|
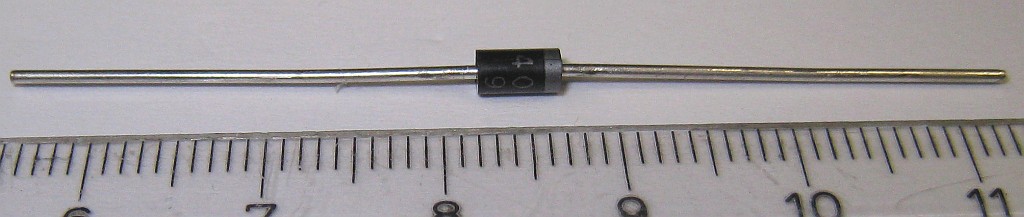
1N4007
The 1N400x (or 1N4001 or 1N4000) series is a family of popular one-ampere general-purpose silicon rectifier diodes commonly used in AC adapter#AC adapter, AC adapters for common household appliances. Its breakdown voltage, blocking voltage varies from 50 volts (1N4001) to 1000 volts (1N4007). This JEDEC device number series is available in the DO-41 axial package. Diodes with similar ratings are available in DO-214, SMA and Metal electrode leadless face, MELF surface mount packages (in other part number series). The 1N540x (or 1N5400) series is a similarly popular family of diodes rated 3 Amperes. These diodes use the larger DO-201AD axial package to dissipate heat better. History The 1N400x series was originally introduced by Motorola's Semiconductor Products Division and registered at JEDEC in 1963 as silicon power rectifiers used primarily for military and industrial applications. It appeared in the Motorola ''Semiconductor Data Manual'' in 1965, as replacements for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freewheeling Diode
A flyback diode is any diode connected across an inductor used to eliminate flyback, which is the sudden voltage spike seen across an inductive load when its supply current is suddenly reduced or interrupted. It is used in circuits in which inductive loads are controlled by switches, and in switching power supplies and inverters. This diode is known by many other names, such as snubber diode, commutating diode, freewheeling diode, suppressor diode, clamp diode, or catch diode. Operation Fig. 1 shows an inductor connected to a battery - a constant voltage source. The resistor represents the small residual resistance of the inductor's wire windings. When the switch is closed, the voltage from the battery is applied to the inductor, causing current from the battery's positive terminal to flow down through the inductor and resistor. The increase in current causes a back EMF (voltage) across the inductor due to Faraday's law of induction which opposes the change in current. Since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flyback Diode
A flyback diode is any diode connected across an inductor used to eliminate flyback, which is the sudden voltage spike seen across an inductive load when its supply current is suddenly reduced or interrupted. It is used in circuits in which inductive loads are controlled by switches, and in switching power supplies and inverters. This diode is known by many other names, such as snubber diode, commutating diode, freewheeling diode, suppressor diode, clamp diode, or catch diode. Operation Fig. 1 shows an inductor connected to a battery - a constant voltage source. The resistor represents the small residual resistance of the inductor's wire windings. When the switch is closed, the voltage from the battery is applied to the inductor, causing current from the battery's positive terminal to flow down through the inductor and resistor. The increase in current causes a back EMF (voltage) across the inductor due to Faraday's law of induction which opposes the change in current. Since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DO-214AA
DO-214 is a standard that specifies a group of semiconductor packages for surface-mounted diodes A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A diode .... Overview The standard includes multiple package variants: * DO-214AA, also known as SMB, is the middle size. * DO-214AB, also known as SMC, is the largest size. * DO-214AC, also known as SMA, is the smallest size. * DO-214BA, also known as GF1 References {{Semiconductor packages Semiconductor packages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DO-41
DO-204 is a family of diode semiconductor packages defined by JEDEC. This family comprises lead-mounted axial devices with round leads. Generally a diode will have a line painted near the cathode end. Dimensions Common variants Several common packages are archived in DO-204 as variants, and may be referred to using their alternative names. DO-7 The DO-7 (also known as DO-204-AA) is a common semiconductor package for 1N34A germanium diodes. DO-35 The DO-35 (also known as DO-204-AH or SOD27) is a semiconductor package used to encapsulate signal diodes (i.e., diodes meant to handle small amounts of current and voltage). It is often used to package small signal, low power diodes such as 1N4148 (a 100 V, 300 mA silicon diode.) DO-41 The DO-41 (also known as DO-204-AL or SOD66) is a common semiconductor package used to encapsulate rectifier diodes (i.e., diodes meant to handle larger currents and voltages than signal diodes). The name is derived from the JEDEC The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DO-15
DO-204 is a family of diode semiconductor packages defined by JEDEC. This family comprises lead-mounted axial devices with round leads. Generally a diode will have a line painted near the cathode end. Dimensions Common variants Several common packages are archived in DO-204 as variants, and may be referred to using their alternative names. DO-7 The DO-7 (also known as DO-204-AA) is a common semiconductor package for 1N34A germanium diodes. DO-35 The DO-35 (also known as DO-204-AH or SOD27) is a semiconductor package used to encapsulate signal diodes (i.e., diodes meant to handle small amounts of current and voltage). It is often used to package small signal, low power diodes such as 1N4148 (a 100 V, 300 mA silicon diode.) DO-41 The DO-41 (also known as DO-204-AL or SOD66) is a common semiconductor package used to encapsulate rectifier diodes (i.e., diodes meant to handle larger currents and voltages than signal diodes). The name is derived from the JEDEC The JED ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DO-214
DO-214 is a standard that specifies a group of semiconductor packages for surface-mounted diodes. Overview The standard includes multiple package variants: * DO-214AA, also known as SMB, is the middle size. * DO-214AB, also known as SMC, is the largest size. * DO-214AC, also known as SMA, is the smallest size. * DO-214BA, also known as GF1 References {{Semiconductor packages Semiconductor packages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DO-214AB
DO-214 is a standard that specifies a group of semiconductor packages for surface-mounted diodes A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A diode .... Overview The standard includes multiple package variants: * DO-214AA, also known as SMB, is the middle size. * DO-214AB, also known as SMC, is the largest size. * DO-214AC, also known as SMA, is the smallest size. * DO-214BA, also known as GF1 References {{Semiconductor packages Semiconductor packages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DO-214AC
DO-214 is a standard that specifies a group of semiconductor packages for surface-mounted diodes A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A diode .... Overview The standard includes multiple package variants: * DO-214AA, also known as SMB, is the middle size. * DO-214AB, also known as SMC, is the largest size. * DO-214AC, also known as SMA, is the smallest size. * DO-214BA, also known as GF1 References {{Semiconductor packages Semiconductor packages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leakage Current
In electronics, leakage is the gradual transfer of electrical energy across a boundary normally viewed as insulating, such as the spontaneous discharge of a charged capacitor, magnetic coupling of a transformer with other components, or flow of current across a transistor in the "off" state or a reverse-polarized diode. In capacitors Gradual loss of energy from a charged capacitor is primarily caused by electronic devices attached to the capacitors, such as transistors or diodes, which conduct a small amount of current even when they are turned off. Even though this off current is an order of magnitude less than the current through the device when it is on, the current still slowly discharges the capacitor. Another contributor to leakage from a capacitor is from the undesired imperfection of some dielectric materials used in capacitors, also known as ''dielectric leakage''. It is a result of the dielectric material not being a perfect insulator and having some non-zero conductivit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface-mount Device
Surface-mount technology (SMT), originally called planar mounting, is a method in which the electrical components are mounted directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). An electrical component mounted in this manner is referred to as a surface-mount device (SMD). In industry, this approach has largely replaced the through-hole technology construction method of fitting components, in large part because SMT allows for increased manufacturing automation which reduces cost and improves quality. It also allows for more components to fit on a given area of substrate. Both technologies can be used on the same board, with the through-hole technology often used for components not suitable for surface mounting such as large transformers and heat-sinked power semiconductors. An SMT component is usually smaller than its through-hole counterpart because it has either smaller leads or no leads at all. It may have short pins or leads of various styles, flat contacts, a matrix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diode 1n4001
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. A diode vacuum tube or thermionic diode is a vacuum tube with two electrodes, a heated cathode and a plate, in which electrons can flow in only one direction, from cathode to plate. A semiconductor diode, the most commonly used type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. Semiconductor diodes were the first semiconductor electronic devices. The discovery of asymmetric electrical conduction across the contact between a crystalline mineral and a metal was made by German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1874. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconducting materials such as gallium arsenide and germanium are also used. Among many uses, diodes are found in rectif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MELF
Metal electrode leadless face (MELF) is a type of leadless cylindrical electronic surface mount device that is metallized at its ends. MELF devices are usually diodes and resistors. The EN 140401-803 and JEDEC DO-213 standards describe multiple MELF components. Handling difficulties Because of their cylindrical shape and small size, in some cases these components can easily roll off the workbench or circuit board before they have been soldered into place. As such, there is a joke which suggests an alternate meaning for the acronym: ''Most End up Lying on the Floor''. Additionally, MELF components are sometimes called a "roll away" package. During automated SMT pick-and-place, this happens mostly if the mechanical pressure of the SMD placer nozzle is too low. If the MELF components are placed into the solder paste with enough pressure, then this problem can be minimized. Care must be taken with glass diodes which are less mechanically robust than resistors and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |