|
1 Samuel 7
1 Samuel 7 is the seventh chapter of the First Book of Samuel in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible or the first part of the Books of Samuel in the Hebrew Bible. According to Jewish tradition the book was attributed to the prophet Samuel, with additions by the prophets Gad and Nathan, but modern scholars view it as a composition of a number of independent texts of various ages from c. 630–540 BCE. This chapter records a victory of Israel under the leadership of Samuel against the Philistines as part of the "Ark Narrative" (1 Samuel 4:1–7:1) within a section concerning the life of Samuel (1 Samuel 1:1–7:17), and also as part of a section comprising 1 Samuel 7–15 which records the rise of the monarchy in Israel and the account of the first years of King Saul. Text This chapter was originally written in the Hebrew language. It is divided into 17 verses. Textual witnesses Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter in Hebrew are of the Masoretic T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Books Of Samuel
The Book of Samuel (, ''Sefer Shmuel'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Samuel) in the Old Testament. The book is part of the narrative history of Ancient Israel called the Deuteronomistic history, a series of books (Joshua, Judges, Samuel, and Kings) that constitute a theological history of the Israelites and that aim to explain God's law for Israel under the guidance of the prophets. According to Jewish tradition, the book was written by Samuel, with additions by the prophets Gad and Nathan, who together are three prophets who had appeared within 1 Chronicles during the account of David's reign. Modern scholarly thinking posits that the entire Deuteronomistic history was composed ''circa'' 630–540 BCE by combining a number of independent texts of various ages. The book begins with Samuel's birth and Yahweh's call to him as a boy. The story of the Ark of the Covenant follows. It tells of Israel's oppression by the Philistines, which brought about Sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septuagint
The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond those contained in the Masoretic text of the Hebrew Bible as canonically used in the tradition of mainstream Rabbinical Judaism. The additional books were composed in Greek, Hebrew, or Aramaic, but in most cases, only the Greek version has survived to the present. It is the oldest and most important complete translation of the Hebrew Bible made by the Jews. Some targums translating or paraphrasing the Bible into Aramaic were also made around the same time. The first five books of the Hebrew Bible, known as the Torah or the Pentateuch, were translated in the mid-3rd century BCE. The remaining translations are presumably from the 2nd century BCE. The full title ( grc , Ἡ μετάφρασις τῶν Ἑβδομήκοντα, , The Translat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramathaim-Zophim
Ramathaim-Zophim ( he, רמתיים־צופים), also called Ramah () and Ramatha in the Douay–Rheims Bible translation (Ramathaimsophim in the Vulgate), is a city from the Hebrew Bible, the home town and resting place of prophet Samuel. The name of the town means "the heights of the views." Identification Ramah, the home of Elkanah, Samuel's father (), the birthplace of Samuel and the seat of his authority (), the town is frequently mentioned in the history of that prophet and of David (). Here Samuel died and was buried (). The historian Josephus distinguishes between Ramathaim, "a city of the tribe of Ephraim," and Ramah, the burial place of Samuel the prophet. Ramathaim-Zophim has been tentatively identified with one of two sites. One of them is the modern Palestinian village of Nabi Samwil, the other the former village, now town, of er-Ram. Er-Ram as Ramah Ramah, according to Eusebius' '' Onomasticon'', was located 6 milestones north of Jerusalem (Ailia), opposite Beth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
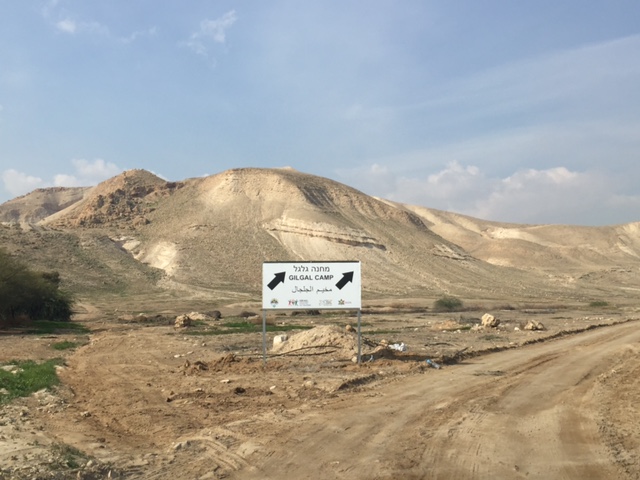
Gilgal
Gilgal ( he, גִּלְגָּל ''Gilgāl''), also known as Galgala or Galgalatokai of the 12 Stones ( grc-gre, Γαλαγα or , ''Dōdekalithōn''), is the name of one or more places in the Hebrew Bible. Gilgal is mentioned 39 times, in particular in the Book of Joshua, as the place where the Israelites camped after crossing the Jordan River (Joshua 4:19 – 5:12). The Hebrew term ''Gilgal'' most likely means "circle of stones". Its name appears in Koine Greek on the Madaba Map. Places named Gilgal in the Bible In Joshua 4–5 According to Joshua 4:19, Gilgal is a location "on the eastern border of Jericho" where the Israelites encamped immediately after crossing the Jordan River. There, they erected 12 stones as a memorial to the miraculous stopping of the river when they crossed. Joshua then ordered the Israelites who had been born during the Exodus to be circumcised at this spot. The Bible refers to this place as ''Givat Ha'aralot'', then says that Joshua called the place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bethel
Bethel ( he, בֵּית אֵל, translit=Bēṯ 'Ēl, "House of El" or "House of God",Bleeker and Widegren, 1988, p. 257. also transliterated ''Beth El'', ''Beth-El'', ''Beit El''; el, Βαιθήλ; la, Bethel) was an ancient Israelite sanctuary frequently mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. Bethel is first referred to in the bible as being near where Abram pitched his tent. Later, Bethel is mentioned as the location where Jacob dreams of a ladder leading to heaven, and which he therefore named Bethel, "House of God". The name is further used for a border city located between the territory of the Israelite tribe of Benjamin and that of the tribe of Ephraim, which first belonged to the Benjaminites and was later conquered by the Ephraimites. In the 4th century CE, Eusebius of Caesarea and Jerome described Bethel as a small village that lay 12 Roman miles north of Jerusalem, to the right or east of the road leading to Neapolis.Robinson and Smith, 1856, pp. 449–450. Most schola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
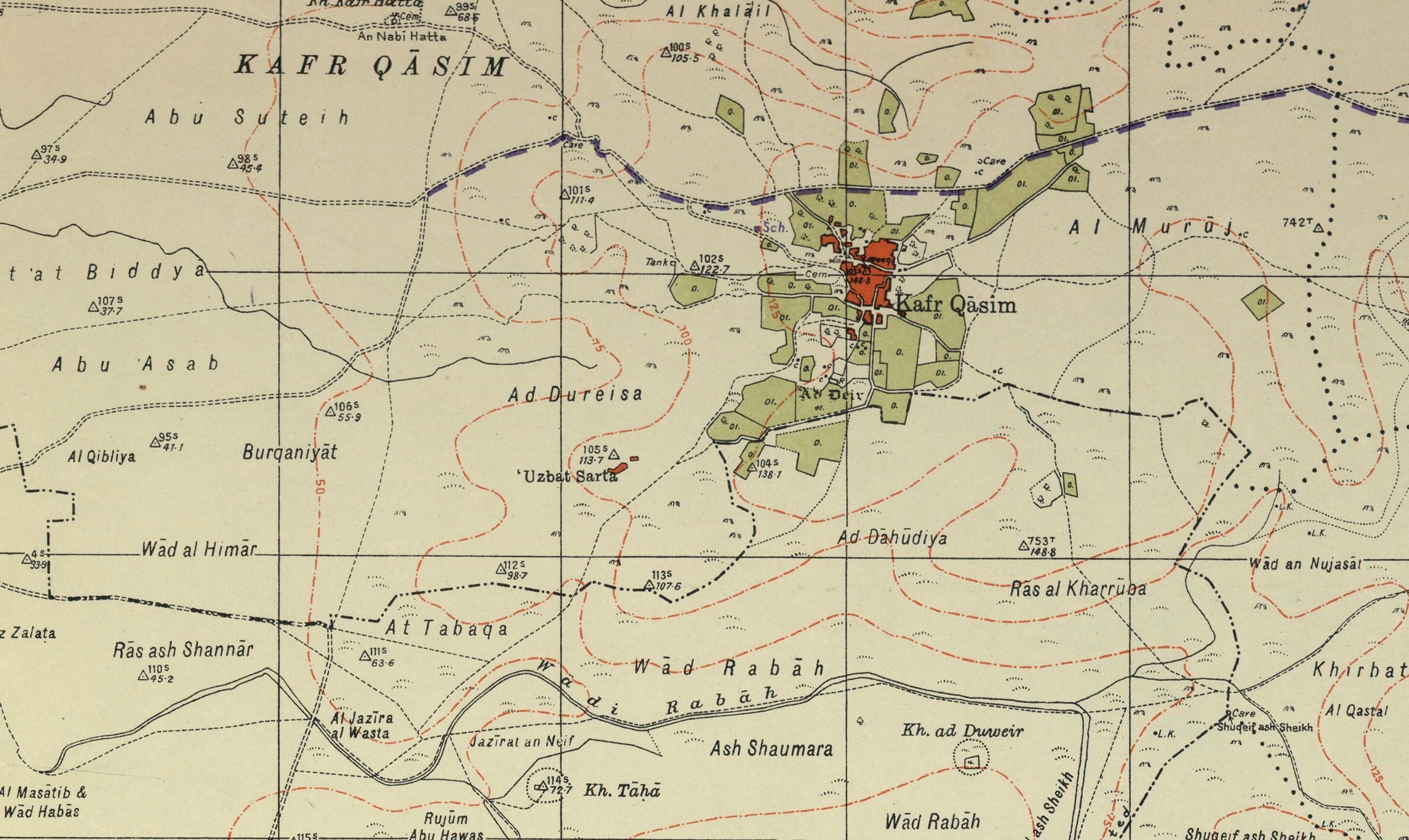
Kafr Qasim
Kafr Qasim ( ar, كفر قاسم, he, כַּפְר קָאסִם), also spelled as Kafr Qassem, Kufur Kassem, Kfar Kassem and Kafar Kassem, is a hill-top city in Israel with an Arab citizens of Israel, Arab population. It is located about east of Tel Aviv, on the Israeli side of the Green Line (Israel), Green Line separating Israel and the West Bank, in the southern portion of the "Triangle (Israel), Little Triangle" of Arab-Israeli towns and villages. In its population was . The town was the site of the Kafr Qasim massacre, in which the Israel Border Police killed 49 civilians on October 29, 1956. On February 12, 2008, Israeli Minister of the Interior Meir Sheetrit declared Kafr Qasim a city in a ceremony held at the town. History The town's area was populated in ancient times, based on remains from the Middle Paleolithic period found in the Qesem Cave. Cisterns, a winepress and terraced fields have also been documented, together with remains from the Byzantine Empire, Byzant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekron
Ekron (Philistine: 𐤏𐤒𐤓𐤍 ''*ʿAqārān'', he, עֶקְרוֹן, translit=ʿEqrōn, ar, عقرون), in the Hellenistic period known as Accaron ( grc-gre, Ακκαρων, Akkarōn}) was a Philistine city, one of the five cities of the Philistine Pentapolis, located in present-day Israel. In 1957 Ekron was first identified with the mound of Tel Miqne (Hebrew) or Khirbet el-Muqanna (Arabic), near the depopulated Palestinian village of 'Aqir, on the basis of the large size of the Iron Age archaeological remains; the judgement was strengthened by the discovery in 1996 of the Ekron inscription. The tell lies west of Jerusalem, and north of Tell es-Safi, the almost certain site of the Philistine city of Gath, on the grounds of Kibbutz Revadim on the eastern edge of the Israeli coastal plain. In the Bible In the Hebrew Bible, Ekron is mentioned initially in : :''This is the land that still remains: all the regions of the Philistines and all those of the Geshurit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gath (city)
Gath or Gat ( he, גַּת, translit=Gaṯ, lit=wine press; la, Geth, Philistine: 𐤂𐤕 *''Gīt''), often referred to as Gath of the Philistines, was a major Philistine city and one of the five Philistine city-states during the Iron Age. It was located in northeastern Philistia, close to the border with Judah. Gath is often mentioned in the Hebrew Bible and its existence is confirmed by Egyptian inscriptions. Already of significance during the Bronze Age, the city is believed to be mentioned in the El-Amarna letters as Gimti/Gintu, ruled by the two Shuwardata and 'Abdi-Ashtarti. Another Gath, known as Ginti-kirmil (Gath of Carmel) also appears in the Amarna letters.Naʼaman, Nadav (2005), p207/ref> The site most favored as the location of Gath is the archaeological mound or tell known as Tell es-Safi in Arabic and Tel Zafit in Hebrew (sometimes written Tel Tzafit), located inside Tel Zafit National Park, but a stone inscription disclosing the name of the city has yet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mizpah In Benjamin
Mizpah ( he, מִצְפָּה ''miṣpāh'', 'watch-tower, look-out') was a city of the tribe of Benjamin referred to in the Hebrew Bible. Tell en-Nasbeh is one of three sites often identified with Mizpah of Benjamin, and is located about 12 kilometers north of Jerusalem. The other suggested locations are Nabi Samwil, which is some 8 kilometers north-west of the Old City of Jerusalem (situated on the loftiest hill in the vicinity, above the plain of Gibeon), and Sh'afat, a village situated on a flat spur to the northwest of Jerusalem and where Jerusalem is visible from the village. Biblical references The first mention of Mizpah was in Genesis where Laban and his son-in-law Jacob made an agreement that God will watch over them while they were apart from each other. It was marked by the piling of rocks. It was a reminder of peace where each would not go beyond these rocks to attack the other. When a Levite traveler's concubine was raped by the men of Gibeah, the other tribes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiriath-Jearim
Kiriath-Jearim (also Kiryat Ye'arim; he, קִרְיַת-יְעָרִים ', "city of woods"; grc, Καριαθιαριμ ; Latin: ') was a city in the Land of Israel. It is mentioned 18 times in the Hebrew Bible. The biblical place was identified with Abu Ghosh. Etymology Other names are Kiriath-Ba'al, Ba'alah and Ba'ale-Judah (see, e.g. Joshua 15:60; 2 Samuel 6:2; 1 Chronicles 13:6), which implies the city was affiliated with Baal worship at an earlier date. History In Eusebius' '' Onomasticon'', Kiryat Ye'arim is placed about 9 Roman miles, or about , from Jerusalem. Palestine Exploration Fund explorers Claude Reignier Conder and Henderson have identified it with the site now known as ''Khirbet 'Erma'', a ruin located south of Kasla and east of . However, starting with Edward Robinson, biblical Kiriath-Jearim has been more often identified with Deir el-Azar (''Tel Qiryat Yearim''), a place near Abu Ghosh on a hill where the Deir El-Azar Monastery currently stands, abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea, and shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, and Egypt to the southwest. Israel also is bordered by the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively. Tel Aviv is the economic and technological center of the country, while its seat of government is in its proclaimed capital of Jerusalem, although Israeli sovereignty over East Jerusalem is unrecognized internationally. The land held by present-day Israel witnessed some of the earliest human occupations outside Africa and was among the earliest known sites of agriculture. It was inhabited by the Canaanites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)