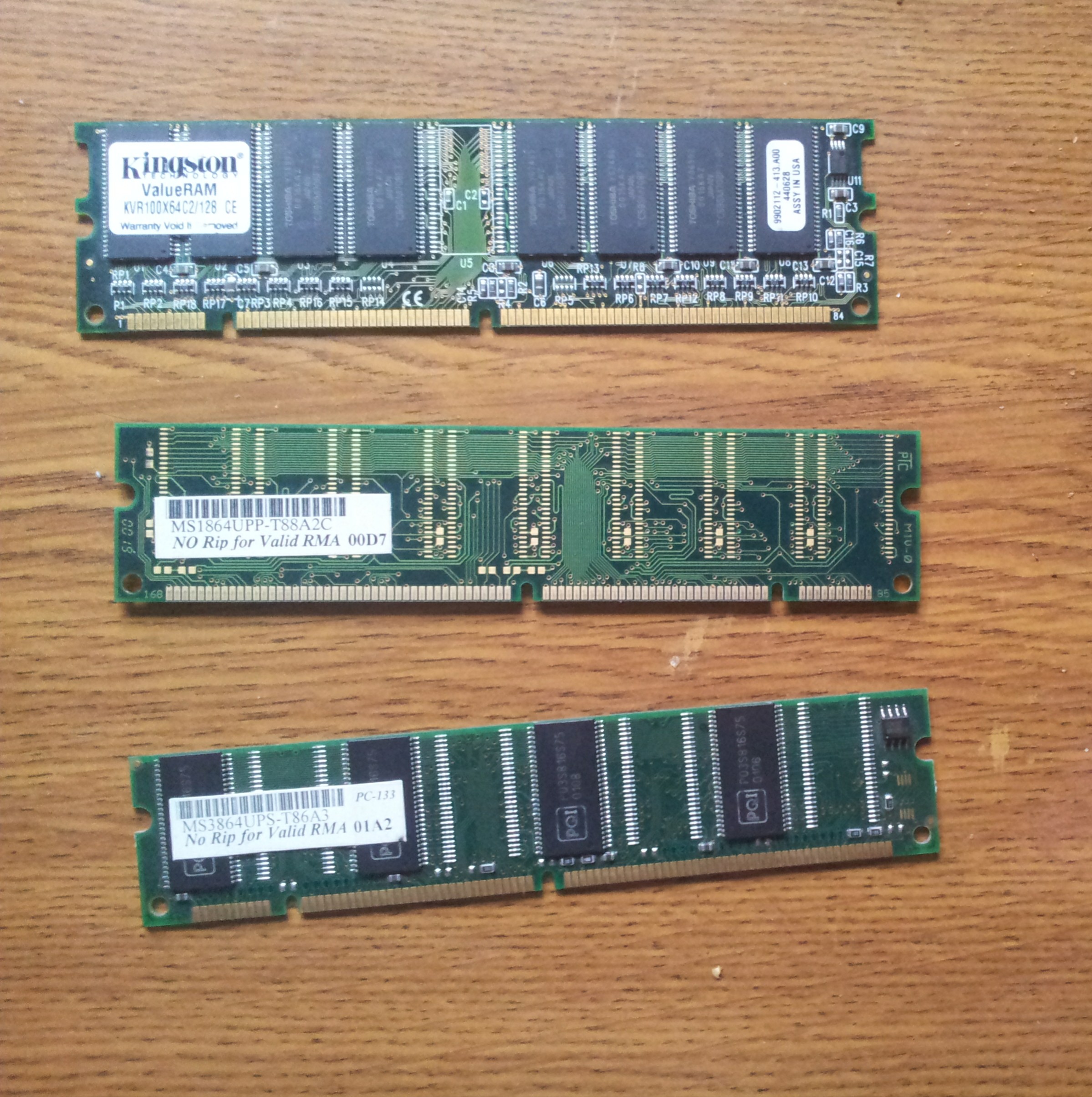
SDRAM
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal. DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the early 1970s to early 1990s used an ''asynchronous'' interface, in which input control signals have a direct effect on internal functions only delayed by the trip across its semiconductor pathways. SDRAM has a ''synchronous'' interface, whereby changes on control inputs are recognised after a rising edge of its clock input. In SDRAM families standardized by JEDEC, the clock signal controls the stepping of an internal finite-state machine that responds to incoming commands. These commands can be pipelined to improve performance, with previously started operations completing while new commands are received. The memory is divided into several equally sized but independent sections called ''banks'', allowing the device to operate on a memory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |